Abstract
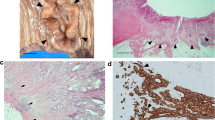
Overexpression of the mucin-type sialoglycoprotein podoplanin in cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) was recently shown to be associated with tumor progression, metastasis and poor prognosis in lung and breast cancer. Here we investigate the role of podoplanin expressing CAFs in esophagal adenocarcinoma (AC), its precursor lesions and metastases. Podoplanin expression was investigated immunohistochemically in 200 formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded specimens of invasive esophagal ACs, their corresponding metastases and 35 precursor lesions. Podoplanin expressing CAFs (CAF+) were observed in 22 % of patients with invasive AC, but not in precursor lesions. CAF+ correlated with tumor stage (p = 0.004), lymphovascular tumor invasion (p = 0.018) and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.0016). Patients with CAF+ had a significant shorter disease free and overall survival (p < 0.05, Cox regression). Podoplanin expressing CAFs were only rarely observed in lymph node and distant metastases, as well as in local recurrences of ACs. Podoplanin expression in AC tumor cells was seen in only four cases. In around 20 % of patients with esophagal AC, podoplanin expressing CAFs are evident, defining a high risk subgroup. In these patients, podoplanin expressing CAFs might represent new therapeutical targets.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70
Jodele S, Blavier L, Yoon JM, DeClerck YA (2006) Modifying the soil to affect the seed: role of stromal-derived matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(1):35–43. doi:10.1007/s10555-006-7887-8
Blankenstein T (2005) The role of tumor stroma in the interaction between tumor and immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 17(2):180–186. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2005.01.008
Kataoka H, Tanaka H, Nagaike K, Uchiyama S, Itoh H (2003) Role of cancer cell-stroma interaction in invasive growth of cancer cells. Hum Cell 16(1):1–14
Hasebe T, Sasaki S, Imoto S, Ochiai A (2000) Proliferative activity of intratumoral fibroblasts is closely correlated with lymph node and distant organ metastases of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Am J Pathol 156(5):1701–1710. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65041-9
Kalluri R, Zeisberg M (2006) Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(5):392–401. doi:10.1038/nrc1877
Hoshino A, Ishii G, Ito T, Aoyagi K, Ohtaki Y, Nagai K, Sasaki H, Ochiai A (2011) Podoplanin-positive fibroblasts enhance lung adenocarcinoma tumor formation: podoplanin in fibroblast functions for tumor progression. Cancer Res 71(14):4769–4779. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3228
Kawase A, Ishii G, Nagai K, Ito T, Nagano T, Murata Y, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Yoshida J, Suzuki K, Ochiai A (2008) Podoplanin expression by cancer associated fibroblasts predicts poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 123(5):1053–1059. doi:10.1002/ijc.23611
Schoppmann SF, Berghoff A, Dinhof C, Jakesz R, Gnant M, Dubsky P, Jesch B, Heinzl H, Birner P (2012) Podoplanin-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts are associated with poor prognosis in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134(1):237–244. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-1984-x
Pietras K, Ostman A (2010) Hallmarks of cancer: interactions with the tumor stroma. Exp Cell Res 316(8):1324–1331. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.02.045
Rasanen K, Vaheri A (2010) Activation of fibroblasts in cancer stroma. Exp Cell Res 316(17):2713–2722. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.032
Hooper S, Gaggioli C, Sahai E (2010) A chemical biology screen reveals a role for Rab21-mediated control of actomyosin contractility in fibroblast-driven cancer invasion. Br J Cancer 102(2):392–402. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605469
Shibahara J, Kashima T, Kikuchi Y, Kunita A, Fukayama M (2006) Podoplanin is expressed in subsets of tumors of the central nervous system. Virchows Arch 448(4):493–499. doi:10.1007/s00428-005-0133-x
Kimura N, Kimura I (2005) Podoplanin as a marker for mesothelioma. Pathol Int 55(2):83–86. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2005.01791.x
Kreppel M, Scheer M, Drebber U, Ritter L, Zoller JE (2010) Impact of podoplanin expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: clinical and histopathologic correlations. Virchows Arch 456(5):473–482. doi:10.1007/s00428-010-0915-7
Ishizawa K, Komori T, Shimada S, Hirose T (2009) Podoplanin is a potential marker for the diagnosis of ependymoma: a comparative study with epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). Clin Neuropathol 28(5):373–378
