Abstract
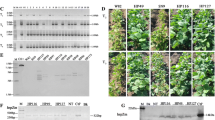
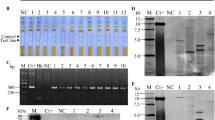
PopW, a harpin protein identified from Ralstonia solanacearum, has multiple beneficial effects in plants, promoting plant growth and development, increasing crop yield, and inducing resistance to pathogens. Tobacco plants transformed with popW, the PopW-encoding gene, exhibited a promoted growth rate and enhanced resistance to Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). Here, it is documented that the transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing popW exhibited a higher resistance to R. solanacearum YN10 infection compared with that of the wild-type plants. In the popW-expressing tobacco lines, an enhanced H2O2 accumulation and hypersensitive reaction (HR) were activated in the inoculated site. In addition, the resistance was accompanied with increased transcripts in numbers of genes related to defense (including HR), reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging, and salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ET) production. These results suggest that popW acted as positive regulator in tobacco resistance against R. solanacearum via modulation of SA-, JA-, and ET-mediated signaling pathways. We report for the first time that the expression of a harpin-encoding gene in vivo improved plant resistance to R. solanacearum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAB:
-
diaminobenzidine
- dpi:
-
days post inoculation
- E:
-
empty vector
- ET:
-
ethylene
- ETI:
-
effector-triggered immunity
- HR:
-
hypersensitive reaction
- JA:
-
jasmonic acid
- PR:
-
pathogenesis-related
- PTI:
-
pathogen/microbe-associated molecular patterns triggered immunity
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
salicylic acid
- TMV:
-
Tobacco mosaic virus
- WT:
-
wild-type
References
Alvarez, M.E., Pennell, R.I., Meijer, P.J., Ishikawa, A., Dixon, R.A., Lamb, C.: Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. — Cell 92: 773–784, 1998.
Bernoux, M., Ellis, J.G., Dodds, P.N.: New insights in plant immunity signaling activation. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 14: 512–518, 2011.
Chen, N., Goodwin, P.H., Hsiang, T.: The role of ethylene during the infection of Nicotiana tabacum by Colletotrichum destructivum. — J. exp. Bot. 54: 2449–2456, 2003.
Choi, M.S., Heu, S., Paek, N.C., Koh, H.J., Lee, J.S., Oh, C.S.: Expression of hpa1 gene encoding a bacterial harpin protein in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae enhances disease resistance to both fungal and bacterial pathogens in rice and Arabidopsis. — Plant Pathol. J. 28: 364–372, 2012.
Choi, M.S., Kim, W., Lee, C., Oh, C.S.: Harpins, multifunctional proteins secreted by gram-negative plantpathogenic bacteria. — Mol. Plant-Microb. Interact. 26: 1115–1122, 2013.
Dang, F., Wang, Y., She, J., Lei, Y., Liu, Z., Eulgem, T., Lai, Y., Lin, J., Yu, L., Lei, D., Guan, D., Li, X., Yuan, Q., He, S.: Overexpression of CaWRKY27, a subgroup IIe WRKY transcription factors of Capsicum annuum, positively regulates tobacco resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. — Physiol. Plant. 150: 397–411, 2014.
Dodds, P.N., Rathjen, J.P.: Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. — Natur. Rev. Genet. 11: 539–548, 2010.
Dong, H., Delaney, T.P., Bauer, D.W., Beer, S.V.: Harpin induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis through the systemic acquired resistance pathway mediated by salicylic acid and the NIM1 gene. — Plant J. 20: 207–215, 1999.
Dong, X.: SA, JA, ethylene, and disease resistance in plants. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 1: 316–323, 1998.
Farmer, E.E., Almeras, E., Krishnamurthy, V.: Jasmonates and related oxylipins in plant responses to pathogenesis and herbivory. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 6: 372–378, 2003.
Feys, B., Parker, J.: Interplay of signaling pathways in plant disease resistance. — Trends Genet. 16: 449–455, 2000.
Flores-Cruz, Z., Allen, C.: Ralstonia solanacearum encounters an oxidative environment during tomato infection. — Mol. Plant-Microb. Interact. 22: 773–782, 2009.
Fu, M., Xu, M., Zhou, T., Wang, D., Tian, S., Han, L., Dong, H., Zhang, C.: Transgenic expression of a functional fragment of harpin protein Hpa1 in wheat induces the phloem-based defence against English grain aphid. — J. exp. Bot. 65: 1439–1453, 2014.
Fu, Z.Q., Dong, X.: Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 64: 839–863, 2013.
Genin, S., Boucher, C.: Ralstonia solanacearum: secrets of a major pathogen unveiled by analysis of its genome. — Mol. Plant Pathol. 3: 111–118, 2002.
