Abstract
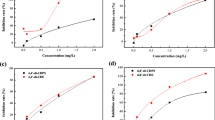
The effect of dodecylethyldimethyl-ammonium bromide (DEAB), a quaternary ammonium, compound widely used as disinfectant, on phytoplankton of inland water systems was analysed by using an experimental model. A toxicity test was based on inhibition of photosynthesis performances (effective quantum yield from photosystem II, ΦPSII and O2 production) of the phytoplanktonic species Scenedesmus intermedius and Dictiosphaerium chlorelloides (Chlorophyceae) under growing doses of DEAB. A concentration-dependent toxic response was obtained in both parameters analysed. In addition, this response was almost immediate. Consequently, the measurement of both parameters (ΦPSII and O2 production) allows to assess DEAB toxicity with higher standards of precision and repeatability. We propose that this procedure could be used to detect presence of quaternary ammonium pollutants in freshwater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamirano M, García-Villada L, Agrelo M, Sánchez-Martín L, Martín-Otero L, Flores-Moya A, Rico M, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2004) A novel approach to improve specificity of algal biosensors using wild-type and resistant mutants: an application to detect TNT. Biosens Bioelctron 19:1319–1323
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (1994) Standard guide for conducting static 96 h toxicity tests with microalgae. Annual book of ASTM standards. ASTM E1218-90. ASTM, Philadelphia, PA
Boyle TP (1984) The effect of environmental contaminants on aquatic algae. In: Shubert LE (ed) Algae as ecological indicators. Academic Press, New York, pp 237–256
Carrasco JM, Sabater C (1997) Toxicity of atrazine and chlorosulfuron to algae. Toxicol Environ Chem 59:89–99
Costas E, Carrillo E, Ferrero LM, Agrelo M, García-Villada L, Juste J, López-Rodas V (2001) Mutation of algae from sensitivity to resistance against environmental selective agents: the ecological genetics of Dictiosphaerium chlorelloides (Cholophyceae) under lethal doses of 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyluera herbicide. Phycologia 40:391–398
Cross J (1994) Cationic surfactants. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 6–15
Falkowski PG, Raven JA (1997) Aquatic photosynthesis. Blackwell Science, Oxford, 375 p.
Garcia MT, Ribosa I, Guindulian T, Sanchez-Leal J, Vives-Rego J (2001) Fate and effect of monoalkyl quaternary ammonium surfactants in the aquatic environment. Environ Pollut 111:169–175
García-Villada L, López-Rodas V, Bañares E, Flores-Moya A, Agrelo M, Martín-Otero L, Costas E (2004) Evolution of microalgae in highly-stressing envrionments: an experimental model analysing the rapid adaptation of Dictiosphaerium chlorelloides (Cholophyceae) from sensitivity to resistence mutations. J Phycol 38:1074–1081
Genty B, Briantais JM, Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochem Biophys Acta 99:87–92
Giolando ST, Rapaport RA, Larson RJ, Federle TW, Stalmans M, Masscheleyn P (1995) Environmental fate and effects of DEEDMAC: a new rapidly biodegradable cationic surfactant for use in fabric softeners. Chemosphere 30:1067–1083
Girling AE, Pascoe D, Janssen CR, Peither A, Wenzel A, Schafer H, Neumeier B, Mitchell GC, Taylor EJ, Maund SJ, Lay JP, Juttner IJ, Crossland NO, Stephenson RR, Persoone G (2000) Development of methods for evaluating toxicity to freshwater ecosystems. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:148–176
Hanstveit AO (1982) Evaluation of the results of the third ISO-interlaboratory study with an algal toxicity test ISO/TC147/SC5/WG5. Nederlands Normalisatie Instituut, Delft
Hanstveit AO, Oldersma H (1981) Evaluation of the results of the second ISO-interlaboratory study with an algal toxicity test. ISO/TC147/SC5/WG5. Nederlands Normalisatie Instituut, Delft
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) (1987) Water quality-algal growth inhibition test. Draft International Standard ISO/DIS 8692. Geneva
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) (1989) Water quality-freshwater algal growth inhibition test with Scenedesmus subspicatus and Selenastrum capricornutum. International Organization for Standardization 8692. Geneva
Issa AA, Ismail MA (1995) Effects of detergents on River Nile water microflora. Acta Hydrobiol 37:93–102
Krause GH, Weis E (1991) Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: the basics. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:313–349
Kümmurer K, Eitel A, Braun U, Hubner P, Daschner F, Mascart G, Milandri M, Reinthaler F, Verhoef J (1997) Analysis of benzalkonium chloride in the effluent from European hospitals by solid-phase extraction and HPLC with post-column ion-pairing and fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 774:281–286
Nyberg H (1988) Growth of selenastrum capricornutum in the presence of synthetic surfactants. Water Res 22:217–223
Nyholm N (1985) Response variable in algal growth inhibition toxicity tests-biomass or growth rate? Water Res 19:273–279
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals, Section 2: effects on biotic systems, procedure 201. Algal growth inhibition test. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2000) Guidance document on aquatic toxic testing of difficult substances and mixtures. Environmental Health and Safety Publications Series on Testing and Assessment, No. 23. Paris
Pandard P, Vasseur P, Rawson DM (1993) Comparison of two types of sensors using eukaryotic algae to monitor pollution of aquatic systems. Water Res 27:427–431
Peterson HG, Boutin C, Martin PA, Freemark KE, Ruecker NJ, Moody MJ (1994) Aquatic phyto-toxicity of 23 pesticides applied at expected environmental concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 28:275–292
Schreiber U, Bilger W, Neubauer C (1994) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a non-invasive indicator for rapid assessment of in vivo photosynthesis. In: Schulze ED, Calswell MM (eds) Ecophysiology of photosynthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 49–70
Singh RP, Gupta N, Singh S, Singh A, Suman R, Annie K (2002) Toxicity of ionic and non-ionic surfactants to six microbes found in Agra, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:265–270
Takamura N, Kasai F, Watanabe MM (1990) Unique response of cyanophyceae to copper. J Appl Phycol 2:293–296
Temart A, Carr G, Webb S, Versteeg D, Feijtel T (2001) Marine risk assessment: linear alkylbenzenesulphonates (LAS) in the North Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 42:635–642
UE (1992) Council Directive 92/32/EEC, relating to the legislation, packaging and labelling of dangerous substances J Eur Communities 35(L 154):1–29
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1996) Ecological effect test guidelines. OPPTS 850.5400. Algal toxicity, tiers I and II
Utsunomiya U, Watanuki T, Matsushita K, Nishina M, Tomita I (1997) Assessment of the toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and quaternary alkylammonium chloride by measuring 13C-glycerol in Dunaliella sp. Chemosphere 35:2479–2490
Verge C, Moreno A, Bravo J, Berna JL (2000) Influence of water hardness on the bioavailability and toxicity of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate (LAS). Chemosphere 44:1749–1757
Waters J (1982) Addendum to the paper on “the aquatic toxicology of DSDMAC and its ecological significance”. Tenside Deterg 19:177
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants CM-S-505/AMB/0374 CAM; CGL 2005-01938/BOS, CGL 2004-02701-HID.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Fortún, S., Marvá, F., D’ors, A. et al. Inhibition of growth and photosynthesis of selected green microalgae as tools to evaluate toxicity of dodecylethyldimethyl-ammonium bromide. Ecotoxicology 17, 229–234 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0189-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0189-2