Abstract
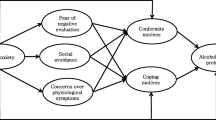
Emerging evidence suggests that increased negative emotions and maladaptive emotion regulation (ER) strategies underlie social anxiety disorder (SAD) and alcohol related problems, but little is known about how specific negative emotions and maladaptive ER strategies interact with one another in predicting drinking in daily life. This study aimed to investigate (1) the impact of within-person level negative emotions and maladaptive ER strategies on drinking among individuals with SAD, and (2) the moderating effect of specific maladaptive ER strategies (avoidance, rumination, suppression) on the relationship between negative emotions and alcohol craving in daily life via an ecological momentary assessment (EMA). Results revealed that the SAD group (n = 66) showed a higher increase rate in alcohol craving when they were socially anxious, tense and lonely than the non-SAD group (n = 53). In moderation analyses, maladaptive ER strategies interacted with negative emotions in predicting alcohol craving and different patterns were observed between groups: rumination was a significant moderator for the SAD group, while avoidance was for the non-SAD group in both concurrent and lagged effect analyses. Implications for the future research and interventions on daily negative emotions and maladaptive ER strategies are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In group-difference analyses, SAD group showed lower levels of positive emotions including excitement and relaxation and less frequent use in adaptive ER strategies including social support seeking and acceptance, all ps < .05. However, there were no significant group differences in calm and positive reinterpretation. Results from multilevel modeling analyses on the positive emotion experiences and adaptive ER strategies are available upon request.
References
Abrams, K., & Kushner, M. G. (2004). The moderating effects of tension-reduction alcohol outcome expectancies on placebo responding in individuals with social phobia. Addictive Behaviors,29(6), 1221–1224.
Abrams, K., Kushner, M., Medina, K. L., & Voight, A. (2001). The pharmacologic and expectancy effects of alcohol on social anxiety in individuals with social phobia. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,64(2), 219–231.
Aldao, A., Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Schweizer, S. (2010). Emotion-regulation strategies across psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review,30(2), 217–237.
Arpin, S. N., Mohr, C. D., & Brannan, D. (2015). Having friends and feeling loney: A daily process examination of transient loneliness, socialization, and drinking behavior. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin,41(4), 615–628.
Babor, T. F., Berglas, S., Mendelson, J. H., Ellingboe, J., & Miller, K. (1983). Alcohol, affect, and the disinhibition of verbal behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl),80(1), 53–60.
Babor, T. F., De la Fuente, J. R., Saunders, J., & Grant, M. (1989). AUDIT-the alcohol use disorders identification test: Guidlines for use in primary health care. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Bonn-Miller, M. O., Vujanovic, A. A., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2008). Emotional dysregulation: Association with coping-oriented marijuana use motives among current marijuana users. Substance Use and Misuse,43(11), 1653–1665.
Bradizza, C. M., Brown, W. C., Ruszczyk, M. U., Dermen, K. H., Lucke, J. F., & Stasiewicz, P. R. (2018). Difficulties in emotion regulation in treatment-seeking alcoholics with and without co-occurring mood and anxiety disorders. Addictive Behaviors,80, 6–13.
Buckner, J. D., Heimber, R. G., Ecker, A. H., & Vinci, C. (2013). A biopsychosocial model of social anxiety and substance use. Depression and Anxiety,30(3), 276–284.
Buckner, J. D., Schmidt, N. B., Lang, A. R., Small, J. W., Schlauch, R. C., & Lewinsohn, P. M. (2008a). Specificity of social anxiety disorder as a risk factor for alcohol and cannabis dependence. Journal of Psychiatric Research,42(3), 230–239.
Buckner, J. D., & Terlecki, M. A. (2016). Social anxiety and alcohol-related impairment: The mediational impact of solitary drinking. Addictive Behaviors,58, 7–11.
Buckner, J. D., Timpano, K. R., Zvolensky, M. J., Sachs-Ericsson, N., & Schmidt, N. B. (2008b). Implications of comorbid alcohol dependence among individuals with social anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety,25(12), 1028–1037.
Butler, T. R., Karkhanis, A. N., Jones, S. R., & Weiner, J. L. (2016). Adolescent social isolation as a model of heightened vulnerability to comorbid alcoholism and anxiety disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research,40(6), 1202–1214.