Greenberg, J.T., Yao, N.: The role and regulation of programmed cell death in plant-pathogen interactions. — Cell Microbiol. 6: 201–211, 2004.
He, S.Y.: Elicitation of the plant hypersensitive response by bacteria. — Plant Physiol. 112: 865–869, 1996.
Heath, M.C.: Hypersensitive response-related death. — Plant mol. Biol. 44: 321–334, 2000.
Jenkins, S.F., Averre, C.W.: Root diseases of vegetables in hydroponic culture systems in North Carolina greenhouse. — Plant Dis. 9: 968–970, 1983.
Jones, J.D., Dangl, J.L.: The plant immune system. — Nature 444: 323–329, 2006.
Kempe, J., Sequeira, L.: Biological control of baterial wilt of potatoes: attempts to induce resistance by treating tubes with bacteria. — Plant Dis. 67: 499–501, 1983.
Koornneef, A., Pieterse, C.M.J.: Cross talk in defense signaling. — Plant Physiol. 146: 839–844, 2008.
Leon-Reyes, A., Du, Y., Koorneef, A., Proietti, S., Körbes, A.P., Memelink, J.: Ethylene signaling renders the jasmonate response of Arabidopsis insensitive to future suppression by salicylic acid. — Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 23:187-197, 2010.
Li, J.G., Cao, J., Sun, F.F., Niu, D.D., Yan, F., Liu, H.X., Guo, J.H.: Control of Tobacco mosaic virus by PopW as a result of induced resistance in tobacco under greenhouse and field conditions. — Phytopathology 101: 1202–1208, 2011.
Li, J.G., Liu, H.X., Cao, J., Chen, L.F., Gu, C., Allen, C., Guo, J.H.: PopW of Ralstonia solanacearum, a new two-domain harpin targeting the plant cell wall. — Mol. Plant Pathol. 11: 371–381, 2010.
Li, L., Feng, X., Tang, M., Hao, W., Han, Y., Zhang, G., Wan, S.: Antibacterial activity of lansiumamide B to tobacco bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum). — Microbiol. Res. 169: 522–526, 2014.
Liang, Z., Xu, J.P., Meng, X.L., Lu, W., Wang, J., Xia, H.: Improve bioavailability of Harpin protein on plant use PLGA based nanoparticle. — J. Biotechnol. 143: 296–301, 2009.
Lumbreras, V., Vilela, B., Irar, S., Sole, M., Capellades, M., Valls, M., Coca, M., Pages, M.: MAPK phosphatase MKP2 mediates disease responses in Arabidopsis and functionally interacts with MPK3 and MPK6. — Plant J. 63: 1017–1030, 2010.
Miao, W., Wang, X., Song, C., Wang, Y., Ren, Y., Wang, J.: Transcriptome analysis of Hpa1Xoo transformed cotton revealed constitutive expression of genes in multiple signalling pathways related to disease resistance. — J. exp. Bot. 61: 4263–4275, 2010.
Pavli, O.I., Kelaidi, G.I., Tampakaki, A.P., Skaracis, G.N.: The hrpZ gene of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola enhances resistance to rhizomania disease in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana and sugar beet. — PLoS ONE 6: e17306, 2011.
Peng, J.L., Bao, Z.L., Ren, H.Y., Wang, J.S., Dong, H.S.: Expression of HarpinXoo in transgenic tobacco induces pathogen defense in the absence of hypersensitive cell death. — Phytopathology 94: 1048–1055, 2004.
Pontier, D., Tronchet, M., Rogowsky, P., Lam, E., Roby, D.: Activation of hsr203, a plant gene expressed during incompatible plant-pathogen interactions, is correlated with programmed cell death. — Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 11: 544–554, 1998.
Schell, M.A.: Control of virulence and pathogenicity genes of Ralstonia solanacearum by an elaborate sensory network. — Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 38: 263–292, 2000.
Shah, J.: Plants under attack: systemic signals in defence. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12: 459–464, 2009.
Shao, M., Wang, J.S., Dean, R.A., Lin, Y.G., Gao, X.W., Hu, S.J.: Expression of a harpin-encoding gene in rice confers durable nonspecific resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. — Plant Biotechnol. J. 6: 73–81, 2008.
Shi, W.N., Hao, L.L., Li, J., Liu, D.D., Guo, X.Q., Li, H.: The Gossypium hirsutum WRKY gene GhWRKY39-1 promotes pathogen infection defense responses and mediates salt stress tolerance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. — Plant Cell Rep. 33: 483–498, 2014.
