Abstract
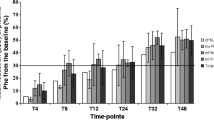
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inherited metabolic disease characterized by phenylalanine (Phe) accumulation due to defects in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). Phe accumulation can lead to cognitive impairment. Some individuals with PKU respond to tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) treatment, the natural cofactor of PAH, by a reduction in blood Phe concentrations. We tested 12 patients with PKU, 8–29 years of age, all carrying the common Y414C mutation in the PAH gene. Three were homozygous and nine were compound heterozygous, with the second mutation being a putative null mutation. During the study period, genuine protein was increased to approximately 1 g/kg. The patients were treated with 20, 10, and 5 mg BH4/kg/day for 1 week on each dose, starting with 20 mg/kg. A positive response was defined as a decline in blood Phe > 30%. Blood Phe was measured four times a week. Nonresponding children were excluded from the study. Eleven of 12 patients had a positive response with 20 mg/kg, 5/10 responded on 10 mg/kg, and 1/9 on 5 mg/kg. Two were late responders, with a response on 20 mg/kg after >48 h. We could confirm the previously reported inconsistent responsiveness of Y414C in the nine heterozygous patients, whereas the three homozygous patients had early median Phe declines of 73%, 51%, and 27%, respectively, on the three different doses. The varying responses despite uniform trial conditions and genotypes may be due to individual differences in BH4 absorption or metabolism. No side effects were observed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BH4:
-
6R-tetrahydrobiopterin
- HPA:
-
Hyperphenylalaninemia
- MHP:
-
Mild hyperphenylalaninemia
- PKU:
-
Phenylketonuria
- S-Phe:
-
Serum phenylalanine
- PAH:
-
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
- PAH :
-
Phenylalanine hydroxylase gene
References
Ahring K, Bélanger-Quintana A, Dokoupil K et al (2009) Dietary management practices in phenylketonuria across European centres. Clin Nutr 28:231–236
Belanger-Quintana A, Garcia MJ, Castro M et al (2005) Spanish BH4-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase-deficient patients: evolution of seven patients on long-term treatment with tetrahydrobiopterin. Mol Genet Metab 86:S61–S66
Blau N (2008) Defining tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-responsiveness in PKU. J Inherit Metab Dis 31:2–3
Blau N, Bélanger-Quintana A, Demirkol M et al (2009) Optimizing the use of sapropterin (BH(4)) in the management of phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 96:158–163
Blau N, Erlandsen H (2004) The metabolic and molecular bases of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 82:101–111
Bóveda MD, Couce ML, Castiñeiras DE et al (2007) The tetrahydrobiopterin loading test in 36 patients with hyperphenylalaninaemia: evaluation of response and subsequent treatment. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:812
Desviat LR, Perez B, Belanger-Quintana A et al (2004) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness: results of the BH4 loading test in 31 Spanish PKU patients and correlation with their genotype. Mol Genet Metab 83:157–162
Erlandsen H, Stevens RC (2001) A structural hypothesis for BH4 responsiveness in patients with mild forms of hyperphenylalaninaemia and phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 24:213–230
Fiege B, Ballhausen D, Kierat L et al (2004) Plasma tetrahydrobiopterin and its pharmacokinetic following oral administration. Mol Genet Metab 81:45–51
Fiori L, Fiege B, Riva E, Giovannini M (2005) Incidence of BH4-responsiveness in phenylalanine-hydroxylase-deficient Italian patients. Mol Genet Metab 86:S67–S74
Gjetting T, Petersen M, Guldberg P, Guttler F (2001) In vitro expression of 34 naturally occurring mutant variants of phenylalanine hydroxylase: correlation with metabolic phenotypes and susceptibility toward protein aggregation. Mol Genet Metab 72:132–143
Gramer G, Garbade SF, Blau N, Lindner M (2009) Pharmacokinetics of tetrahydrobiopterin following oral loadings with three single dosages in patients with phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:52–57
Guldberg P, Rey F, Zschocke J et al (1998) A European multicenter study of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: classification of 105 mutations and a general system for genotype-based prediction of metabolic phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 63:71–79