Campbell-Sills, L., Ellard, K., & Barlow, D. (2013). Emotion regulation in anxiety disorders. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (2nd ed., pp. 393–412). New York: Guilford Press.
Carver, C. S., Scheier, M. F., & Weintraub, J. K. (1989). Assessing coping strategies: A theoretically based approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,56(2), 267–283.
Chandley, R. B., Luebbe, A. M., Messman-Moore, T. L., & Ward, R. M. (2014). Anxiety sensitivity, coping motives, emotion dysregulation, and alcohol-related outcomes in college women: A moderated-mediation model. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs,75(1), 83–92.
Cho, Y. (2007). Assessing emotion dysregulation: Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology.,26, 1015–1038.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral science (2nd ed.). London: Psychology Press.
Collins, J. L., Sherry, S. B., McKee, K., Thompson, K., & Stewart, S. H. (2019). Do drinking motives and drinking contexts mediate the relationship between social avoidance and alcohol problems? Evidence from two studies of undergraduate drinkers. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-019-00092-3.
Conger, J. J. (1956). Reinforcement theory and the dynamics of alcoholism. Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol,17, 296–305.
Earleywine, M., & Erblich, J. (1996). A confirmed factor structure for the biphasic alcohol effects scale. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology,4(1), 107.
Eggleston, A. M., Woolaway-Bickel, K., & Schmidt, N. B. (2004). Social anxiety and alcohol use: Evaluation of the moderating and mediating effects of alcohol expectancies. Journal of Anxiety Disorders,18(1), 33–49.
Falk, D. E., Yi, H. Y., & Hilton, M. E. (2008). Age of onset and temporal sequencing of lifetime DSM-IV alcohol use disorders relative to comorbid mood and anxiety disorders. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,94(1–3), 234–245.
Farmer, A. S., & Kashdan, T. B. (2012). Social anxiety and emotion regulation in daily life: Spillover effects on positive and negative social events. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy,41(2), 152–162.
Fox, H. C., Hong, K. A., & Sinha, R. (2008). Difficulties in emotion regulation and impulse control in recently abstinent alcoholics compared with social drinkers. Addictive Behaviors,33(2), 388–394.
Goldin, P. R., Manber-Ball, T., Werner, K., Heimberg, R., & Gross, J. J. (2009). Neural mechanisms of cognitive reappraisal of negative self-beliefs in social anxiety disorder. Biological Psychiatry,66(12), 1091–1099.
Grant, B. F., Hasin, D. S., Blanco, C., Stinson, F. S., Chou, S. P., Goldstein, R. B.,… & Huang, B. (2005). The epidemiology of social anxiety disorder in the United States: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 66(11), 1351–1361
Grant, B. F., Stinson, F. S., Dawson, D. A., Chou, S. P., Dufour, M. C., Compton, W.,… & Kaplan, K. (2004). Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independentmood and anxiety disorders: Results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and relatedconditions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 61(8), 807–816
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment,26(1), 41–54.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,85(2), 348–362.
Ham, L. S., & Hope, D. A. (2005). Incorporating social anxiety into a model of college student problematic drinking. Addictive Behaviors,30(1), 127–150.
Hayes, S. C., Strosahl, K., & Wilson, K. G. (1999). Acceptance and commitment therapy: Understanding and treating human suffering. New York: Guilford.
Hodgins, D. C., el-Guebaly, N., & Armstrong, S. (1995). Prospective and retrospective reports of mood states before relapse to substance use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology,63(3), 400–407.
Kashdan, T. B., & Collins, R. L. (2010). Social anxiety and the experience of positive emotion and anger in everyday life: An ecological momentary assessment approach. Anxiety Stress and Coping,23(3), 259–272.
Kashdan, T. B., Weeks, J. W., & Savostyanova, A. A. (2011). Whether, how, and when social anxiety shapes positive experiences and events: A self-regulatory framework and treatment implications. Clinical Psychology Review,31(5), 786–799.
Keough, M. T., Battista, S. R., O’Connor, R. M., Sherry, S. B., & Stewart, S. H. (2016). Getting the party started—Alone: Solitary predrinking mediates the effect of social anxiety on alcohol-related problems. Addictive Behaviors,55, 19–24.
Kessler, R. C., Berglund, P., Demler, O., Jin, R., Merikangas, K. R., & Walters, E. E. (2005). Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry,62(6), 593–602.
