Abstract
Purpose
The association between ABO blood group and the risk of esophageal carcinoma (EC) in previously published studies is uncertain and conflicting. The aim of the current study was to determine the correlation of ABO blood group with EC risk via a case–control study and meta-analysis.
Methods
We performed a population-based case–control study of 3,595 cases and 41,788 controls in Chinese population to evaluate the association between ABO blood group and EC risk. Then, a comprehensive meta-analysis combining our original data and previously published data was conducted to clearly discern the real relationship. The strength of association was measured by odds ratios (ORs) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI).
Results
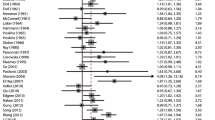
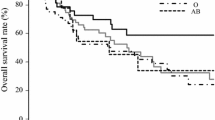
In our case–control study, the risk of EC in blood group B was significantly higher than that in non-B groups (A, O, and AB) (OR = 1.15, 95 % CI 1.09–1.21). Compared with non-O groups (A, B, and AB), individuals with blood group O demonstrated a reduced risk of EC (OR = 0.90, 95 % CI 0.85–0.94). The meta-analysis also indicated that blood group B was associated with significantly higher EC risk (OR = 1.20, 95 % CI 1.10–1.31), and people with blood group O had a decreased EC risk (OR = 0.94, 95 % CI 0.90–0.99). Neither the case–control study nor the meta-analysis produced any significant association of blood group A or AB with EC risk.
Conclusion
Results from our case–control study and the followed meta-analysis confirmed that there was an increased risk of EC in blood group B individuals, whereas a decreased risk of EC was observed in blood group O individuals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C, Ward EM (2010) Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 19:1893–1907
Wang JB, Jiang Y, Liang H et al (2012) Attributable causes of cancer in China. Ann Oncol : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO. 23:2983–2989
Wu M, Zhang ZF, Kampman E et al (2011) Does family history of cancer modify the effects of lifestyle risk factors on esophageal cancer? A population-based case-control study in China. Int J Cancer 128:2147–2157
Yamamoto F, Clausen H, White T, Marken J, Hakomori S (1990) Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature 345:229–233
Yamamoto F (1990) Cloning the ABH genes. Transfusion 30:671–672
Ben Q, Wang K, Yuan Y, Li Z (2011) Pancreatic cancer incidence and outcome in relation to ABO blood groups among Han Chinese patients: a case-control study. Int J Cancer 128:1179–1186
Li Q, Yu CH, Yu JH et al (2012) ABO blood group and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study in patients with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS One 7:e29928
Urun Y, Utkan G, Cangir AK et al (2013) Association of ABO blood group and risk of lung cancer in a multicenter study in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:2801–2803
Poole EM, Gates MA, High BA et al (2012) ABO blood group and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer within the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium. Cancer Causes Control : CCC. 23:1805–1810
Sheng L, Sun X, Zhang L, Su D (2013) ABO blood group and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk in a population of Southeast China. Int J Cancer 133:893–897
Gong Y, Yang YS, Zhang XM et al (2012) ABO blood type, diabetes and risk of gastrointestinal cancer in northern China. World J Gastroenterol 18:563–569
Hoffmann R, Craik DJ, Bokonyi K, Varga I, Otvos L Jr (1999) High level of aspartic acid-bond isomerization during the synthesis of an N-linked tau glycopeptide. J Pept Sci : an official publication of the European Peptide Society. 5:442–456
Sato E, Maruta K, Yonezawa S, Nakamura T (1984) Blood group H(O) antigen in normal, dysplastic and carcinomatous esophageal epithelium. Gann 75:223–229
Meany DL, Chan DW (2011) Aberrant glycosylation associated with enzymes as cancer biomarkers. Clin Proteomics 8:7
Iodice S, Maisonneuve P, Botteri E, Sandri MT, Lowenfels AB (2010) ABO blood group and cancer. Eur J Cancer 46:3345–3350
Sauerland S, Seiler CM (2005) Role of systematic reviews and meta-analysis in evidence-based medicine. World J Surg 29:582–587
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA, J Am Med Assoc 283:2008–2012
Wells GA, Shea B, O’connell D et al (2000) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 20 March 2014
