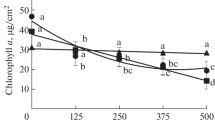
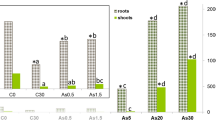
Abstract
Anatomical, histochemical and biochemical approaches were used to study mercury uptake and phytotoxicity as well as anti-oxidative responses in two species of ferns [Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata) and Boston fern (Nephrolepis exaltata)], grown in a hydroponic system. The roots of both cultivars accumulated large amounts of mercury, but exhibited limited mercury translocation to shoots. Mercury exposure led to more pronounced phytotoxicity accompanied by stronger oxidative stress in the shoots of P. vittata than in N. exaltata. N. exaltata established a more effective anti-oxidative system against mercury-induced oxidative stress than did P. vittata. The activity of anti-oxidative enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase) increased. The reduced ascorbate (ASA) and oxidized ascorbate (DHA) are regulated. Mercury exposure led to an increase in the concentration of glutathione (GSH) in both fern species. The present study suggests that N. exaltata is more tolerant to mercury exposure than P. vittata, which has been also reported to be more tolerant to arsenic exposure. N. exaltata may thus have potential for phytostabilization of soils or phytofiltration of waste water contaminated with mercury.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS (2002) Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot 53:1331–1341. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1331
Angela M, Farida M, Richard B, Sabine L (2004) Possible functions of extracellular peroxidases in stress-induced generation and detoxification of active oxygen species. Phytochem Rev 3:173–193. doi:10.1023/B:PHYT.0000047806.21626.49
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:73–399. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Beers RF, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brooks RR (1998) Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Cao XD, Ma LQ, Tu C (2004) Antioxidative responses to arsenic in the arsenic-hyperaccumulator Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata L.). Environ Pollut 128:317–325. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.018
Cargnelutti D, Tabaldi LA, Spanevello RM, Jucoski GO, Battisti V, Redin M et al (2006) Mercury toxicity induces oxidative stress in growing cucumber seedlings. Chemosphere 65:999–1006. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.037
Cherian S, Oliveira MM (2005) Transgenic plants in phytoremediation: recent advances and new possibilities. Environ Sci Technol 39:9377–9390. doi:10.1021/es051134l
Cho UH, Park JO (2000) Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci 156:1–9. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00227-2
Córdoba-Pedregosa MC, Córdoba F, Villalba JM, González-Reyes JA (2003) Differential distribution of ascorbic acid, peroxidase activity, and hydrogenperoxide along the root axis in Allium cepa L. and its possible relationship with cell growth and differentiation. Protoplasma 221:57–65. doi:10.1007/s00709-002-0069-9
Dat JF, Foyer CH, Scott IM (1998) Changes in salicylic acid and antioxidants during induced thermotolerance in mustard seedlings. Plant Physiol 118:1455–1461. doi:10.1104/pp.118.4.1455
David RJ (1990) Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radic Biol Med 9:515–540. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(90)90131-2
Gossett DR, Millhollon EP, Lucas MC (1994) Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton. Crop Sci 34:706–714
Gupta M, Tripathi RD, Rai UN, Chandra P (1998) Role of glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (I.f.) royle and Valusneria spiraus L. under mercury stress. Chemosphere 37:785–800. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00073-3
Gupta M, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld H, Clijsters H (1999) Copper affects the enzymes of the ascorbate–glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the roots of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 106:262–267. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.1999.106302.x
Halliwell B (1982) The toxic effects of oxygen on plant tissues. In: Oberley LW (ed) Superoxide dismutase, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 89–124
Han FX, Banin A, Su Y, Monts DL, Plodinec MJ, Kingery WL et al (2002) Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere. Naturwissenschaften 89:497–504. doi:10.1007/s00114-002-0373-4
Han FX, Su Y, Monts DL, Waggoner CA, Plodinec MJ (2006) Binding, distribution, and plant uptake of mercury in a soil from Oak Ridge, TN, USA. Sci Total Environ 368:753–768. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.02.026
Heaton ACP, Rugh CL, Wang NJ, Meagher RB (2005) Physiological responses of transgenic merA-tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) to foliar and root mercury exposure. Water Air Soil Pollut 161:137–155. doi:10.1007/s11270-005-7111-4
Israr M, Sahi S, Datta R, Sarkar D (2006) Bioaccumulation and physiological effects of mercury in Sesbania drummondii. Chemosphere 65:591–598. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.016
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1981) Glycolate metabolism of three submersed aquatic angiosperms during ageing. Aquat Bot 12:345–354. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(82)90026-2
Law MY, Charles SA, Halliwell B (1983) Glutathione and ascorbic acid in spinach (Spmacia oleracea) chloroplasts. Biochem J 210:899–903
