Abstract
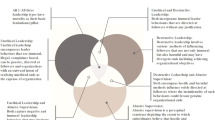
Interest in ethical leadership from academics and practitioners has grown enormously in recent years. This article addresses this literature through a framework that identifies three interlocking questions. First, who are ethical leaders and what are their characteristics? Second, how do ethical leaders do what they do? Third, why do leaders do as they do and what are the outcomes of ethical leadership? Different dimensions to ethical leadership are examined and presented as three interlocking circles; Virtues, Purposes and Practices. This framework presents an integrated approach to ethical leadership and argues that future research take this holistic framework and apply it to different sectors or contexts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristotle, (1947). Nicomachean ethics. Translated by W.D. Ross. New York: Random House.
Arjoon, S. (2000). Virtue theory as a dynamic theory of business. Journal of Business Ethics, 28(2), 159–178.
Avolio, B. J., & Gardner, W. L. (2005). Authentic leadership development: Getting to the root of positive forms of leadership. The Leadership Quarterly, 16(3), 315–338.
Avolio, B., Luthans, F., Walumbwa, F.O. (2004). Authentic leadership: Theory-building for veritable sustained performance. Working paper. Lincoln: Gallup Leadership Institute, University of Nebraska.
Badaracco, J. L, Jr, & Ellsworth, R. R. (1991). Leadership, integrity and conflict. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 4(4), 46–55.
Barnard, C. (1938). The functions of the executive. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Beabout, G. R. (2012). Management as a domain-relative practice that requires and develops practical wisdom. Business Ethics Quarterly, 22(2), 405–432.
Beadle, R. (2008). Why business cannot be a practice. Analyse & Kritik, 30, 229–241.
Beauchamp, T., & Childress, J. (2008). Principles of biomedical ethics (6th ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
Bragues, G. (2006). Seek the good life, not money: The Aristotelian approach to business ethics. Journal of Business Ethics, 67(4), 341–357.
Brenkert, G. G. (2004). Corporate integrity and accountability. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Brown, M. E., & Treviño, L. K. (2006). Ethical leadership: A review and future directions. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(6), 595–616.
Brown, M. E., Treviño, L. K., & Harrison, D. A. (2005). Ethical leadership: A social learning perspective for construct development and testing. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 97(2), 117–134.
Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. New York: Harper & Row.
Caldwell, C. (2009). Identity, self-awareness, and self-deception: Ethical implications for leaders and organizations. Journal of Business Ethics, 90(3), 393–406.
Caldwell, C., Bischoff, S. J., & Karri, R. (2002). The four umpires: A paradigm for ethical leadership. Journal of Business Ethics, 36(1/2), 153–163.
Caldwell, C., & Dixon, R. D. (2010). Love, forgiveness, and trust: Critical values of the modern leader. Journal of Business Ethics, 93(1), 91–101.
Cameron, K. S., Bright, D., & Caza, A. (2004). Exploring the relationships between organizational virtuousness and performance. The American Behavioral Scientist, 47(6), 766–790.
Cameron, K. S., Dutton, J. E., & Quinn, R. E. (2003). Positive organizational scholarship: Foundations of a new discipline. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers Inc.
Carlisle, Y. M., & Manning, D. J. (1996). The Domain of Professional Business Ethics. Organization, 3(3), 341–360.
Cawley, M. J., Martin, J. E., & Johnson, J. A. (2000). A virtues approach to personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 28(5), 997–1013.
Ciulla, J. B. (2005). The state of leadership ethics and the work that lies before us. Business Ethics: A European Review, 14(4), 323–335.
Coady, C. A. J. (2008). Messy morality: The challenge of politics. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Cunliffe, A. L. (2009). The philosopher leader: On relationalism, ethics and reflexivity—A critical perspective to teaching leadership. Management Learning, 40(1), 87–101.
De Hoogh, A. H. B., & Den Hartog, D. N. (2008). Ethical and despotic leadership, relationships with leader’s social responsibility, top management team effectiveness and subordinates’ optimism: A multi-method study. Leadership Quarterly, 19(3), 297–311.
Den Hartog, D. N., & De Hoogh, A. H. B. (2009). Empowering behaviour and leader fairness and integrity: Studying perceptions of ethical leader behaviour from a levels-of-analysis perspective. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 18(2), 199–230.
Den Hartog, D. N., House, R. J., Hanges, P. J., Ruiz-Quintanilla, S. A., Dorfman, P. W., et al. (1999). Culturally specific and cross-culturally generalizable implicit leadership theories: Are attributes of charismatic/transformational leadership universally endorsed? The Leadership Quarterly, 10(2), 219–256.