Yuan P, Temam S, El-Naggar A, Zhou X, Liu DD, Lee JJ, Mao L (2006) Overexpression of podoplanin in oral cancer and its association with poor clinical outcome. Cancer 107(3):563–569. doi:10.1002/cncr.22061
Schoppmann SF, Berghoff AS, Jesch B, Zacherl J, Nirtl N, Jomrich G, Maroske F, Streubel B, Mesteri I, Birner P (2012) Expression of podoplanin is a rare event in sporadic gastrointestinal stromal tumors and does not influence prognosis. Future Oncol 8(7):859–866. doi:10.2217/fon.12.71
Tong L, Yuan S, Feng F, Zhang H (2012) Role of podoplanin expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective study. Dis Esophagus 25(1):72–80. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01211.x
Kitano H, Kageyama S, Hewitt SM, Hayashi R, Doki Y, Ozaki Y, Fujino S, Takikita M, Kubo H, Fukuoka J (2010) Podoplanin expression in cancerous stroma induces lymphangiogenesis and predicts lymphatic spread and patient survival. Arch Pathol Lab Med 134(10):1520–1527. doi:10.1043/2009-0114-OA.1
Ito M, Ishii G, Nagai K, Maeda R, Nakano Y, Ochiai A (2012) Prognostic impact of cancer-associated stromal cells in stage I lung adenocarcinoma patients. Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.11-2458
Afonso LA, Moyses N, Cavalcanti SM (2010) Human papillomavirus detection and p16 methylation pattern in a case of esophageal papilloma. Braz J Med Biol Res 43(7):694–696
Yamanashi T, Nakanishi Y, Fujii G, Akishima-Fukasawa Y, Moriya Y, Kanai Y, Watanabe M, Hirohashi S (2009) Podoplanin expression identified in stromal fibroblasts as a favorable prognostic marker in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Oncology 77(1):53–62. doi:10.1159/000226112
Aishima S, Nishihara Y, Iguchi T, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, Maehara Y, Tsuneyoshi M (2008) Lymphatic spread is related to VEGF-C expression and D2–40-positive myofibroblasts in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 21(3):256–264. doi:10.1038/Modpathol.3800985
Neri S, Ishii G, Taira T, Hishida T, Yoshida J, Nishimura M, Nagai K, Ochiai A (2012) Recruitment of podoplanin positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in metastatic lymph nodes predicts poor prognosis in pathological N2 stage III lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-012-2421-4
Shen Y, Chen CS, Ichikawa H, Goldberg GS (2010) SRC induces podoplanin expression to promote cell migration. J Biol Chem 285(13):9649–9656. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.047696
Ito S, Ishii G, Hoshino A, Hashimoto H, Neri S, Kuwata T, Higashi M, Nagai K, Ochiai A (2012) Tumor promoting effect of podoplanin-positive fibroblasts is mediated by enhanced RhoA activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422(1):194–199. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.158
Potenta S, Zeisberg E, Kalluri R (2008) The role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Br J Cancer 99(9):1375–1379. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604662
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M, Kalluri R (2007) Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res 67(21):10123–10128. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3127
Fernandez-Munoz B, Yurrita MM, Martin-Villar E, Carrasco-Ramirez P, Megias D, Renart J, Quintanilla M (2011) The transmembrane domain of podoplanin is required for its association with lipid rafts and the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43(6):886–896. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2011.02.010
Martin-Villar E, Megias D, Castel S, Yurrita MM, Vilaro S, Quintanilla M (2006) Podoplanin binds ERM proteins to activate RhoA and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 21):4541–4553. doi:10.1242/jcs.03218
Micke P, Ostman A (2005) Exploring the tumour environment: cancer-associated fibroblasts as targets in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9(6):1217–1233. doi:10.1517/14728222.9.6.1217
Ostman A, Augsten M (2009) Cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor growth—bystanders turning into key players. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19(1):67–73. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.01.003
Conflict of interest
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoppmann, S.F., Jesch, B., Riegler, M.F. et al. Podoplanin expressing cancer associated fibroblasts are associated with unfavourable prognosis in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Exp Metastasis 30, 441–446 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9549-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9549-2