Abstract
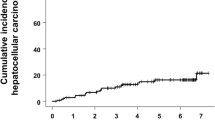
It is known that there is a very high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) among patients with type C chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis, and α -fetoprotein (AFP) has been widely used as a diagnostic marker for HCC. However, there are some patients showing continuous high AFP values but no evidence of HCC, and some studies have defined such patients as a high-risk group for HCC. In vitro study has shown that interferon (IFN) inhibits cell proliferation and enhances apoptosis as well as specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes against HCC, resulting in direct anticancer actions. In this study, we investigated the effect of IFN on AFP changes in chronic hepatitis C patients. Of 40 patients with chronic hepatitis C in whom diagnostic imaging confirmed the absence of HCC, 24 patients showed high pretreatment AFP values (high AFP group: AFP level > 10 ng/dl; mean ± SD, 46.3 ± 41.5 ng/dl) and 16 showed low pretreatment AFP values (low AFP group: pretreatment AFP level ≤ 10 ng/dl; mean ± SD, 5.3 ± 2.2 ng/dl). Pretreatment clinical parameters were statistically evaluated in relation to the AFP value. In the high AFP group, the platelet count, albumin level, and prothrombin (%) were significantly lower (P = 0.047, P = 0.0002, and P = 0.044, respectively), suggesting that AFP value increases with advancing liver disease. Subsequently 27 patients were administered IFN (IFN group), and the remaining 13 patients were administered Stronger Neo-minophagen C (SNMC), a glycyrrhizin preparation (SNMC group), as a control group receiving liver-protective therapy. Alanine aminotransferase was reduced in both the IFN and the SNMC group (mean, 132.56 to 60.07 mg/ml [P < 0001] and 147.85 to 56.23 mg/ml [P = 0.0240], respectively). AFP was significantly reduced in the IFN group (mean, 30.03 to 12.65 ng/ml; P = 0.0034), but there was no significant change in AFP in the SNMC group (mean, 29.70 to 39.17 ng/ml). AFP is useful for diagnosing HCC; however, some patients show a persistently high AFP level in the absence of HCC, and these patients have been described as a high-risk group for HCC. In this study, we found that IFN therapy but not SNMC universally reduced the AFP baseline. Since AFP is a significant predictor for HCC, therapeutic strategies for hepatitis C, e.g., long-term low-dose IFN treatment, may reduce hepatocarcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK: Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 358:958–965, 2001
Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, Smith C, Marinos G, Goncales FL Jr, Haussinger D, Diago M, Carosi G, Dhumeaux D, Craxi A, Lin A, Hoffman J, Yu J: Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 347:975–982, 2002
Takano S, Ito Y, Yokosuka O, Ohto M, Uchiumi K, Hirota K, Omata M: A multicenter randomized controlled dose study of ursodeoxycholic acid for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 22:1002, 1995
Arase Y, Ikeda K, Murashima N, Chayama K, Tsubota A, Koida I, Suzuki Y, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, Kumada H: The long term efficacy of glycyrrhizin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Cancer 79:1949–1500, 1997
van Rossum TG, Vulto AG, Hop WC, Brouwer JT, Niesters HG, Schalm SW: Intravenous glycyrrhizin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase I/II trial: J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:1093–1099, 1999
Szymendera JJ, Zborzil J, Sikorowa L, Lenko J, Kaminska JA, Gadek A: Evaluation of five tumor markers (AFP, CEA, hCG, hPL and SP1) in monitoring therapy and follow-up of patients with testicular germ cell tumors. Oncology 40:1–10, 1983
Okuda K, Kotoda K, Obata H, Hayashi N, Hisamitsu T: Clinical observations during a relatively early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma, with special reference to serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Gastroenterology 69:26–234, 1975
Ikeda K, Saitoh S, Koida I, Arase Y, Tsubota A, Chayama K, Kumada H: A multivariate analysis of risk factors for hepatocellular carcinogenesis: a prospective observation of 795 patients with viral and alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology 18:47–53, 1993
Tsukuma H, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Nakao M, Yabuuchi T, Kitamura T, Nakanishi K, Fujimoto I, Inoue A, Yamazaki H: Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med 428:1797–1801, 1993
Hu KQ, Kyulo NL, Lim N, Elhazin B, Hillebrand DJ: Clinical significance of elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 99:860–865, 2004
Alpert E: Serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in benign and malignant gastrointestinal diseases: evaluation of an immunoenzymatic assay. Clin Chim Acta 58:77–83, 1975
Jagiello-Wojtowicz E, Rzeszowska G, Krawczuk G, Baran E, Surmaczynska B, Fijalka-Rymar M, Bielec D: Alpha-fetoprotein in acute viral hepatitis type A. Przegl Epidemiol 47:17–20, 1993
Francioni S, Pastore M: Alpha-fetoprotein and acute viral hepatitis type B. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 33(Suppl 3):103–106, 1989
Pastore G, Lapedota E, Dentico P, Buongiorno R, Mallardi M, Angarano G, Schiraldi: Prognostic value of alpha-foetoprotein in fulminant hepatitis. Quad Sclavo Diagn 15:14–21, 1979
Innis MA, Miller DL: alpha-Fetoprotein gene expression. Control of alpha-fetoprotein mRNA levels in cultured rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 254:9148–9154, 1979
Yoshida T, Hanada T, Tokuhisa T, Kosai K, Sata M, Kohara M, Yoshimura A: Activation of STAT3 by the hepatitis C virus core protein leads to cellular transformation. J Exp Med 196:641–653, 2002
Yano H, Iemura A, Haramaki M, Ogasawara S, Takayama A, Akiba J, Kojiro M: Interferon alfa receptor expression and growth inhibition by interferon alfa in human liver cancer cell lines. Hepatology 29:1708–1717, 1999
Kubo S, Nishiguchi S, Hirohashi K, Tanaka H, Shuto T, Yamazaki O, Shiomi S, Tamori A, Oka H, Igawa S, Kuroki T, Kinoshita H: Effects of long-term postoperative interferon-alpha therapy on intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 134:963–967, 2001
Sakon M, Nagano H, Dono K, Nakamori S, Umeshita K, Yamada A, Kawata S, Imai Y, Iijima S, Monden M: Combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-alpha therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major portal branches. Cancer 94:435–442, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murashima, S., Tanaka, M., Haramaki, M. et al. A Decrease in AFP Level Related to Administration of Interferon in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C and a High Level of AFP. Dig Dis Sci 51, 808–812 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3211-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-3211-2