Abstract
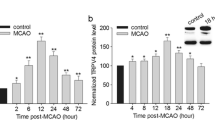
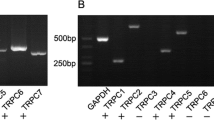
Transient receptor potential canonical channel (TRPC) is a nonselective cation channel permeable to Ca2+, which express in many cell types, including neurons. However the alterations in TRPC receptor expressions in response to status epilepticus (SE) have not been explored. Therefore, the present study was designated to elucidate the roles of TRPC3 in neuronal death and vasogenic edema within the rat piriform cortex (PC) following SE. In non-SE animals, TRPC3 immunoreactivity was abundantly detected in the PC. Following SE, TRPC3 immunoreactivity was increased in neurons. Furthermore, TRPC3 expression was detected in endothelial cells that did not contain it in non-SE animals. Loss of SMI-71 (a blood–brain barrier antigen) immunoreactivity was also observed in TRPC3 positive endothelial cells. In addition, FJB positive neurons and vasogenic edema were noticeably detected in the PC. To directly determine whether TRPC3 activation is correlated to SE-induced vasogenic edema formation and neuronal damages in the PC, the effect of Pyr-3 (a TRPC3 antagonist) on SE-induced insults were investigated. Pyr-3 infusion effectively attenuated vasogenic edema in the PC as compared to the vehicle. Therefore, our findings indicate that TRPC3 activation/overexpression induced by SE may involve BBB disruption and neuronal damages in the rat PC following SE. Therefore, the present study was TRPC3 may play an important role in SE-induced vasogenic edema formation through BBB disruptions in the rat PC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmmed GU, Malik AB (2005) Functional role of TRPC channels in the regulation of endothelial permeability. Pflugers Arch 451:131–142
Amaral MD, Pozzo-Miller L (2007) BDNF induces calcium elevations associated with IBDNF, a nonselective cationic current mediated by TRPC channels. J Neurophysiol 98:2476–2482
Ates N, van Luijtelaar EL, Drinkenburg WH, Vossen JM, Coenen AM (1992) Effects of loreclezole on epileptic activity and on EEG and behaviour in rats with absence seizures. Epilepsy Res 13:43–48
Bedi KS (1991) Effects of undernutrition during early life on granule cell numbers in the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 311:425–433
Beech DJ, Bahnasi YM, Dedman AM, Al-Shawaf E (2009) TRPC channel lipid specificity and mechanisms of lipid regulation. Cell Calcium 45:583–588
Clapham DE (2003) TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 426:517–524
Cornford EM, Oldendorf WH (1986) Epilepsy and the blood–brain barrier. Adv Neurol 44:787–812
Deli MA, Abrahám CS, Kataoka Y, Niwa M (2005) Permeability studies on in vitro blood–brain barrier models: physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25:59–127
Freichel M, Suh SH, Pfeifer A, Schweig U, Trost C, Weissgerber P, Biel M, Philipp S, Freise D, Droogmans G, Hofmann F, Flockerzi V, Nilius B (2001) Lack of an endothelial store-operated Ca2+ current impairs agonist-dependent vasorelaxation in TRP4−/− mice. Nat Cell Biol 3:121–127
Greka A, Navarro B, Oancea E, Duggan A, Clapham DE (2003) TRPC5 is a regulator of hippocampal neurite length and growth cone morphology. Nat Neurosci 6:837–845
Harteneck C, Plant TD, Schultz G (2000) From worm to man: three subfamilies of TRP channels. Trends Neurosci 23:159–166
Huang JH, He GW, Xue HM, Yao XQ, Liu XC, Underwood MJ, Yang Q (2011) TRPC3 channel contributes to nitric oxide release: significance during normoxia and hypoxia-reoxygenation. Cardiovasc Res 91:472–482
Janzer RC, Raff MC (1987) Astrocytes induce blood–brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature 325:253–257
Jia Y, Zhou J, Tai Y, Wang Y (2007) TRPC channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nat Neurosci 10:559–567
Jo SM, Ryu HJ, Kim JE, Yeo SI, Kim MJ, Choi HC, Song HK, Kang TC (2011) Up-regulation of endothelial endothelin-1 expression prior to vasogenic edema formation in the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. Neurosci Lett 501:25–30
