Abstract
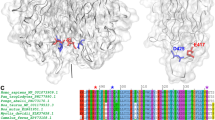
Ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin (EoCen) is an EF-hand calcium-binding protein closely related to the prototypical calcium sensor protein calmodulin. Four mutants (D37K, D73K, D110K and D146K) were created firstly to elucidate the importance of the first aspartic acid residues (Asp37, Asp73, Asp110 and Asp146) in the beginning of the four EF-loops of EoCen. Aromatic-sensitized Tb3+ fluorescence indicates that the aspartic acid residues are very important for the metal-binding of EoCen, except for Asp73 (in EF-loop II). Resonance light scattering (RLS) measurements for different metal ions (Ca2+ and Tb3+) binding proteins suggest that the order of four conserved aspartic acid residues for contributing to the self-assembly of EoCen is Asp37 > Asp146 > Asp110 > Asp73. Cross-linking experiment also exhibits that Asp37 and Asp146 play critical role in the self-assembly of EoCen. Asp37, in site I, which is located in the N-terminal domain, plays the most important role in the metal ion-dependent self-assembly of EoCen, and there is cooperativity between N-terminal and C-terminal domain (especially the site IV). In addition, the dependence of Tb3+ induced self-assembly of EoCen and the mutants on various factors, including ionic strength and pH, were characterized using RLS. Finally, 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate (TNS) binding, ionic strength and pH control experiments indicate that in the process of EoCen self-assembly, molecular interactions are mediated by both electrostatic and hydrophobic forces, and the hydrophobic interaction has the important status.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki M, Masutani C, Takemura M, Uchida A, Sugasawa K, Kondoh J, Ohkuma Y, Hanaoka F (2001) Centrosome protein centrin 2/caltractin 1 is part of the xeroderma pigmentosum group C complex that initiates global genome nucleotide excision repair. J Biol Chem 276:18665–18672. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100855200
Baum P, Furlong C, Byers B (1986) Yeast gene required for spindle pole body duplication: homology of its product with Ca2+-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83:5512–5516
Duan L, Zhao YQ, Wang ZJ, Li GT, Liang AH, Yang BS (2008) Lutetium(III)-dependent self-assembly study of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. J Inorg Biochem 102:268–277. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.08.010
Duan L, Liu W, Wang ZJ, Liang AH, Yang BS (2010) Critical role of tyrosine 79 in the fluorescence resonance energy transfer and terbium(III)-dependent self-assembly of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. J Biol Inorg Chem 15:995–1007. doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0660-z
Durussela I, Blouquitb Y, Middendorpc S, Craescu CT, Cox JA (2000) Cation-and peptide-binding properties of human centrin 2. FEBS Lett 472:208–212. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01452-6
He XJ, Feng JY, Wang W, Chai BF, Yang BS, Liang AH (2004) High level expression of a Euplotes centrin in Eschericia coli and preparation of its polyclonal antibody. Acta Zool Sin 50:447–451
Hu HT, Chazin WJ (2003) Unique features in the C-terminal domain provide caltractin with target specificity. J Mol Biol 330:473–484. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00619-3
Hu J, Jia X, Li Q, Yang X, Wang K (2004) Binding of La3+ to calmodulin and its effects on the interaction between calmodulin and calmodulin binding peptide, polistes mastoparan. Biochemistry 43:2688–2698. doi:10.1021/bi035784i
Huang CZ, Li YF (2003) Resonance light scattering technique used for biochemical and pharmaceutical analysis. Anal Chim Acta 500:105–117. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00630-5
Kawasaki H, Nakayama S, Kretsinger RH (1998) Classification and evolution of EF-hand proteins. Biometals 11:277–295. doi:10.1023/A:1009282307967
Lewit-Bentley A, Rety S (2000) EF-hand calcium-binding proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:637–643. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00142-1
Li GT, Wang ZJ, Zhao YQ, Ren LX, Liang AH, Yang BS (2007) The spectral studies on the effect of Glu 101 to the metal binding characteristic of Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Spectrochim Acta Part A 67:1189–1193. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2006.10.006
Liu W, Duan L, Zhao YQ, Liang AH, Yang BS (2010) Metal ion-binding properties of wild-type and mutant D37K of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Chin Sci Bull 55:3112–3118. doi:10.1007/s11434-010-3279-0
Mallamace F, Micali N, Romeo A, Scolaro LM (2000) Fractal aggregation of dyes such as porphyrins and related compounds under stacking. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 5:49–55. doi:10.1016/S1359-0294(00)00037-6
McClure WO, Edelman GM (1966) Fluorescent probes for conformational states of proteins. I. mechanism of fluorescence of 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate, a hydrophobic probe. Biochemistry 5:1908–1919. doi:10.1021/bi00870a018
Nelson MR, Chazin WJ (1998) Structures of EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins: diversity in the organization, packing and response to Ca2+ binding. Biometals 11:297–318. doi:10.1023/A:1009253808876
Pace CN, Vajdos F, Fee L, Grimsley G, Gray T (1995) How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 4:2411–2423. doi:10.1002/pro.5560041120
Popescu A, Miron S, Blouquit Y, Duchambon P, Christova P, Craescu CT (2003) Xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein possesses a high affinity binding site to human centrin 2 and calmodulin. J Biol Chem 278:40252–40261. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302546200