Detert, J. R., Treviño, L. K., Burris, E. R., & Andiappan, M. (2007). Managerial modes of influence and counter productivity in organizations: A longitudinal business-unit-level investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92(4), 993–1005.
Dobel, J. P. (1999). Public integrity. Baltimore: John Hopkins University Press.
Dukerich, J. M., Nichols, M. L., Elm, D. R., & Vollrath, D. A. (1990). Moral reasoning in groups: Leaders make a difference. Human Relations, 43(5), 473–493.
Dworkin, R. (2012). Justice for Hedgehogs. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Eisenbeiss, S. A. (2012). Re-thinking ethical leadership: An interdisciplinary integrative approach. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(5), 791–808.
Eisenbeiß, S. A., & Giessner, S. R. (2012). The emergence and maintenance of ethical leadership in organizations: A question of embeddedness? Journal of Personnel Psychology, 11(1), 7–19.
Enderle, G. (1987). Some perspectives of managerial ethical leadership. Journal of Business Ethics, 6(8), 657–663.
Engelbrecht, A. S., van Aswegen, A. S., & Theron, C. C. (2005). The effect of ethical values on transformational leadership and ethical climate in organisations. South African Journal of Business Management, 36(2), 19–26.
Fairhurst, G. T., & Grant, D. (2010). The social construction of leadership: A sailing guide. Management Communications Quarterly, 24(2), 171–210.
Fijnaut, C. J. C. F., & Huberts, L. W. J. C. (2002). Corruption, integrity and law enforcement. Dordrecht: Kluwer Law International.
Flynn, G. (2008). The virtuous manager: A vision for leadership in business. Journal of Business Ethics, 78(3), 359–372.
Ford, J. (2006). Discourses of leadership: Gender, identity and contradiction in a UK public sector organization. Leadership, 2(1), 77–99.
Freeman, R. E., Martin, K., Parmar, B., Cording, M. P., & Werhane, P. H. (2006). Leading through values and ethical principles. In R. J. Burke & C. L. Cooper (Eds.), Inspiring leaders (pp. 149–174). Abingdon: Routledge.
Gardner, W. L., Avolio, B. J., Luthans, F., May, D. R., & Walumbwa, F. (2005). Can you see the real me? A self-based model of authentic leader and follower development. The Leadership Quarterly, 16(3), 343–372.
Grint, K. (2005). Problems, problems, problems: The social construction of ‘leadership’. Human Relations, 58, 1467–1494.
Guillen, M., & Gonzalez, T. F. (2001). The ethical dimension of managerial leadership: Two illustrative case studies in TQM. Journal of Business Ethics, 34(3/4), 175–189.
Hendrix, W. H., Barlow, C. B., & Luedtke, C. J. (2004). Multimethod approach for measuring changes in character. Journal of Research in Character Education, 2(1), 59–80.
Heres, L. (2010). What makes the difference? Ethical leadership across the public-private continuum. Amsterdam: Faculty of Social Sciences, Vrije Universitei.
Hofstede, G. (1980). Culture’s consequences. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications Inc.
Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture’s consequences: Comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications Inc.
Hogan, R., Curphy, G. J., & Hogan, J. (1994). What we know about leadership. American Psychologist, 49(6), 493–504.
House, R. J., Hanges, P. J., Javidan, M., Dorfman, P., & Gupta, V. (2004). Culture, leadership, and organizations: The GLOBE study of 62 societies. California: Sage Publications Inc.
House, R., Hanges, P., Ruiz-Quintanilla, S., Dorfman, P., Javidan, M., Dickson, M., et al. (1999). Cultural influences on leadership and organizations: Project GLOBE. In W. Mobley, M. Gessner, & V. Arnold (Eds.), Advances in global leadership (Vol. 1, pp. 171–233). Stamford: JAI Press.
Howell, J. M., & Avolio, B. J. (1992). The ethics of charismatic leadership: Submission or liberation? Academy of Management Executive, 6(2), 43–52.
Huberts, L. W. J. C., Kaptein, M., & Lasthuizen, K. (2007). A study of the impact of three leadership styles on integrity violations committed by police officers. Policing: An International Journal of Police Strategies & Management, 30(4), 587–607.
Ilies, R., Morgeson, F. P., & Nahrgang, J. D. (2005). Authentic leadership and eudaemonic wellbeing: Understanding leader-follower outcomes. Leadership Quarterly, 16(3), 373–394.