Kang TC, Kim DS, Kwak SE, Kim JE, Won MH, Kim DW, Choi SY, Kwon OS (2006) Epileptogenic roles of astroglial death and regeneration in the dentate gyrus of experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Glia 54:258–271
Kim JE, Kang TC (2011) The P2X7 receptor-pannexin-1 complex decreases muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated seizure susceptibility in mice. J Clin Invest 121:2037–2047
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Yeo SI, Seo CH, Lee BC, Choi IG, Kim DS, Kang TC (2009) Differential expressions of aquaporin subtypes in astroglia in the hippocampus of chronic epileptic rats. Neuroscience 163:781–789
Kim JE, Yeo SI, Ryu HJ, Kim MJ, Kim DS, Jo SM, Kang TC (2010) Astroglial loss and edema formation in the rat piriform cortex and hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Comp Neurol 518:4612–4628
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Choi SY, Kang TC (2012) Tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated threonine 435 phosphorylation of p65 nuclear factor-κB subunit in endothelial cells induces vasogenic edema and neutrophil infiltration in the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. J Neuroinflamm 9:6
Kiselyov K, Mignery GA, Zhu MX, Muallem S (1999) The N-terminal domain of the IP3 receptor gates store-operated hTrp3 channels. Mol Cell 4:423–429
Koenig S, Schernthaner M, Maechler H, Kappe CO, Glasnov TN, Hoefler G, Braune M, Wittchow E, Groschner K (2013) A TRPC3 blocker, ethyl-1-(4-(2,3,3-trichloroacrylamide)phenyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate (Pyr3), prevents stent-induced arterial remodeling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344:33–40
Lassmann H, Petsche U, Kitz K, Baran H, Sperk G, Seitelberger F, Hornykiewicz O (1984) The role of brain edema in epileptic brain damage induced by systemic kainic acid injection. Neuroscience 13:691–704
Lee EH, Cherednichenko G, Pessah IN, Allen PD (2006) Functional coupling between TRPC3 and RyR1 regulates the expressions of key triadic proteins. J Biol Chem 281:10042–10048
Lepage PK, Lussier MP, Barajas-Martinez H, Bousquet SM, Blanchard AP, Francoeur N, Dumaine R, Boulay G (2006) Identification of two domains involved in the assembly of transient receptor potential canonical channels. J Biol Chem 281:30356–30364
Li Y (2005) Essential role of TRPC channels in the guidance of nerve growth cones by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature 434:894–898
Li W, Ehrich M (2012) Transient alterations of the blood–brain barrier tight junction and receptor potential channel gene expression by chlorpyrifos. J Appl Toxicol. doi:10.1002/jat.2762
Mayhan WG (2001) Regulation of blood–brain barrier permeability. Microcirculation 8:89–104
McKay RR, Szymeczek-Seay CL, Lievremont JP, Bird GS, Zitt C, Jüngling E, Lückhoff A, Putney JW Jr (2000) Cloning and expression of the human transient receptor potential 4 (TRP4) gene: localization and functional expression of human TRP4 and TRP3. Biochem J 351:735–746
Montell C, Birnbaumer L, Flockerzi V (2002) The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell 108:595–598
Nilius B, Droogmans G, Wondergem R (2003) Transient receptor potential channels in endothelium: solving the calcium entry puzzle? Endothelium 10:5–15
Nitsch C, Suzuki R, Fujiwara K, Klatzo I (1985) Incongruence of regional cerebral blood flow increase and blood–brain barrier opening in rabbits at the onset of seizures induced by bicuculline, methoxypyridoxine, and kainic acid. J Neurol Sci 67:67–79
Nitsch C, Goping G, Klatzo I (1986) Pathophysiological aspects of blood–brain barrier permeability in epileptic seizures. Adv Exp Med Biol 203:175–189
Oztaş B, Kaya M (1991) The effect of acute hypertension on blood–brain barrier permeability to albumin during experimentally induced epileptic seizures. Pharmacol Res 23:41–46
Park HW, Kim JY, Choi SK, Lee YH, Zeng W, Kim KH, Muallem S, Lee MG (2011) Serine–threonine kinase with-no-lysine 4 (WNK4) controls blood pressure via transient receptor potential canonical 3 (TRPC3) in the vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:10750–10755
