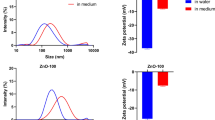
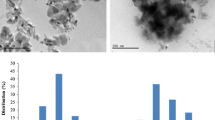
Abstract
A route of accumulation and elimination of therapeutic engineered nanoparticles (NPs) may be the kidney. Therefore, the interactions of different solid-core inorganic NPs (titanium-, silica-, and iron oxide-based NPs) were studied in vitro with the MDCK and LLC-PK epithelial cells as representative cells of the renal epithelia. Following cell exposure to the NPs, observations include cytotoxicity for oleic acid-coated iron oxide NPs, the production of reactive oxygen species for titanium dioxide NPs, and cell depletion of thiols for uncoated iron oxide NPs, whereas for silica NPs an apparent rapid and short-lived increase of thiol levels in both cell lines was observed. Following cell exposure to metallic NPs, the expression of the tranferrin receptor/CD71 was decreased in both cells by iron oxide NPs, but only in MDCK cells by titanium dioxide NPs. The tight association, then subsequent release of NPs by MDCK and LLC-PK kidney epithelial cells, showed that following exposure to the NPs, only MDCK cells could release iron oxide NPs, whereas both cells released titanium dioxide NPs. No transfer of any solid-core NPs across the cell layers was observed.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Carboxy-H2DCFDA:
-
5/6-Carboxy-2,7-dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein
- DAPI:
-
4′,6′-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- HBSS:
-
Hank’s buffer solution
- 3H-T:
-
Tritiated thymidine
- LY:
-
Lucifer Yellow
- MTT:
-
3,4,5-Dimethylthiazol-yl-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- NEM:
-
N-Ethyl-maleimide
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TBHP:
-
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide
- TEER:
-
Transepithelial electrical resistance
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- USPIO:
-
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide
References
Alexiou C, Jurgons R, Seliger C, Iro H. Medical applications of magnetic nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2006;6:2762–8.
Caruthers SD, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. Nanotechnological applications in medicine. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18:26–30.
Cengelli F, Voinesco F, Juillerat-Jeanneret L. Interaction of cationic ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with human melanoma cells. Nanomedicine. 2010;5:1075–87.
Chen Z, Meng H, Xing G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G, Wang T, Yuan H, Ye C, Zhao F, Chai Z, Zhu C, Fang X, Ma B, Wan L. Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol Lett. 2006;163:109–20.
Choi CH, Zuckerman JE, Webster P, Davis ME. Targeting kidney mesangium by nanoparticles of defined size. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:6656–61.
Gomes A, Fernandes E, Lima JLFC. Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2005;65:45–80.
Halamoda Kenzaoui B, Vila MR, Miquel JM, Cengelli F, Juillerat-Jeanneret L. Evaluation of uptake and transport of cationic and anionic ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles by human colon cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012a;7:1275–86.
Halamoda Kenzaoui B, Chapuis Bernasconi C, Guney-Ayra S, Juillerat-Jeanneret L. Induction of oxidative stress, lysosome activation and autophagy by nanoparticles in human brain endothelial cells. Biochem J. 2012b;441:813–21.
Halamoda Kenzaoui B, Chapuis Bernasconi C, Hofmann H, Juillerat-Jeanneret L. Evaluation of uptake and transport of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by human brain-derived endothelial cells. Nanomedicine. 2012c;7:39–53.
Heath JR, Davis ME. Nanotechnology and cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:251–65.
Jain TK, Reddy MK, Morales MA, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V. Biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles in rats. Mol Pharm. 2008;5:316–27.
Johnson-Lyles DN, Peifley K, Lockett S, Neun BW, Hansen M, Clogston J, Stern ST, McNeil SE. Fullerenol cytotoxicity in kidney cells is associated with cytoskeleton disruption, autophagic vacuole accumulation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;248:249–58.
Kim W, Kim J, Park JD, Ryu HY, Yu IJ. Histological study of gender differences in accumulation of silver nanoparticles in kidneys of Fischer 344 rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2009;72:1279–84.
Kuniaki T, Yuk T, Toshiyuki M, Takeo A, Takeshi S, Ablimit A, Haruo H. Molecular mechanisms and drug development in aquaporin water channel diseases: water channel aquaporin-2 of kidney collecting duct cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004;96:255–9.
L’Azou B, Jorly J, On D, Sellier E, Moisan F, Fleury-Feith J, Cambar J, Brochard P, Ohayon-Courtès C. In vitro effects of nanoparticles on renal cells. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2008;5:22.
Lee KG, Wi R, Park TJ, Yoon SH, Lee J, Lee SJ, Kim Do H. Synthesis and characterization of gold-deposited red, green and blue fluorescent silica nanoparticles for biosensor application. Chem Commun. 2010;46:6374–6.
