Summary
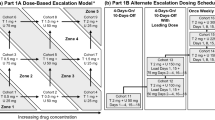
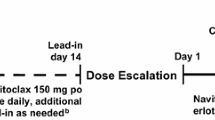
Purpose. Dasatinib is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) of BCR-ABL and SRC family and ixabepilone is an epothilone B analog. Synergistic activity has been reported when combining dasatinib with chemotherapy. This study was conducted to determine the dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) and the maximum tolerated doses (MTDs) for this combination. Patients and methods. Patients with metastatic solid tumors who progressed on standard therapy received dasatinib orally daily and ixabepilone IV every 3 weeks at escalating doses using 3 + 3 design. An expansion cohort was studied after reaching the MTD. Pharmacokinetic studies were performed. Results. Nineteen patients were enrolled. No DLTs were observed at dose level (DL) 1 (dasatinib 100 mg and ixabepilone 30 mg/m2). At DL 2 (dasatinib 100 mg and ixabepilone 40 mg/m2), one patient had multiple DLTs. At DL 3 (dasatinib 150 mg and ixabepilone 40 mg/m2), the first patient developed grade 3 AE during cycle 2, the second patient had a DLT and a grade 3 AE during cycle 2. The accrual to DL 3 was halted without reaching the maximally administered dose (MAD) and MTDs were determined to be dasatinib 100 mg and ixabepilone 40 mg/m2 (DL 2). One patient had a partial response and 12 patients stable disease as their best response. Fourteen patients came off study due to toxicities. Conclusion. The combination of dasatinib and ixabepilone showed modest clinical activity with doses 100 mg orally daily and 40 mg/m2 IV every 3 weeks, respectively. Treatment related toxicities were seen frequently.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleshin A, Finn RS (2010) SRC: A century of science brought to the clinic. Neoplasia 12(8):599–607
Tal J, Fujita DJ, Kawai S, Varmus HE, Bishop JM (1977) Purification of DNA complementary to the env gene of avian sarcoma virus and analysis of relationships among the env genes of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses. J Virol 21(2):497–505
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70
Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL (2004) Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science 305(5682):399–401
Lombardo LJ, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Barrish JC, Behnia K, Castaneda S, Cornelius LA, Das J, Doweyko AM, Fairchild C, Hunt JT, Inigo I, Johnston K, Kamath A, Kan D, Klei H, Marathe P, Pang S, Peterson R, Pitt S, Schieven GL, Schmidt RJ, Tokarski J, Wen ML, Wityak J, Borzilleri RM (2004) Discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methyl-phenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino) thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays. J Med Chem 47(27):6658–6661
Sprycel (dasatinib): package insert. Rev. ed. New York: Bristol-Myers Squibb, November 2007
Montero JC, Seoane S, Ocana A, Pandiella A (2011) Inhibition of Src family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases by dasatinib: possible combinations in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 17(17):5546–5552
Nettles JH, Li H, Cornett B, Krahn JM, Snyder JP, Downing KH (2004) The binding mode of epothilone A on alpha, beta-tubulin by electron crystallography. Science 305(5685):866–869
Goodin S, Kane MP, Rubin EH (2004) Epothilones: Mechanism of action and biologic activity. J Clin Oncol 22(10):2015–2025
Ixempra (ixabepilone) kit for injection: package insert. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb, 2009
Suter DM, Schaefer AW, Forscher P (2004) Microtubule dynamics are necessary for SRC family kinase-dependent growth cone steering. Curr Biol 14(13):1194–1199
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE (2004) Inhibition of Src tyrosine kinase impairs inherent and acquired gemcitabine resistance in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10(7):2307–2318
Chen T, Pengetnze Y, Taylor CC (2005) Src inhibition enhances paclitaxel cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer cells by caspase-9-independent activation of caspase-3. Mol Cancer Ther 4(2):217–224
Park BJ, Whichard ZL, Corey SJ (2012) Dasatinib synergizes with both cytotoxic and signal transduction inhibitors in heterogeneous breast cancer cell lilnes—lessons for design of combination targeted therapy. Cancer Lett Feb1. [Epub ahead of print]
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(3):205–216