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Pencea V, Bingaman KD, Wiegand SJ, Luskin MB (2001) Infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor into the lateral ventricle of the adult rat leads to new neurons in the parenchyma of the striatum, septum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. J Neurosci 21:6706–6717
Peppiatt CM, Howarth C, Mobbs P, Attwell D (2006) Bidirectional control of CNS capillary diameter by pericytes. Nature 443:700–704
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Redondo PC, Harper AG, Salido GM, Pariente JA, Sage SO, Rosado JA (2004) A role for SNAP-25 but not VAMPs in store-mediated Ca2+ entry in human platelets. J Physiol 558:99–109
Risau W, Dingler A, Albrecht U, Dehouck MP, Cecchelli R (1992) Blood–brain barrier pericytes are the main source of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity in brain capillaries. J Neurochem 58:667–672
Rosado JA, Redondo PC, Salido GM, Sage SO, Pariente JA (2004) Cleavage of SNAP-25 and VAMP-2 impairs store-operated Ca2+ entry in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C214–C221
Ruth RE (1984) Increased cerebrovascular permeability to protein during systemic kainic acid seizures. Epilepsia 25:259–268
Scharfman HE, Goodman JH, Sollas AL, Croll SD (2002) Spontaneous limbic seizures after intrahippocampal infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Exp Neurol 174:201–214
Segal M (1988) Effects of mu opioid receptor activation in rat hippocampal slice. NIDA Res Monogr 82:133–145
Seiffert E, Dreier JP, Ivens S, Bechmann I, Tomkins O, Heinemann U, Friedman A (2004) Lasting blood–brain barrier disruption induces epileptic focus in the rat somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci 24:7829–7836
Sheen SH, Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Yang Y, Choi KC, Kang TC (2010) Decrease in dystrophin expression prior to disruption of brain–blood barrier within the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. Brain Res 1369:173–183
Siuciak JA, Boylan C, Fritsche M, Altar CA, Lindsay RM (1996) BDNF increases monoaminergic activity in rat brain following intracerebroventricular or intraparenchymal administration. Brain Res 710:11–20
Smolders I, Bogaert L, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (1997) Muscarinic modulation of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and GABA release, as measured with in vivo microdialysis. J Neurochem 68:1942–1948
Unsain N, Montroull LE, Mascó DH (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor facilitates TrkB down-regulation and neuronal injury after status epilepticus in the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 111:428–440
Van Vliet EA, da Costa Araújo S, Redeker S, van Schaik R, Aronica E, Gorter JA (2007) Blood–brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 130:521–534
Vazquez G, Wedel BJ, Aziz O, Trebak M, Putney JW Jr (2004) The mammalian TRPC cation channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1742:21–36
Venkatachalam K, Zheng F, Gill DL (2003) Regulation of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channel function by diacylglycerol and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 278:29031–29040
Wes PD, Chevesich J, Jeromin A, Rosenberg C, Stetten G, Montell C (1995) TRPC1, a human homolog of a Drosophila store-operated channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9652–9656
Yao X, Garland CJ (2005) Recent developments in vascular endothelial cell transient receptor potential channels. Circ Res 97:853–863
Zhu X, Chu PB, Peyton M, Birnbaumer L (1995) Molecular cloning of a widely expressed human homologue for the Drosophila trp gene. FEBS Lett 373:193–198
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (Grant number A111313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, H.J., Kim, JE., Kim, YJ. et al. Endothelial Transient Receptor Potential Conical Channel (TRPC)-3 Activation Induces Vasogenic Edema Formation in the Rat Piriform Cortex Following Status Epilepticus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 575–585 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9931-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9931-x