Abstract
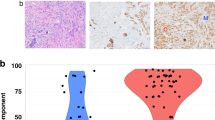
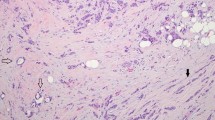
Invasive ductal carcinoma with lobular features (IDC-L) is not recognized as a distinct subtype of breast cancer, and its clinicopathologic features and outcomes are unknown. In this retrospective study, we focused on characterization of clinicopathologic features and outcomes of IDC-L and compared them to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). 183 cases of IDC-L from 1996 to 2011 were compared with 1,499 cases of IDC and 375 cases of ILC. Available slides of IDC-L (n = 150) were reviewed to quantify the lobular component (≤20, 21–50, 51–80, >80 %), defined as small cells individually dispersed, arranged in linear cords, or in loose aggregates without the formation of tubules or cohesive nests. E-cadherin immunostain was performed to confirm ductal origin. Compared to IDC, IDC-L was more likely to have lower histologic grade (p < 0.001), be positive for estrogen receptor (96 vs. 70 %; p < 0.0001) and progesterone receptor (84 vs. 57 %; p < 0.0001), and less likely to overexpress HER-2/neu (12 vs. 23 %; p = 0.001). Despite these favorable prognostic features, IDC-L had a higher frequency of nodal metastases (51 vs. 34 %; p < 0.0001) and a worse 5-year disease-free survival than IDC (hazard ratio = 0.454; p = 0.0004). ILC and IDC-L had similar clinicopathologic features and outcomes. The proportion of the lobular component in IDC-L had no impact on the size, nodal status, stage, or outcome. Our data suggest that although IDC-L may be a variant of IDC, with >90 % of cases being E-cadherin positive, the clinical and biological characteristics are more similar to that of ILC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sastre-Garau X, Jouve M, Asselain B et al (1996) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Clinicopathologic analysis of 975 cases with reference to data on conservative therapy and metastatic patterns. Cancer 75(1):113–120
Lamovec J, Bracko M (1991) Metastatic pattern of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: an autopsy study. J Surg Oncol 48(1):28–33
Arpino G, Bardou VJ, Clark GM, Elledge RM (2004) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: tumor characteristics and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res 6(3):R149–R156
Borst MJ, Ingold JA (1993) Metastatic patterns of invasive lobular versus invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Surgery 114(4):637–642
Li CI, Uribe DJ, Daling JR (2005) Clinical characteristics of different histologic types of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 93(9):1046–1052
Dixon JM, Anderson TJ, Page DL, Lee D, Duffy SW (1982) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Histopathology 6(2):149–161
Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW, Elston CW (1992) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 20(6):479–489
Li CI, Anderson BO, Daling JR, Moe RE (2003) Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA 289(11):1421–1424
Reeves GK, Beral V, Green J, Gathani T, Bull D (2006) Hormonal therapy for menopause and breast-cancer risk by histological type: a cohort study and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 7(11):910–918
Lesser ML, Rosen PP, Kinne DW (1982) Multicentricity and bilaterality in invasive breast carcinoma. Surgery 91(2):234–240
Nesland JM, Holm R, Johannessen JV (1985) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of lobular carcinoma of the breast. J Pathol 145(1):39–52
Mendelson EB, Harris KM, Doshi N, Tobon H (1989) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma: mammographic patterns with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 153(2):265–271
Kumar ND, Hart WR (1982) Metastases to the uterine corpus from extragenital cancers. A clinicopathologic study of 63 cases. Cancer 50(10):2163–2169
Silverstein MJ, Lewinsky BS, Waisman JR et al (1994) Infiltrating lobular carcinoma. Is it different from infiltrating duct carcinoma? Cancer 73(6):1673–1677
Li CI, Moe RE, Daling JR (2003) Risk of mortality by histologic type of breast cancer among women aged 50–79 years. Arch Intern Med 163(18):2149–2153
Acs G, Lawton TJ, Rebbeck TR, LiVolsi VA, Zhang PJ (2001) Differential expression of E-cadherin in lobular and ductal neoplasms of the breast and its biologic and diagnostic implications. Am J Clin Pathol 115(1):85–98
Wasif N, Maggard MA, Ko CY, Giuliano AE (2010) Invasive lobular versus ductal breast cancer: a stage-matched comparison of outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol 17(7):1862–1869
Korhonen T, Huhtala H, Holli K (2004) A comparison of the biological and clinical features of invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 85(1):23–29
Lee JH, Park S, Park HS, Park BW (2010) Clinicopathological features of infiltrating lobular carcinomas comparing with infiltrating ductal carcinomas: a case control study. World J Surg Oncol 8:34
Li CI, Daling JR, Malone KE et al (2006) Relationship between established breast cancer risk factors and risk of seven different histologic types of invasive breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15(5):946–954
Suryadevara A, Paruchuri LP, Banisaeed N, Dunington G, Rao KA (2010) The clinical behavior of mixed ductal/lobular carcinoma of the breast: a clinicopathologic analysis. World J Surg Oncol 8:51
Rakha EA, Gill MS, El-Sayed ME et al (2009) The biological and clinical characteristics of breast carcinoma with mixed ductal and lobular morphology. Breast Cancer Res Treat 114(2):43–50
Af Bharat, Gao F, Margenthaler JA (2009) Tumor characteristics and patient outcomes are similar between invasive lobular and mixed invasive ductal/lobular breast cancers but differ from pure invasive ductal breast cancers. Am J Surg 198(4):516–519
Nassar H, Wallis T, Andea A, Dey J, Adsay V, Vischer D (2001) Clinicopathologic analysis of invasive micropapillary differentiation in breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol 14(9):836–841
Sabel MS, Jorns JM, Wu A, Myers J, Newman LA, Breslin TM (2012) Development of an intraoperative pathology consultation service at a free-standing ambulatory surgical center: clinical and economic impact for patients undergoing breast cancer surgery. Am J Surg 204(1):66–77
Moore MM, Borossa G, Imbrie JZ et al (2000) Association of infiltrating lobular carcinoma with positive surgical margins after breast-conservation therapy. Ann Surg 231(6):877–882
Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Mallon E et al (2008) Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 26(18):3006–3014
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the UMHS Cancer Center Research Histology & Immunoperoxidase Lab for performing the E-cadherin immunostains and Steven C. Smith, M.D., Ph.D. for his assistance in the preparation of Fig. 2.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no disclosures or conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arps, D.P., Healy, P., Zhao, L. et al. Invasive ductal carcinoma with lobular features: a comparison study to invasive ductal and invasive lobular carcinomas of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 719–726 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2493-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2493-2