Kessler, R. C., Davis, C. G., & Kendler, K. S. (1997). Childhood adversity and adult psychiatric disorder in the US National Comorbidity Survey. Psychological Medicine,27(5), 1101–1119.
Kessler, R. C., McGonagle, K. A., Zhao, S., Nelson, C. B., Hughes, M., Eshleman, S.,… & Kendler, K. S. (1994). Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Archives of General Psychiatry, 51(1), 8–19
Khantzian, E. J. (1997). The self-medication hypothesis of substance use disorders: A reconsideration and recent applications. Harvard Review of Psychiatry,4(5), 231–244.
Khosravani, V., Bastan, F. S., Ghorbani, F., & Kamali, Z. (2017). Difficulties in emotion regulation mediate negative and positive affects and craving in alcoholic patients. Addictive Behaviors,71, 75–81.
Kidorf, M., & Lang, A. R. (1999). Effects of social anxiety and alcohol expectancies on stress-induced drinking. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,13(2), 134–142.
Kim, H. S. (2001). Memory bias in subtypes of social phobia. (Master’s Degree), Seoul University, Seoul, Korea.
Kim, S., Yoon, H. Y., & Kwon, J. H. (2013). Validation of the short form of the Korean Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (K-SIAS) and the Korean Social Phobia Scale (K-SPS). Cognitive Behavior Therapy in Korea,13(3), 511–535.
Koval, P., Kuppens, P., Allen, N. B., & Sheeber, L. (2012). Getting stuck in depression: The roles of rumination and emotional inertia. Cognition and Emotion,26(8), 1412–1427.
Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, D. V., Weiller, E., Amorim, P., Bonora, I., Sheehan, K. H., ··· Dunbar, G. C. (1997). The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI). A short diagnostic structured interview: reliability and validity according to the CIDI. European Psychiatry, 12(5), 224–231.
Lee, B. O., Lee, C. H., Lee, P. G., Choi, M. J., & Namkoong, K. (2000). Development of Korean version of Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT-K): Its reliability and validity. Journal of Korean Academy of Addiction Psychiatry,4(2), 83–92.
Lewis, M. A., Hove, M. C., Whiteside, U., Lee, C. M., Kirkeby, B. S., Oster-Aaland, L., et al. (2008). Fitting in and feeling fine: Conformity and coping motives as mediators of the relationship between social anxiety and problematic drinking. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,22(1), 58–67.
Magee, W. J., Eaton, W. W., Wittchen, H. U., McGonagle, K. A., & Kessler, R. C. (1996). Agoraphobia, simple phobia, and social phobia in the National Comorbidity Survey. Archives of General Psychiatry,53(2), 159–168.
Mattick, R. P., & Clarke, J. C. (1998). Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behaviour Research and Therapy,36(4), 455–470.
McMahon, T. P., & Naragon-Gainey, K. (2018). The moderating effect of maladaptive emotion regulation strategies on reappraisal: A daily diary study. Cognitive Therapy and Research,42(5), 552–564.
Morris, E., Stewart, S., Theakston, J., & Mellings, T. (2004). Relations of social anxiety variables to drinking motives, levels, and problems in young adult drinkers. Paper presented at the 24th Annual Meeting of the Anxiety Disorders Association of America, Miami, FL, March.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Morrow, J. (1991). A prospective study of depression and posttraumatic stress symptoms after a natural disaster: The 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,61(1), 115–121.
Norberg, M. M., Norton, A. R., Olivier, J., & Zvolensky, M. J. (2010). Social anxiety, reasons for drinking, and college students. Behavior Therapy,41(4), 555–566.
O’Toole, M. S., Jensen, M. B., Fentz, H. N., Zachariae, R., & Hougaard, E. (2014). Emotion differentiation and emotion regulation in high and low socially anxious individuals: An experience sampling study. Cognitve Therapy and Resarch,38, 428–438.
Pe, M. L., Raes, F., Koval, P., Brans, K., Verduyn, P., & Kuppens, P. (2013). Interference resolution moderates the impact of rumination and reappraisal on affective experiences in daily life. Cognition and Emotion,27(3), 492–501.
Posner, J., Russell, J. A., & Peterson, B. S. (2005). The circumplex model of affect: An integrative approach to affective neuroscience, cognitive development, and psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology,17(03), 715–734.