Sohn, S., Kim, Y., Kim, B., Lee, S., Lim, C.K., Hur, J.H., Lee, J.: Transgenic tobacco expressing the hrpNEP gene from Erwinia pyrifoliae triggers defense responses against Botrytis cinerea. — Mol. Cells 24: 232–239, 2007.
Sonnewald, S., Priller, J.P.R., Schuster, J., Glickmann, E., Hajirezaei, M.R., Siebig, S., Mudgett, M.B., Sonnewald, U.: Regulation of cell wall-bound invertase in pepper leaves by Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria type three effectors. — PLoS ONE 7: e51763, 2012.
Takahashi, H., Chen, Z., Du, H., Liu, Y., Klessig, D.F.: Development of necrosis and activation of disease resistance in transgenic tobacco plants with severely reduced catalase levels. — Plant J. 11: 993–1005, 1997.
Takahashi, Y., Nagata, T.: parB: an auxin-regulated gene encoding glutathione S-transferase. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 56–59, 1992.
Ton, J., De Vos, M., Robben, C., Buchala, A., Métraux, J.P., Van Loon, L.C., Pieterse, C.M.: Characterization of Arabidopsis enhanced disease susceptibility mutants that are affected in systemically induced resistance. — Plant J. 29: 11–21, 2002.
Torres, M.A., Jones, J.D.G., Dangl, J.L.: Reactive oxygen species signalling in response to pathogens. — Plant Physiol. 141: 373–378, 2006.
Vlot, A.C., Dempsey, D.M.A., Klessig, D.F.: Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. — Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 47: 177–206, 2009.
Wang, C., Cao, J., Wang, T.T., Zheng, L., Wang, C., Liu, H.X.: [Effect of PopW from Ralstonia solanacearum on inducing plants disease resistance.] — Chin. J. biol. Control 30: 79–85, 2014a. [In Chin.]
Wang, C., Liu, H.X., Cao, J., Wang, C., Guo, J.H.: [Construction of transgenic tobacco expressing popW and analysis of its biological phenotype.] — Chin. J. Biotechnol. 30: 569–580, 2014b. [In Chin.]
Wang, D., Wang, Y., Fu, M., Mu, S., Han, B., Ji, H., Cai, H., Dong, H., Zhang, C.: Transgenic expression of the functional fragment Hpa1(10-42) of the harpin protein Hpa1 imparts enhanced resistance to powdery mildew in wheat. — Plant Dis. 98: 448–455, 2014c.
Ward, E.R., Payne, G.B., Moyer, M.B., Williams, S.C., Dincher, S.S., Sharkey, K.C., Beck, J.J., Taylor, H.T., Ahl-Goy, P., Meins, F., Ryals, J.A.: Differential regulation of beta-1,3-glucanase messenger RNAs in response to pathogen infection. — Plant Physiol. 96: 390–397, 1991.
Wei, Z.M., Laby, R.J., Zumoff, C.H., Bauer, D.W., He, S.Y., Collmer, A., Beer, S.V.: Harpin, elicitor of the hypersensitive response produced by the plant pathogen Ervinia amylovora. — Science 257: 85–88, 1992.
Xiao, S., Chye, M.L.: Overexpression of Arabidopsis ACBP3 enhances NPR1-dependent plant resistance to Pseudomonas syringe pv. tomato DC3000. — Plant Physiol. 156: 2069–2081, 2011.
Yao, J., Allen, C.: Chemotaxis is required for virulence and competitive fitness of the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. — J. Bacteriol. 188: 3697–3708, 2006.
Zhang, L., Xiao, S., Li, W., Feng, W., Li, J., Wu, Z., Gao, X., Liu, F., Shao, M.: Overexpression of a Harpin-encoding gene hrf1 in rice enhances drought tolerance. — J. exp. Bot. 62: 4229–4238, 2011a.
Zhang, W., Yang, X., Qiu, D., Guo, L., Zeng, H., Mao, J., Gao, Q.: PeaT1-induced systemic acquired resistance in tobacco follows salicylic acid-dependent pathway. — Mol. Biol. Rep. 38: 2549–2556, 2011b.
Zheng, L., Luo, Y.M., Xue, Q.Y., Li, S.M., Liu, H.X., Guo, J.H.: [Control and growth promotion of PopW to cucumber downy mildew under greenhouse and field conditions.] — Acat. phytopathol. sin. 43: 179–186, 2013. [In Chinese]
Zipfel, C.: Early molecular events in PAMP-triggered immunity. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12: 414–420, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgments: This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371925 and 31571992). The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Wang, C., Li, H.W. et al. Overexpression of a harpin-encoding gene popW in tobacco enhances resistance against Ralstonia solanacearum . Biol Plant 60, 181–189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0571-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0571-5