Abstract
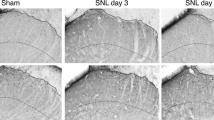
Previous studies demonstrated that the number of c-Fos protein-like immunoreactive (c-Fos-IR) neurons in the medullary dorsal horn (MDH) evoked by noxious stimulation was increased after peripheral nerve injury, and such increase has been proposed to reflect the development of neuropathic pain state. The aim of this study was to examine the MDH for convergent collateral primary afferent input to second order neurons deafferented by peripheral nerve injury, and to explore a possibility of its contribution to the c-Fos hyperinducibility. Double immunofluorescence labeling for c-Fos and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) was performed to detect convergent synaptic input. c-Fos expression and the phosphorylation of ERK were induced by the intraoral application of capsaicin and by electrical stimulation of the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN), respectively. The number of c-Fos-IR neurons in the MDH induced by the intraoral application of capsaicin was increased after IAN injury, whereas the number of p-ERK immunoreactive neurons remained unchanged. The number of double-labeled neurons, that presumably received convergent primary afferent input from the lingual nerve and the IAN, was significantly increased after IAN injury. These results indicated that convergent primary nociceptive input through neighboring intact nerves may contribute to the c-Fos hyperinducibility in the MDH and the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain following trigeminal nerve injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullitt E (1990) Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 296:517–530
Devor M, Govrin-Lippmann R (1983) Axoplasmic transport block reduces ectopic impulse generation in injured peripheral nerves. Pain 16:73–85
Dubner R, Bennett GJ (1983) Spinal and trigeminal mechanisms of nociception. Annu Rev Neurosci 6:381–418. doi:10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.002121
Fujisawa N, Terayama R, Yamaguchi D, Omura S, Yamashiro T, Sugimoto T (2012) Fos protein-like immunoreactive neurons induced by electrical stimulation in the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex of rats with chronically injured peripheral nerve. Exp Brain Res 219:191–201. doi:10.1007/s00221-012-3078-8
Hughes AS, Averill S, King VR, Molander C, Shortland PJ (2008) Neurochemical characterization of neuronal populations expressing protein kinase C gamma isoform in the spinal cord and gracile nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience 153:507–517. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.082
Hunt SP, Pini A, Evan G (1987) Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature 328:632–634
Ji RR, Woolf CJ (2001) Neuronal plasticity and signal transduction in nociceptive neurons: implications for the initiation and maintenance of pathological pain. Neurobiol Dis 8:1–10. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2000.0360
Ji RR, Baba H, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ (1999) Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci 2:1114–1119. doi:10.1038/16040
Ji RR, Befort K, Brenner GJ, Woolf CJ (2002) ERK MAP kinase activation in superficial spinal cord neurons induces prodynorphin and NK-1 upregulation and contributes to persistent inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci 22:478–485
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Woolf CJ (2003) Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 26:696–705
Liu Y, Obata K, Yamanaka H, Dai Y, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Noguchi K (2004) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in dorsal horn neurons in the rat neuropathic intermittent claudication model. Pain 109:64–72. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.01.010
Molander C, Hongpaisan J, Grant G (1992) Changing pattern of c-FOS expression in spinal cord neurons after electrical stimulation of the chronically injured sciatic nerve in the rat. Neuroscience 50:223–236
Noma N et al (2008) Organization of pERK-immunoreactive cells in trigeminal spinal nucleus caudalis and upper cervical cord following capsaicin injection into oral and craniofacial regions in rats. J Comp Neurol 507:1428–1440. doi:10.1002/cne.21620
Nomura H, Ogawa A, Tashiro A, Morimoto T, Hu JW, Iwata K (2002) Induction of Fos protein-like immunoreactivity in the trigeminal spinal nucleus caudalis and upper cervical cord following noxious and non-noxious mechanical stimulation of the whisker pad of the rat with an inferior alveolar nerve transection. Pain 95:225–238
Sessle BJ (2000) Acute and chronic craniofacial pain: brainstem mechanisms of nociceptive transmission and neuroplasticity, and their clinical correlates. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 11:57–91
Shimizu K et al (2006) Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in medullary and upper cervical cord neurons following noxious tooth pulp stimulation. Brain Res 1072:99–109. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.12.040
Shortland P, Molander C (1998) The time-course of abeta-evoked c-fos expression in neurons of the dorsal horn and gracile nucleus after peripheral nerve injury. Brain Res 810:288–293
Strassman AM, Vos BP (1993) Somatotopic and laminar organization of fos-like immunoreactivity in the medullary and upper cervical dorsal horn induced by noxious facial stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 331:495–516
Sugimoto T, Ichikawa H, Hijiya H, Mitani S, Nakago T (1993) c-Fos expression by dorsal horn neurons chronically deafferented by peripheral nerve section in response to spared, somatotopically inappropriate nociceptive primary input. Brain Res 621:161–166
Sugimoto T, Fujiyoshi Y, He YF, Xiao C, Ichikawa H (1997) Trigeminal primary projection to the rat brain stem sensory trigeminal nuclear complex and surrounding structures revealed by anterograde transport of cholera toxin B subunit-conjugated and bandeiraea simplicifolia isolectin B4-conjugated horseradish peroxidase. Neurosci Res 28:361–371
Sugimoto T, He YF, Xiao C, Ichikawa H (1998) c-fos induction in the subnucleus oralis following trigeminal nerve stimulation. Brain Res 783:158–162
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Sakai A (1987) Topographic organization of central terminal region of different sensory branches of the rat mandibular nerve. Exp Neurol 96:540–557
Terayama R, Maruhama K, Tsuchiya H, Mizutani M, Iida S, Sugimoto T (2014) Assessment of intraoral mucosal pain induced by the application of capsaicin. Arch Oral Biol 59:1334–1341. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.08.008
Tokunaga A, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Miki K, Dai Y, Tsujino H, Noguchi K (1999) Excitability of spinal cord and gracile nucleus neurons in rats with chronically injured sciatic nerve examined by c-fos expression. Brain Res 847:321–331
Woda A (2003) Pain in the trigeminal system: from orofacial nociception to neural network modeling. J Dent Res 82:764–768
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (24592764).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terayama, R., Tsuchiya, H., Omura, S. et al. Possible Involvement of Convergent Nociceptive Input to Medullary Dorsal Horn Neurons in Intraoral Hyperalgesia Following Peripheral Nerve Injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 417–423 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0137-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0137-7