Rodriguez, B. F., Bruce, S. E., Pagano, M. E., Spencer, M. A., & Keller, M. B. (2004). Factor structure and stability of the Anxiety Sensitivity Index in a longitudinal study of anxiety disorder patients. Behaviour Research and Therapy,42(1), 79–91.
Russell, J. A. (1980). A circumplex model of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,39, 1161–1178.
Saunders, J. B., Aasland, O. G., Amundsen, A., & Grant, M. (1993a). Alcohol consumption and related problems among primary health care patients: WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption—I. Addiction,88(3), 349–362.
Saunders, J. B., Aasland, O. G., Babor, T. F., De la Fuente, J. R., & Grant, M. (1993b). Development of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II. Addiction,88(6), 791–804.
Schneier, F. R., Foose, T. E., Hasin, D. S., Heimberg, R. G., Liu, S.-M., Grant, B. F., et al. (2010). Social anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorder co-morbidity in the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Psychological Medicine,40(6), 977–988.
Schneier, F. R., Martin, L. Y., Liebowitz, M. R., Gorman, J. M., & Fyer, A. J. (1989). Alcohol abuse in social phobia. Journal of Anxiety Disorders,3(1), 15–23.
Schry, A. R., & White, S. W. (2013). Understanding the relationship between social anxiety and alcohol use in college students: A meta-analysis. Addictive Behaviors,38(11), 2690–2706.
Sheehan, D. V., Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, K. H., Amorim, P., Janavs, J., Weiller, E., et al. (1998). The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry,59, 22–33.
Sheehan, D. V., Lecrubier, Y., Sheehan, K. H., Janavs, J., Weiller, E., Keskiner, A., et al. (1997). The validity of the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) according to the SCID-P and its reliability. European Psychiatry,12(5), 232–241.
Sher, K. J., & Levenson, R. W. (1982). Risk for alcoholism and individual differences in the stress-response-dampening effect of alcohol. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,91(5), 350–367.
Stewart, S. H., Morris, E., Mellings, T., & Komar, J. (2006). Relations of social anxiety variables to drinking motives, drinking quantity and frequency, and alcohol-related problems in undergraduates. Journal of Mental Health,15(6), 671–682.
Swendsen, J. D., Tennen, H., Carney, M. A., Affleck, G., Willard, A., & Hromi, A. (2000). Mood and alcohol consumption: an experience sampling test of the self-medication hypothesis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,109(2), 198–204.
Terlecki, M. A., Ecker, A. H., & Buckner, J. D. (2014). College drinking problems and social anxiety: The importance of drinking context. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,28(2), 545–552.
Thomas, S. E., Randall, C. L., & Carrigan, M. H. (2003). Drinking to cope in socially anxious individuals: A controlled study. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research,27(12), 1937–1943.
Wenzel, A., & Jager-Hyman, S. (2014). Social anxiety disorder and its relation to clinical syndromes in adulthood. In S. G. Hofmann & P. M. DiBartolo (Eds.), Social anxiety clinical, developmental, and social perspectives (pp. 227–251). London: Academic Press.
Willinger, U., Lenzinger, E., Hornik, K., Fischer, G., Schönbeck, G., Aschauer, H. N., et al. (2002). Anxiety as a predictor of relapse in detoxified alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol and Alcoholism,37(6), 609–612.
Wong, Q. J., McEvoy, P. M., & Rapee, R. M. (2019). Repetitive thinking in social anxiety disorder: Are anticipatory processing and post-event processing facets of an underlying unidimensional construct? Behavior Therapy,50(3), 571–581.
Yoo, S. W., Kim, Y. S., Noh, J. S., Oh, K. S., Kim, C. H., Namkoong, K., et al. (2006). Validation of Korean version of the mini-international neuropsychiatric interview. Anxiety and Mood,2(1), 50–55.
Zinbarg, R. E., Barlow, D. H., & Brown, T. A. (1997). Hierarchical structure and general factor saturation of the anxiety sensitivity index: Evidence and implications. Psychological Assessment,9(3), 277–284.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Sojung Kim and Jung-Hye Kwon declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All participants gave informed consent.
Animal Rights
No animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Kwon, JH. The Impact of Negative Emotions on Drinking Among Individuals with Social Anxiety Disorder in Daily Life: The Moderating Effect of Maladaptive Emotion Regulation Strategies. Cogn Ther Res 44, 345–359 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-019-10045-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-019-10045-8