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Leucht S, Kissling W, Davis JM (2009) How to read and understand and use systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Acta Psychiatr Scand 119:443–450
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Aird I, Lee DR, Roberts JA (1960) ABO blood groups and cancer of oesophagus, cancer of pancreas, and pituitary adenoma. Br Med J 1:1163–1166
Beasley WH (1964) The ABO blood groups of carcinoma of the oesophagus and of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Clin Pathol 17:42–44
Hartmann O, Stavem P (1964) ABO blood-groups and cancer. Lancet 1:1305–1306
Macafee AL (1967) Blood groups and gastrointestinal cancer. A comparison of the ABO distribution by site of lesion. Ulster Med J 36:51–52
Ray KA (1980) Blood groups and cancer in India. Curr Anthropol 21:794–795
Su M, Lu SM, Tian DP et al (2001) Relationship between ABO blood groups and carcinoma of esophagus and cardia in Chaoshan inhabitants of China. World J Gastroenterol 7:657–661
Afrose S (2005) Association of ABO blood group with malignancies. J Bangladesh Coll Phys Surg 23:18–24
Guleria K, Singh PH, Kaur HS, Sambyal V (2005) ABO blood groups in gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and breast carcinoma patients. Anthropologist 7:189–192
Aminian A, Mirsharifi R, Alibakhshi A, Khorgami Z, Dashti H, Hasani MS (2010) Relationship between esophageal cancer and blood groups. World Appl Sci J 8:503–508
Wang Z, Liu L, Ji J et al (2012) ABO blood group system and gastric cancer: a case-control study and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 13:13308–13321
Risch HA, Lu L, Wang J et al (2013) ABO blood group and risk of pancreatic cancer: a study in shanghai and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 177:1326–1337
Larsen RD, Ernst LK, Nair RP, Lowe JB (1990) Molecular cloning, sequence, and expression of a human GDP-L-fucose:beta-D-galactoside 2-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase cDNA that can form the H blood group antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6674–6678
Yazer MH (2005) What a difference 2 nucleotides make: a short review of ABO genetics. Transfus Med Rev 19:200–209
Tauchi K, Kakudo K, Machimura T, Makuuchi H, Mitomi T (1991) Immunohistochemical studies of blood group-related antigens in human superficial esophageal carcinomas. Cancer 67:3042–3050
Le Pendu J, Marionneau S, Cailleau-Thomas A, Rocher J, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Clement M (2001) ABH and Lewis histo-blood group antigens in cancer. APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica. 109:9–31
Pare G, Chasman DI, Kellogg M et al (2008) Novel association of ABO histo-blood group antigen with soluble ICAM-1: results of a genome-wide association study of 6,578 women. PLoS Genet 4:e1000118
Paterson AD, Lopes-Virella MF, Waggott D et al (2009) Genome-wide association identifies the ABO blood group as a major locus associated with serum levels of soluble E-selectin. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1958–1967
Barbalic M, Dupuis J, Dehghan A et al (2010) Large-scale genomic studies reveal central role of ABO in sP-selectin and sICAM-1 levels. Hum Mol Genet 19:1863–1872
Melzer D, Perry JR, Hernandez D et al (2008) A genome-wide association study identifies protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs). PLoS Genet 4:e1000072
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Songyao Jiang from Department of Surgery, Eastern Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai, for his skillful technical assistance. This study was supported in part by grant funding of NSFC (Natural Science Foundation of China, 81101847), Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (20110073120089), project supported by the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (124119a4801), mandatory project from Nantong Science and Technology Commission (Grant no.: HS2011006).
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei Wang and Lei Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Liu, L., Wang, Z. et al. ABO blood group and esophageal carcinoma risk: from a case–control study in Chinese population to meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 25, 1369–1377 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-014-0442-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-014-0442-y