Abstract
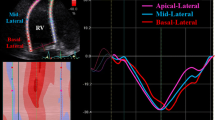
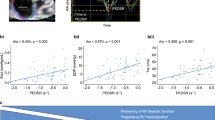
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is a practical and widely used tool for risk stratification in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). We hypothesized that right atrial (RA) reservoir function, represented by peak RA systolic strain, correlates with invasive hemodynamic measurements and clinical outcomes in PAH. Patients with group 1 PAH who had TTE within 6 months of index PAH clinic visit and right heart catheterization were included in this retrospective study. Peak RA strain in the 2D apical 4-chamber view was measured with speckle-tracking software. The primary endpoint was a composite of prostacyclin initiation, lung transplantation, and death. RA strain was also measured in healthy control subjects. Among the 37 patients studied, 25 (68%) met the primary endpoint. RA strain was significantly lower among patients who met the primary endpoint than among those who did not (mean 20% vs. 33%, P = 0.002). Strain was lower in PAH patients than in controls (mean 24% vs. 35%, P = 0.0001). RA strain correlated negatively with hemodynamic data including RA pressure (R = −0.31), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (R = −0.33), and pulmonary vascular resistance (R = −0.39), and positively with cardiac index (R = 0.44). In receiver operating characteristic analysis to distinguish between patients meeting the primary endpoint and event-free survivors, RA strain was not significantly different from RA volume, right ventricular (RV) fractional area change, RV basal diameter, or right ventricular systolic pressure (area under the curve 0.82, 0.81, 0.83, 0.86, and 0.97, respectively). Our results demonstrate that RA strain is predictive of clinical outcomes in PAH. Further research is needed to determine if RA strain is independently associated with outcomes in this population.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
McLaughlin V, Shah SJ, Souza R, Humbert M (2015) Management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:1976–1997. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.540
Haddad F, Spruijt OA, Denault AY, Mercier O, Brunner N, Furman D et al (2015) Right heart score for predicting outcome in patients with idiopathic, familial or drug and toxin associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 8:627–638. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2014.12.029
Bustamante-Labarta M, Perrone S, De La Fuente RL, Stutzbach P, De La Hoz RP, Torino A, Favaloro R (2002) Right atrial size and tricuspid regurgitation severity predict mortality or transplantation in primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 15:1160–1164
D’Alto M, Scognamiglio G, Dimopoulos K, Bossone E, Vizza D, Romeo E et al (2015) Right heart and pulmonary vessels structure and function. Echocardiography 32:S3–S10. doi:10.1111/echo.12227
Addetia K, Takeuchi M, Maffessanti F, Nagata Y, Hamilton J, Mor-Avi V, Lang RM (2016) Simultaneous longitudinal strain in all 4 cardiac chambers: a novel method for comprehensive functional assessment of the heart. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 9:e003895. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003895
Farsalinos KE, Daraban AM, Unlu S, Thomas JD, Badano LP, Voigt JU (2015) Head-to-head comparison of global longitudinal strain measurements among nine different vendors: the EACVI/ASE inter-vendor comparison study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 28:1171–1181. doi:10.1016/j.echo.2015.06.011
Sakata K, Uesugi Y, Isaka A, Minamishima T, Matsushita K, Satoh T, Yoshino H (2016) Evaluation of right atrial function using right atrial speckle tracking analysis in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension. J Echocardiogr 14:30–38. doi:10.1007/s12574-015-0270-4
Querejeta Roca G, Campbell P, Claggett B, Solomon SD, Shah AM (2015) Right atrial function in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 8:e003521. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003521
Saha SK, Soderberg S, Lindqvist P (2016) Association of right atrial mechanics with hemodynamics and physical capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: insight from a single-center cohort in northern Sweden. Echocardiography 33:46–56. doi:10.1111/echo.12993
Brunner NW, Haddad F, Kobayashi Y, Hsi A, Swiston JR, Gin KG, Zamanian RT (2015) Prognostic utility of right atrial emptying fractions in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ 5:473–480. doi:10.1086/682218.
Fukuda Y, Tanaka H, Ryo-Koriyama K, Motoji Y, Sano H, Shimoura H et al (2016) Comprehensive functional assessment of right-sided heart using speckle tracking strain for patients with pulmonary hypertension. Echocardiography 33:1001–1008. doi:10.1111/echo.13205
D’Andrea A, D’Alto M, Di Maio M, Vettori S, Benjamin N, Cocchia R et al (2016) Right atrial morphology and function in patients with systemic sclerosis compared to healthy controls: a two-dimensional strain study. Clin Rheumatol 35:1733–1742. doi:10.1007/s10067-016-3279-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Drs. Bhave, Visovatti, and Kolias and Mr. Kulick report no conflict of interest relevant to this manuscript. Dr. McLaughlin acts as a consultant and/or receives support from Actelion, Arena, Bayer, Gilead, Steadymed, St. Jude Medical, and United Therapeutics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhave, N.M., Visovatti, S.H., Kulick, B. et al. Right atrial strain is predictive of clinical outcomes and invasive hemodynamic data in group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 33, 847–855 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1081-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1081-7