Kalshoven, K. (2010). Ethical leadership: Through the eyes of employees. Doctoral dissertation. The Netherlands: Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Amsterdam. ISBN 978-90-9024946-9.
Kalshoven, K., Den Hartog, D. N., & De Hoogh, A. H. B. (2011). Ethical leadership at work questionnaire (ELW): Development and validation of a multidimensional measure. The Leadership Quarterly, 22(1), 51–69.
Keating, M., Martin, G. S., Resick, C. J., & Dickson, M. W. (2007). A comparative study of the endorsement of ethical leadership in Ireland and the United States. The Irish Journal of Management, 28(1), 5–30.
Kemavuthanon, S., & Duberley, J. (2009). A Buddhist view of leadership: The case of the OTOP project. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 30(8), 737–758.
Kempster, S., Jackson, B., & Conroy, M. (2011). Leadership as purpose: Exploring the role of purpose in leadership practice. Leadership, 7(3), 317–334.
Kieran, M. (1995). Applied philosophy and business ethics. Journal of Applied Philosophy, 12(2), 175–187.
Knights, D., & O’Leary, M. (2006). Leadership, ethics and responsibility to the other. Journal of Business Ethics, 67(2), 125–137.
Kolthoff, E., Erakovich, R., & Lasthuizen, K. (2010). Comparative analysis of ethical leadership and ethical culture in local government: The USA, The Netherlands, Montenegro and Serbia. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 23(7), 596–612.
Lawton, A., Rayner, J., & Lasthuizen, K. (2013). Ethics and management in the public sector. London and New York: Routledge.
Levinas, E. (1966). On the Trail of the Other (D J. Hoy, Trans.) Philosophy Today, 10(1), 34-46.
London, M. (1999). Principled leadership and business diplomacy: A practical, values-based direction for management development. Journal of Management Development, 18(2), 170–192.
Luthans, F., & Avolio, B. (2003). Authentic leadership: A positive development approach. In K. S. Cameron, J. E. Dutton, & R. E. Quinn (Eds.), Positive organizational scholarship. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler.
Maak, T., & Pless, N. M. (2006). Responsible leadership in a stakeholder society: A relational perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 66(1), 99–115.
Macaulay, M., & Lawton, A. (2006). From virtue to competence: Changing the principles of public service. Public Administration Review, 66(5), 702–710.
MacIntyre, A. (1985). After virtue: A study in moral theory (2nd ed.). London: Duckworth.
Mangini, M. (2000). Character and well-being: Towards an ethic of character. Philosophy and Social Criticism, 26(2), 79–98.
Martin, G. S., Resick, C. J., Keating, M. A., & Dickson, M. W. (2009). Ethical leadership across cultures: A comparative analysis of German and US perspectives. Business Ethics: A European Review, 18(2), 127–144.
May, D. R., Chan, A. Y., Hodges, T. D., & Avolio, B. J. (2003). Developing the moral component of authentic leadership. Organizational Dynamics, 32(3), 247–260.
Mayer, D. M., Kuenzi, M., Greenbaum, R., Bardes, M., & Salvador, R. (2009). How low does ethical leadership flow? Test of a trickle-down model. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 108(1), 1–13.
McCrae, R. R., & John, O. P. (1992). An introduction to the five-factor model and its applications. Journal of Personality, 60(2), 175–215.
Mendonca, M. (2001). Preparing for ethical leadership in organizations. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, 18(4), 266–276.
Mendus, S. (2009). Politics and Morality. Cambridge: Polity Press.
Moore, G. (2005). Corporate character: Modern virtue ethics and the virtuous corporation. Business Ethics Quarterly, 15(4), 657–685.
Moore, G. (2008). Re-imaging the morality of management: A modern virtue ethics approach. Business Ethics Quarterly, 18(4), 483–511.
Mumford, M. D. (2011). A hale farewell: The state of leadership research. The Leadership Quarterly, 22, 1–7.
Murphy, P. E., & Enderle, G. (1995). Managerial ethical leadership: examples do matter. Business Ethics Quarterly, 5(1), 117–128.
Naquin, S. S., & Holton, E. F. (2003). Redefining state leadership and management development: A process for competence-based development. Public Personnel Management, 32(1), 23–46.
Neubert, M. J., Carlson, D. S., Kacmar, K. M., Roberts, J. A., & Chonko, L. B. (2009). The virtuous influence of ethical leadership behavior: Evidence from the field. Journal of Business Ethics, 90(2), 157–170.