Ren LX, Zhao YQ, Feng JY, He XJ, Liang AH, Yang BS (2006) Terbium- and calcium-binding properties of N-terminal domain of Euplotes Centrin. Chin J Inorg Chem 22:87–90
Rigden DJ, Galperin MY (2004) The DxDxDG motif for calcium binding: multiple structural contexts and implications for evolution. J Mol Biol 343:971–984. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.077
Rong ZJ, Zhao YQ, Liu B, Tian YN, Yang BS (2013) Adsorption of Euplotes octocarinatus centrin on glassy carbon electrodes as substrates to study europium-protein interactions. J Electroanal Chem 707:102–109. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.08.035
Rong ZJ, Tian YN, Yang BS et al (2014) A comparative study on binding ability of three lanthanide ions with centrin using impedance method. RSC Adv 4:43262–43269. doi:10.1039/C4RA08099H
Salisbury JL (1995) Centrin, centrosomes, and mitotic spindle poles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:39–45. doi:10.1016/0955-0674(95)80043-3
Strynadka NC, James MN (1989) Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 58:951–998. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511
Taillon BE, Adler SA, Suhan JP, Jarvik JW (1992) Mutational analysis of centrin: an EF-hand protein associated with three distinct contractile fibers in the basal body apparatus of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol 119:1613–1624. doi:10.1083/jcb.119.6.1613
Tourbez M, Firanescu C, Yang A, Unipan L, Duchambon P, Blouquit Y, Craescu CT (2004) Calcium-dependent self-assembly of human centrin 2. J Biol Chem 279:47672–47680. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404996200
Veeraraghavan S, Fagan PA, Hu HT, Lee V, Harper JF, Huang B, Chazin WJ (2002) Structural independence of the two EF-hand domains of caltractin. J Biol Chem 277:28564–28571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112232200
Wang ZJ, Ren LX, Zhao YQ, Li GT, Liang AH, Yang BS (2007a) Metal ions-induced conformational change of P23 by using TNS as fluorescence probe. Spectrochim Acta Part A 66:1323–1326. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2006.06.021
Wang ZJ, Zhao YQ, Ren LX, Li GT, Liang AH, Yang BS (2007b) Spectral study on the interaction of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin and metal ions. J Photochem Photobiol A 186:178–186. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.08.007
Wang ZJ, Ren LX, Zhao YQ, Li GT, Duan L, Liang AH, Yang BS (2008) Investigation on the binding of TNS to centrin, an EF-hand protein. Spectrochim Acta Part A 70:892–897. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2007.10.001
Weber C, Lee VD, Chazin WJ, Huang B (1994) High level expression in Escherichia coli and characterization of the EF-hand calcium-binding protein caltractin. J Biol Chem 269:15795–15802
Wiech H, Geier BM, Paschke T, Spang A, Grein K, Steinkötter J, Melkonian M, Schiebe E (1996) Characterization of green alga, yeast, and human centrins specific subdomain features determine functional diversity. J Biol Chem 271:22453–22461. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.37.22453
Wright RL, Sakisbury J, Jarvik JW (1985) A nucleus-basal body connector in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that may function in basal body localization or segregation. J Cell Biol 101:1903–1912. doi:10.1083/jcb.101.5.1903
Yang A, Miron S, Duchambon P, Assairi L, Blouquit Y, Craescu CT (2006) The N-terminal domain of human centrin 2 has a closed structure, binds calcium with a very low affinity, and plays a role in the protein self-assembly. Biochemistry 45:880–889. doi:10.1021/bi051397s
Ye Y, Lee H, Yang W, Shealy S, Yang JJ (2005) Probing site-specific calmodulin calcium and lanthanide affinity by grafting. J Am Chem Soc 127:3743–3750. doi:10.1021/ja042786x
Zhao YQ, Feng JY, Liang AH, Yang BS (2009a) The characterization for the binding of calcium and terbium to Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Spectrochim Acta A 71:1756–1761. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2008.06.029
Zhao YQ, Song L, Liang AH, Yang BS (2009b) Characterization of self-assembly of Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. J Photochem Photobiol B 95:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2008.12.006
Zhao YQ, Yan J, Song L, Feng YN, Liang AH, Yang BS (2012a) The interaction between lanthanide(III) and N-terminal domain of Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Spectrochim Acta A 87:163–170. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2011.11.032
Zhao YQ, Yan J, Song L, Feng YN, Liang AH, Yang BS (2012b) Analysis of lanthanide-induced conformational change of the C-terminal domain on centrin. J Fluoresc 22:485–494. doi:10.1007/s10895-011-0982-4
Zhao YQ, Yan J, Chao JB, Liang AH, Yang BS (2013) The biochemical effect of Ser166 phosphorylation on Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. J Biol Inorg Chem 18:123–136. doi:10.1007/s00775-012-0957-1
Zhou BJ, Wang ZW, Tian YN, Wang ZJ, Yang BS (2010) Electrochemical study of the interaction between Eu3+ and ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Electrochim Acta 55:4124–4129. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.02.084
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of PR China (Nos. 20771068 and 20901048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Duan, L., Sun, T. et al. Role of four conserved aspartic acid residues of EF-loops in the metal ion binding and in the self-assembly of ciliate Euplotes octocarinatus centrin. Biometals 29, 1047–1058 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9975-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9975-8