Hennermann JB, Buhrer C, Blau N, Vetter B, Monch E (2005) Long-term treatment with tetrahydrobiopterin increases phenylalanine tolerance in children with severe phenotype of phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 86:S86–S90
Karačić I, Meili D, Sarnavka V et al (2009) Genotype-predicted tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-responsiveness and molecular genetics in Croatian patients with phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 97:165–171
Kure S, Hou DC, Ohura T et al (1999) Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr 135:375–378
Lee P, Treacy EP, Crombez E et al (2008) Safety and efficacy of 22 weeks of treatment with sapropterin dihydrochloride in patients with phenylketonuria. Am J Med Genet 146A:2851–2859
Leuzzi V, Carducci C, Carducci C et al (2006) The spectrum of phenylalanine variations under tetrahydrobiopterin load in subjects affected by phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:38–46
Levy H, Burton B, Cederbaum S, Scriver C (2007) Recommendations for evaluation of responsiveness to tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) in phenylketonuria and its use in treatment. Mol Genet Metab 92:287–291
Lindner M, Haas D, Mayatepek E, Zschocke J, Burgard P (2001) Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in phenylketonuria differs between patients with the same genotype. Mol Genet Metab 73:104–106
Lindner M, Steinfeld R, Burgard P, Schulze A, Mayatepek E, Zschocke J (2003) Tetrahydrobiopterin sensitivity in German patients with mild phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Mutat 21:400
Lindner M, Gramer G, Garbade SF, Burgard P (2009) Blood phenylalanine concentrations in patients with PAH-deficient hyperphenylalaninaemia off diet without and with three different single oral doses of tetrahydrobiopterin. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:514–522
Matalon R, Koch R, Michals-Matalon K et al (2004) Biopterin responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Genet Med 6:27–32
Matalon R, Michals-Matalon K, Koch R, Grady J, Tyring S, Stevens RC (2005) Response of patients with phenylketonuria in the US to tetrahydrobiopterin. Mol Genet Metab 86:S17–S21
Muntau AC, Roschinger W, Habich M et al (2002) Tetrahydrobiopterin as an alternative treatment for mild phenylketonuria. N Engl J Med 347:2122–2132
Pey AL, Pérez B, Desviat LR et al (2004) Mechanisms underlying responsiveness to tetrahydrobiopterin in mild phenylketonuria mutations. Hum Mutat 24:388–399
Ponzone A, Guardamagna O, Spada M et al (1993) Differential diagnosis of hyperphenylalaninaemia by a combined phenylalanine-tetrahydrobiopterin loading test. Eur J Pediatr 152:655–661
Rocha JC, Martel F (2009) Large neutral amino acids supplementation in phenylketonuric patients. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:472–480
Shintaku H, Kure S, Ohura T et al (2004) Long-term treatment and diagnosis of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive hyperphenylalaninemia with a mutant phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Pediatr Res 55:425–430
Trefz FK, Scheible D, Frauendienst-Egger G, Korall H, Blau N (2005) Long-term treatment of patients with mild and classical phenylketonuria by tetrahydrobiopterin. Mol Genet Metab 86:S75–S80
Trefz FK, Scheible D, Götz H, Frauendienst-Egger G (2009) Significance of genotype in tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:22–26
Zurflüh MR, Zschocke J, Lindner M et al (2008) Molecular genetics of tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Mutat 29:167–175
Wibrand F (2004) A microplate-based enzymatic assay for the simultaneous determination of phenylalanine and tyrosine in serum. Clin Chim Acta 347:89–96
Acknowledgements
We thank professor Karen Brøndum-Nielsen for critical and constructive reading of the manuscript. The study was supported by grants from The Danish Health Insurance Foundation and Else Hjort’s Fund, the widow of MSc. in engineering Stenild Hjorth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: John H. Walter
Competing interest: None declared.
References to electronic databases: Phenylketonuria: OMIM 261600. Phenylalanine hydroxylase: EC 1.14.16.1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, J.B., Nielsen, K.E. & Güttler, F. Tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness after extended loading test of 12 Danish PKU patients with the Y414C mutation. J Inherit Metab Dis 33, 9–16 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-9002-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-9002-0