O’Fallon, M. J., & Butterfield, K. D. (2005). A review of the empirical ethical decision-making literature: 1996–2003. Journal of Business Ethics, 59(4), 375–413.
Oakley, J., & Cocking, D. (2001). Virtue ethics and professional roles. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Painter-Morland, M. (2008). Systemic leadership and the emergence of ethical responsiveness. Journal of Business Ethics, 82(2), 509–524.
Palanski, M. E., & Yammarino, F. J. (2007). Integrity and leadership: Clearing the conceptual confusion. European Management Journal, 25(3), 171–184.
Parry, K. W., & Proctor-Thomson, S. B. (2002). Perceived integrity of transformational leaders in organisational settings. Journal of Business Ethics, 35(2), 75–96.
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2003). Character strengths before and after September 11. Psychological Science, 14(4), 381–384.
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Character strengths and virtues: A handbook and classification. New York: Oxford University Press.
Petrick, J. A., & Quinn, J. F. (1997). Management ethics: Integrity at work. Thousand Oaks: Sage Series in Business Ethics.
Piccolo, R. F., Greenbaum, R., Den Hartog, D. N., & Folger, R. (2010). The relationship between ethical leadership and core job characteristics. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 31(2/3), 259–278.
Price, T. L. (2008). Leadership ethics: An introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Prince, L. (2005). Eating the menu rather than the dinner: Tao and leadership. Leadership, 1(1), 105–126.
Resick, C. J., Hanges, P. J., Dickson, M. W., & Mitchelson, J. K. (2006). A cross-cultural examination of the endorsement of ethical leadership. Journal of Business Ethics, 63(4), 345–359.
Resick, C. J., Martin, G. S., Keating, M. A., Dickson, M. W., Kwan, H. K., & Peng, C. (2011). What ethical leadership means to me: Asian, American and European perspectives. Journal of Business Ethics, 101, 435–457.
Rost, J. C. (1995). Leadership: A discussion about ethics. Business Ethics Quarterly, 5(1), 129–142.
Rowold, J., Borgmann, L., & Heinitz, K. (2009). Ethical leadership: Psychometric properties of a German adaptation of Brown et al. (2005) Ethical Leadership Scale (ELS-D). Zeitschrift fur arbeits-und organizations psychologie, 53(2), 57–69.
Rubin, R. S., Dierdorff, E. C., & Brown, M. E. (2010). Do ethical leaders get ahead? Exploring ethical leadership and promotability. Business Ethics Quarterly, 20(2), 215–236.
Sarros, J. C., Cooper, B. K., & Hartican, A. M. (2006). Leadership and character. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 27(8), 682–699.
Selznick, P. (1957). Leadership in administration: A sociological interpretation. New York: Harper and Row.
Shamir, B., & Eilam, G. (2005). What’s your story? A life-stories approach to authentic leadership development. The Leadership Quarterly, 16(3), 395–417.
Simons, T. (2002). Behavioral integrity: The perceived alignment between manager’s words and deeds as a research focus. Organization Science, 13(1), 18–35.
Solomon, R. (1999). A better way to think about business: How personal integrity leads to corporate success. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Taylor, C. (1991). The ethics of authenticity. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Tenbrunsel, A. E., & Smith-Crowe, K. (2008). Ethical decision making: Where we’ve been and where we’re going. The Academy of Management Annals, 2(1), 545–607.
Treviño, L. K., Hartman, L. P., & Brown, M. (2000). Moral person and moral manager: How executives develop a reputation for ethical leadership. California Management Review, 42(4), 128–142.
Treviño, L. K., Weaver, G. R., & Reynolds, S. J. (2006). Behavioral ethics in organizations: A review. Journal of Management, 32(6), 951–990.
Walumbwa, F. O., Avolio, B. J., Gardner, W. L., Wernsing, T. S., & Peterson, S. J. (2008). Authentic leadership: Development and validation of a theory-based measure. Journal of Management, 34(1), 89–126.
Walumbwa, F. O., & Schaubroeck, J. (2009). Leader personality traits and employee voice behavior: Mediating roles of ethical leadership and work group psychological safety. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(5), 1275–1286.
Whetstone, J. T. (2005). A framework for organizational virtue: The interrelationship of mission, culture and leadership. Business Ethics: A European Review, 14(4), 367–378.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers of this article who provided comprehensive and thought-provoking feedback on earlier versions of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawton, A., Páez, I. Developing a Framework for Ethical Leadership. J Bus Ethics 130, 639–649 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2244-2