Lenti K, Fodor F, Boddi B (2002) Mercury inhibits the activity of the NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (POR). Photosynthetica 40:145–151. doi:10.1023/A:1020143602973
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C, Zhang WH, Cai Y, Kennelley ED (2001) A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic: a hardy versatile, fast growing plant helps to remove arsenic from contaminated soils. Nature 409:579. doi:10.1038/35054664
Mitsuhara I, Malik KA, Miura M, Ohashi Y (1999) Animal cell-death suppressors Bcl-xL and Ced-9 inhibit cell death in tobacco plants. Curr Biol 9:775–778. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80341-8
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi Y (1979) Assay of lipid peroxides in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Orozco-Cádenas ML, Ryan CA (1999) Hydrogen peroxide is generated systematically in plant leaves by wounding and systemin via the octadecanoid pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6553–6557. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6553
Pickering IJ, Prince RC, George MJ, Smith RD, George GN, Salt DE (2000) Reduction and coordination of arsenic in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 122:1171–1177. doi:10.1104/pp.122.4.1171
Pilon-Smith E, Pilon M (2000) Breeding mercury-breathing plants for environmental cleanup. Trends Plant Sci 5:235–236. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01630-7
Rasico N (1977) Metal accumulation by some plants growing on zinc-mine deposits. OIKOS 29:250–253. doi:10.2307/3543610
Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants. In: Raskin I, Ensley BD (eds) Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 193–229
Rellán-Álvarez R, Ortega-Villasante C, Álvarez-Fernández A, Campo FF, Hernández LE (2006) Stress responses of Zea mays to cadmium and mercury. Plant Soil 279:41–50. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-3900-1
Ron M (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02312-9
Sahi SV, Bryant NL, Sharma NC, Singh SR (2002) Characterization of a lead hyperaccumulator shrub, Sesbania drummondii. Environ Sci Technol 36:4676–4680. doi:10.1021/es020675x
Scheller HV, Huang B, Hatch E, Goldsbrough PB (1987) Phytochelatin synthesis and glutathione levels in response to heavy metals in tomato cells. Plant Physiol 85:1031–1035
Severne BC, Brooks RR (1972) A nickel accumulation plant from Western Australia. Planta 103:91–94. doi:10.1007/BF00394610
Sgherri CLM, Liggini B, Puliga S, Navari-Izzo F (1994) Antioxidant in Sporobolus stapfianus: changes in response to desiccation and rehydration. Phytochemistry 35:561–565. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)90561-2
Singh N, Ma LQ, Srivastava M, Rathinasabapathi B (2006) Metabolic adaptations to arsenic-induced oxidative stress in Pteris vittata L. and Pteris ensiformis L. Plant Sci 170:274–282. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.08.013
Sinha S, Gupta M, Chandra P (1996) Bioaccumulation and biochemical effects of mercury in the plant Bacopa monnieri (L). Environ Toxicol Water Qual 11:105–112. doi :10.1002/(SICI)1098-2256(1996)11:2<105::AID-TOX5>3.0.CO;2-D
Smith IK (1985) Stimulation of glutathione synthesis in photorespiring plants by catalase inhibitors. Plant Physiol 79:1044–1047
Srivastava M, Ma LQ, Singh N, Singh S (2005) Antioxidant responses of hyper-accumulator and sensitive fern species to arsenic. J Exp Bot 56:1335–1342. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri134
Su Y, Han FX, Sridhar BBM, Monts DL (2005) Phytotoxicity and phytoaccumulation of trivalent and hexavalent chromium in brake fern. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2019–2026. doi:10.1897/04-329R.1
Suszcynsky EM, Shann JR (1995) Phytotoxicity and accumulation of mercury in tobacco subjected to different exposure routes. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:61–67. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1995)14[61:PAAOMI]2.0.CO;2
Zenk MH (1996) Heavy metal detoxification in higher plants: a review. Gene 179:21–30. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00422-2
Zhao FJ, Wang R, Baker JHA, Schat H, Bleeker PM, McGrath SP (2003) The role of phytochelatins in arsenic tolerance in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. New Phytol 159:403–410. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00784.x
Zhou ZS, Huang SQ, Guo K, Mehta SK, Zhang PC, Yang ZM (2007) Metabolic adaptations to mercury-induced oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa L. J Inorg Biochem 101:1–9
Zhou ZS, Wang SJ, Yang ZM (2008) Biological detection and analysis of mercury toxicity to alfalfa (Mdeicago sativa) plants. Chemosphere 70:1500–1509. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.028
Zhu YL, Pilon-Smits EAH, Jouanin L, Terry N (1999) Overexpression of glutathione synthetase in Indian mustard enhances cadmium accumulation and tolerance. Plant Physiol 119:73–79. doi:10.1104/pp.119.1.73
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Yunju Xia and Mr. Dean W. Patterson for chemical analyses. We also gratefully acknowledge the electronic microscopy study assistance provided by Ms. Amanda M. Lawrence. This research is supported by U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science and Technology through Cooperative Agreement DE-FC01-06EW-07040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Shiyab, S., Han, F.X. et al. Bioaccumulation and physiological effects of mercury in Pteris vittata and Nephrolepis exaltata . Ecotoxicology 18, 110–121 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0264-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0264-3