Xu XS, Zeng J, Mylott W, Arnold M, Waltrip J, Iacono L, Mariannino T, Stouffer B (2010) Liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry for the quantitative determination of ixabepilone (BMS-247550, Ixempra) in human plasma: method validation, overcoming curve splitting issues and eliminating chromatographic interferences from degradants. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878(5–6):525–537
Furlong MT, Agrawal S, Hawthorne D, Lago M, Unger S, Krueger L, Stouffer B (2012) A validated LC-MS/MS assay for the simultaneous determination of the anti-leukemic agent dasatinib and two pharmacologically active metabolites in human plasma: application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal 58:130–135
Low JA, Wedam SB, Lee JJ, Berman AW, Brufsky A, Yang SX, Poruchynsky MS, Steinberg SM, Mannan N, Fojo T, Swain SM (2005) Phase II clinical trial of ixabepilone (BMS-247550), an epothilone B analog, in metastatic and locally advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(12):2726–2734
Denduluri N, Low JA, Lee JJ, Berman AW, Walshe JM, Vatas U, Chow CK, Steinberg SM, Yang SX, Swain SM (2007) Phase II trial of ixabepilone, an epothilone B analog, in patients with metastatic breast cancer previously untreated with taxanes. J Clin Oncol 25(23):3421–3427
Perez EA, Lerzo G, Pivot X, Thomas E, Vahdat L, Bosserman L, Viens P, Cai C, Mullaney B, Peck R, Hortobagyi GN (2007) Efficacy and safety of ixabepilone (BMS-247550) in a phase II study of patients with advanced breast cancer resistant to an anthracycline, a taxane and capecitabine. J Clin Oncol 25(23):3407–3414
Thomas E, Tabernero J, Fornier M, Conte P, Fumoleau P, Lluch A, Vahdat LT, Bunnell CA, Burris HA, Viens P, Baselga J, Rivera E, Guarneri V, Poulart V, Klimovsky J, Lebwohl D, Martin M (2007) Phase II clinical trial of ixabepilone (BMS-247550), an epothilone B analog, in patients with taxane-resistant metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(23):3399–3406
Shah NP, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Rea D, Dorlhiac-Llacer PE, Milone JH, Vela-Ojeda J, Silver RT, Khoury HJ, Charbonnier A, Khoroshko N, Paquette RL, Deininger M, Collins RH, Otero I, Hughes T, Bleickardt E, Strauss L, Francis S, Hochhaus A (2008) Intermittent target inhibition with dasatinib 100 mg once daily preserves efficacy and improved tolerability in imatinib-resistant and –intolerant chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 26(19):3204–3212
Cortes J, Rousselot P, Kim DW, Ritchie E, Hamerschlak N, Coutre S, Hochhaus A, Guilhot F, Saglio G, Apperley J, Ottman O, Shah N, Erben P, Branford S, Agarwal P, Gollerkeri A, Baccarani M (2007) Dasatinib indoces complete hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with imatinib-resistant or –intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis. Blood 109(8):3207–3213
Talpaz M, Shah NP, Kantarjian H, Donato N, Nicoll J, Paquette R, Cortes J, O’Brien S, Nicaise C, Bleickardt E, Blackwood-Chirchir MA, Iyer V, Chen TT, Huang F, Decillis AP, Sawyers CL (2006) Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med 354(24):2531–2541
Evans TR, Morgan JA, van den Abbeele AD et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of the SRC and multi-kinase inhibitor BMS-354825 in patients (pts) with GIST and other solid tumors (2005) J Clin Oncol 23(16S). Abstract 3034.
Fornier MN, Morris PG, Abbruzzi A, D’Andrea G, Gilewski T, Bromberg J, Dang C, Dickler M, Modi S, Seidman AD, Sklarin N, Chang J, Norton L, Hudis CA (2011) A phase I study of dasatinib and weekly paclitaxel for metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 22(12):2575–2581
Araujo J, Gallick G, Trudel P, et al. Dasatinib and docetaxel combination treatment for patients with castration-resistant progressive prostate cancer: a phase I/II study (CA180-086) (2009) Genitourinary Cancers Symposium. Abstract 177
Acknowledgements
The contribution of Kristin Ferguson, a research nurse, is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
This work was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Disclosures
Dr. Sandra M. Swain has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and travel support from Sanofi-Aventis. Dr. Swain is involved in the advisory boards (uncompensated) for Sanofi-Aventis and Roche (Genentech).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbolsheimer, P., Kapoor, R., Smith, K.L. et al. Phase I trial of dasatinib and ixabepilone in patients with solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 31, 92–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9805-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9805-y