Abstract
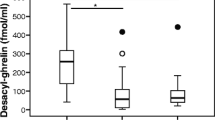
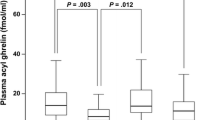
The stomach is the main source of circulating ghrelin. Plasma concentrations of this hormone in patients with various upper gastrointestinal diseases remain undetermined. Thus we measured plasma ghrelin levels by radioimmunoassay in 225 subjects, including 134 Helicobacter pylori-infected and 91 uninfected subjects. They included 67 patients with chronic gastritis (CG), 26 with benign gastric polyp (BGP), 24 with gastric ulcer (GU), 24 with reflux esophagitis (RE), 18 with duodenal ulcer (DU), 28 with acute gastritis (AG), 23 with gastric cancer (GC), and 39 who had normal mucosa on upper endoscopy (N). Plasma pepsinogen I and II levels were also measured. The extent of gastritis was assessed endoscopically. Ghrelin levels differed significantly among the different disease groups. Plasma ghrelin concentrations were lowest in the CG group, followed by the GU group, and highest in the AG patients. There was a significant difference in the levels between differentiated and undifferentiated GC. Ghrelin concentrations in BGP, RE, and DU patients were comparable to those in the N group. Ghrelin circulating levels were lower in H. pylori-positive than –negative individuals, but the significant differences among disease groups were still observed in H. pylori-infected and uninfected populations. Ghrelin concentrations correlated positively with plasma pepsinogen I levels and I/II ratios and inversely with the extent of H. pylori-related gastritis. Plasma ghrelin levels varied widely in diverse conditions of the upper digestive tract, reflecting the inflammatory and atrophic events of the background gastric mucosa. Further investigation is warranted to unravel the mechanisms of the high circulating ghrelin levels in certain upper gastrointestinal diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K: Ghrelin is a growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660, 1999
Murray CD, Kamm MA, Bloom SR, Emmanuel AV: Ghrelin for the gastroenterologists: history and potential. Gastroenterology 125:1492–1502, 2003
St-Pierre DH, Wang L, Tache Y: Ghrelin: a novel player in the gut-brain regulation of growth hormone and energy balance. News Physiol Sci 18:242–246, 2003
Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A, Mondal MS, Suganuma T, Matsukura S, Kangawa K, Nakazato M: Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 141:4255–4261, 2000
Blaser MJ: Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis 161:626–633, 1990
Ernst PB, Gold BD: The disease spectrum of Helicobacter pylori: the immunopathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:615–640, 2000
Borch K, Skarsgard J, Franzen L, Mardh SR, Ehfeld JF: Benign gastric polyps. Dig Dis Sci 48:1292–1297, 2003
Labenz J, Blum AL, Bayerdorffer E, Meining A, Stolte M, Borsch G: Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 112:1442–1447, 1997
O’Connor HJ. Review article: Helicobacter pylori and gastro-esophageal reflux disease-clinical implications and management. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13:117–127, 1999
Gokcel A, Gumurdulu Y, Kayaselcuk F, Serin E, Ozer B, Ozsahin AK, Guvener N: Helicobacter pylori has no effect on plasma ghrelin levels. Eur J Endocrinol 148:423–426, 2003
Isomoto H, Nakazato M, Ueno H, Date Y, Nishi Y, Mukae H, Mizuta Y, Ohtsuru A, Yamashita S, Kohno S: Low plasma ghrelin levels in patients with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Am J Med 117:429–432, 2004
Broutet N, Plebani M, Sakarovitch C, Sipponen P, Megraud F: Eurohepygast Study Group: Pepsinogen A, pepsinogen C and gastrin as markers of atrophic chronic gastritis in European dyspeptics. Br J Cancer 88:1239–1247, 2003
Korstanje A, den Hartog G, Biemond I, Lamers BHW: The serological gastric biopsy: a non-endoscopical diagnostic approach in management of the dyspeptic patient. Scand J Gastroenterol 37:22–26, 2002
Isomoto H, Inoue K, Furusu H, Nishiyama H, Shikuwa S, Omagari K, Mizuta Y, Murase K, Murata I, Kohno S: Lafutidine, a novel histamine H2-receptor antagonist, vs lansoprazole in combination with amoxicillin and clarithromycin for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 8:111–119, 2003
Price AB: The Sydney system; histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:209–222, 1991
Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Tagami T, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Akamizu T, Suda M, Koh T, Natsui K, Toyooka S, Shirakami G, Usui T, Shimatsu A, Doi K, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K: Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2753–2758, 2001
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, Breen PA, Ma MK, Dellinger EP, Purnell JQ: Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 346:1623–1630, 2002
Nwokolo CU, Freshwater DA, O’Hare P, Randeva HS: Plasma ghrelin following cure of Helicobacter pylori. Gut 52:637–640, 2003
Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Hosoda H, Ota T, Minegishi Y, Nomura S, Kangawa K, Ishii H: Helicobacter pylori infection modified gastric and plasma ghrelin dynamics in Mongolian gerbils. Gut 53:187–194, 2004
Honda S, Fujioka T, Tokieda M, Gotoh T, Nishizono A, Nasu M: Gastric ulcer, atrophic gastritis, and intestinal metaplasia caused by Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils. Scand J Gastroenterol 33:454–460, 1998
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS: A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 50:1714–1719, 2001
Shimizu Y, Nagaya N, Isobe T, Imazu M, Okumura H, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Kohno N: Increased plasma ghrelin level in lung cancer cachexia. Clin Cancer Res 9:774–778, 2003
Asakawa A, Inui A, Kaga T, Yuzuriha H, Nagata T, Fujimiya M, Katsuura G, Makino S, Fujino MA, Kasuga M: Arole of ghrelin in neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to stress in mice. Neuroendocrinology 74:143–147, 2001
Arosio M, Ronchi CL, Gebbia C, Cappiello V, Beck-Peccoz P, Peracchi M: Stimulatory effects of ghrelin on circulating somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:701–704, 2003
Dornonville de la Cour C, Bjorkqvist M, Sandvik AK, Bakke I, Zhao CM, Chen D, Hakanson R: A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control. Regul Pept 99:141–150, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isomoto, H., Ueno, H., Nishi, Y. et al. Circulating Ghrelin Levels in Patients with Various Upper Gastrointestinal Diseases. Dig Dis Sci 50, 833–838 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2648-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2648-z