Liu Y, Lou C, Yang H, Shi M, Miyosh H. Silica nanoparticles as promising drug/gene delivery carriers and fluorescent nano-probes: recent advances. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011;11:156–63.
Longmire M, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: consideration and caveats. Nanomedicine. 2008;3:703–17.
Longmire M, Ogawa M, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Biologically optimized nanosized molecules and particles: more than just size. Bioconjug Chem. 2011;22:993–1000.
Magdolenova Z, Bilanicova D, Pojana G, Fjellsbø LM, Hudecova A, Hasplova K, Marcomini A, Dusinska M. Impact of agglomeration and different dispersions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the human related in vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. J Environ Monitor. 2012;14:455–64.
Mahmoudi M, Laurent S, Shokrgozar MA, Hosseinkhani M. Toxicity evaluation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: cell vision versus physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2011;5:7263–76.
Marquis BJ, Love SA, Braun KL, Haynes CL. Analytical methods to assess nanoparticle toxicity. Analyst. 2009;134:425–39.
Napierska D, Thomassen LC, Rabolli V, Lison D, Gonzalez L, Kirsch-Volders M, Martens JA, Hoet PH. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small. 2009;5:846–53.
Naqvi S, Samim M, Abdin M, Ahmed FJ, Maitra A, Prashant C, Dinda AK. Concentration-dependent toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles mediated by increased oxidative stress. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010;5:983–9.
Passagne I, Morille M, Rousset M, Pujalté I, L’Azou B. Implication of oxidative stress in size-dependent toxicity of silica nanoparticles. Toxicology. 2012;299:112–24.
Petri-Fink A, Chastellain M, Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Ferrari A, Hofmann H. Development of functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for interaction with human cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26:639–46.
Pujalté I, Passagne I, Brouillaud B, Tréguer M, Durand E, Ohayon-Courtès C, L’Azou B. Cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by different metallic nanoparticles on human kidney cells. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2011;8:10.
Rupp F, Haup M, Klostermann H, Kim HS, Eichler M, Peetsch A, Scheideler L, Doering C, Oehr C, Wendel HP, Sinn S, Decker E, von Ohle C, Geis-Gerstorfer J. Multifunctional nature of UV-irradiated nanocrystalline anatase thin films for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:4566–77.
Semete B, Booysen L, Lemmer Y, Kalombo L, Katata L, Verschoor J, Swai HS. In vivo evaluation of the biodistribution and safety of PLGA nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Nanomedicine. 2010;6:662–71.
Singh S. Nanomedicine—nanoscale drugs and delivery systems. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10:7906–18.
Stern S, Zolnik BS, McLeland CB, Clogston J, Zheng J, McNeil SE. Induction of autophagy in porcine kidney cells by quantum dots: a common cellular response to nanomaterials? Toxicol Sci. 2008;106:140–52.
Tang J, Xiong L, Wang S, Wang J, Liu L, Li J, Yuan F, Xi TJ. Distribution, translocation and accumulation of silver nanoparticles in rats. Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2009;9:4924–32.
Wang YXJ, Hussain SM, Krestin GP. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:2319–31.
Wang J, Zhou G, Chen C, Yu H, Wang T, Ma Y, Jia G, Gao Y, Li B, Sun J, Li Y, Jiao F, Zhao Y, Chai Z. Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168:176–85.
Wang F, Gao F, Lan M, Yuan H, Huang Y, Liu J. Oxidative stress contributes to silica nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity in human embryonic kidney cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009;23:808–15.
Weinstein JS, Varallyay CG, Dosa E, Gahramanov S, Hamilton B, Rooney WD, Muldoon LL, Neuwelt EA. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging and potential therapeutic applications in neurooncology and central nervous system inflammatory pathologies, a review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30:15–35.
Wu EX, Tang H, Jensen JH. Applications of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents in the MR study of animal models. NMR Biomed. 2004;17:478–83.
Wu P, He X, Wang K, Tan W, Ma D, Yang W, He C. Imaging breast cancer cells and tissue using peptide-labeled fluorescent silica nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008;8:2483–7.
Yuan Y, Ding J, Xu J, Deng J, Guo J. TiO2 nanoparticles co-doped with silver and nitrogen for antibacterial application. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10:4868–74.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank S. Güney-Ayra for excellent technical assistance and P. Bowen and H. Hofmann from EPFL, Lausanne, for providing the thermogravimetric analyses of the silica nanoparticles. This research was supported by a grant from the European Community 7th Framework Program (project no. 2007–201335 “NanoTEST”).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant affiliation or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest or conflict concerning the information presented in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1210 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halamoda Kenzaoui, B., Chapuis Bernasconi, C. & Juillerat-Jeanneret, L. Stress reaction of kidney epithelial cells to inorganic solid-core nanoparticles. Cell Biol Toxicol 29, 39–58 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-012-9236-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-012-9236-8