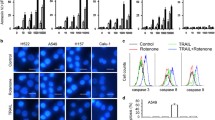
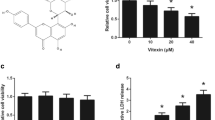
Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 cells are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis. Therefore, combination therapy using sensitizing agents to overcome TRAIL resistance may provide new strategies for treatment of NSCLC. Here, we investigated whether lithium chloride (LiCl), a drug for mental illness, could sensitize A549 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. We observed that LiCl significantly enhanced A549 cells apoptosis through up-regulation of death receptors DR4 and DR5 and activation of caspase cascades. In addition, G2/M arrest induced by LiCl also contributed to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Concomitantly, LiCl strongly inhibited the activity of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), and the inhibition of JNKs by SP600125 also induced G2/M arrest and augmented cell death caused by TRAIL or TRAIL plus LiCl. However, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) inhibition was not involved in TRAIL sensitization induced by LiCl. Collectively, these findings indicated that LiCl sensitized A549 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through caspases-dependent apoptotic pathway via death receptors signaling and G2/M arrest induced by inhibition of JNK activation, but independent of GSK3β.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3(9):745–756
Ballin A, Aladjem M, Banyash M, Boichis H, Barzilay Z, Gal R et al (1983) The effect of lithium chloride on tumour appearance and survival of melanoma-bearing mice. Br J Cancer 48(1):83–87
Beurel E, Blivet-Van EM, Kornprobst M, Moritz S, Delelo R, Paye F et al (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors augment TRAIL-induced apoptotic death in human hepatoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 77(1):54–65
Beyaert R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Suffys P, Van Roy F, Fiers W (1989) Lithium chloride potentiates tumor necrosis factor-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(23):9494–9498
Bilir A, Erguven M, Ermis E, Sencan M, Yazihan N (2011) Combination of imatinib mesylate with lithium chloride and medroxyprogesterone acetate is highly active in Ishikawa endometrial carcinoma in vitro. J Gynecol Oncol 22(4):225–232
Chen RW, Qin ZH, Ren M, Kanai H, Chalecka-Franaszek E, Leeds P et al (2003) Regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38 kinase and AP-1 DNA binding in cultured brain neurons: roles in glutamate excitotoxicity and lithium neuroprotection. J Neurochem 84(3):566–575
Choi SE, Jang HJ, Kang Y, Jung JG, Han SJ, Kim HJ et al (2010) Atherosclerosis induced by a high-fat diet is alleviated by lithium chloride via reduction of VCAM expression in ApoE-deficient mice. Vasc Pharmacol 53(5–6):264–272
Cohen Y, Chetrit A, Cohen Y, Sirota P, Modan B (1998) Cancer morbidity in psychiatric patients: influence of lithium carbonate treatment. Med Oncol 15(1):32–36
Densmore CL (2006) Advances in noninvasive pulmonary gene therapy. Curr Drug Deliv 3(1):55–63
Ding QQ, Xia WY, Liu JC, Yang JY, Lee DF, Xia JH et al (2005) Erk associates with and primes GSK-3 beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol Cell 19(2):159–170
D’Souza R, Rajji TK, Mulsant BH, Pollock BG (2011) Use of lithium in the treatment of bipolar disorder in late-life. Curr Psychiatry Rep 13(6):488–492
Filyak Y, Filyak O, Stoika R (2007) Transforming growth factor beta-1 enhances cytotoxic effect of doxorubicin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells of A549 line. Cell Biol Int 31(8):851–855
Fuke H, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Tanaka J, Beppu T, Yoneda K et al (2007) Jak inhibitor induces S phase cell-cycle arrest and augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363(3):738–744
Gomez-Benito M, Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Anela A, Marzo I, Naval J (2007) Membrane expression of DR4, DR5 and caspase-8 levels, but not Mcl-1, determine sensitivity of human myeloma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL. Exp Cell Res 313(11):2378–2388
Gupta A, Schulze TG, Nagarajan V, Akula N, Corona W, Jiang XY et al (2012) Interaction networks of lithium and valproate molecular targets reveal a striking enrichment of apoptosis functional clusters and neurotrophin signaling. Pharmacogenomics J 12(4):328–341
Hager ED, Dziambor H, Hohmann D, Winkler P, Strama H (2001) Effects of lithium on thrombopoiesis in patients with low platelet cell counts following chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Biol Trace Elem Res 83(2):139–148
Hager ED, Dziambor H, Winkler P, Hohmann D, Macholdt K (2002) Effects of lithium carbonate on hematopoietic cells in patients with persistent neutropenia following chemotherapy or radiotherapy. J Trace Elem Med Biol 16(2):91–97
Hu D, Bi XL, Fang WF, Han AJ, Yang WC (2009) GSK3 beta is involved in JNK2-mediated beta-catenin inhibition. PLOS One 4:(e66408)
Ivanov VN, Zhou HN, Hei TK (2007) Sequential treatment by ionizing radiation and sodium arsenite dramatically accelerates TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 67(11):5397–5407
Jeremic B, Milicic B, Milisavljevic S (2012) Toxicity of concurrent hyperfractionated radiation therapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced (stage III) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): single institution experience in 600 patients. Clin Transl Oncol 14(8):613–618
Kim BM, Chung HW (2008) Desferrioxamine (DFX) induces apoptosis through the p38-caspase8-Bid-Bax pathway in PHA-stimulated human lymphocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 228(1):24–31
Kim EH, Kim HS, Kim SU, Noh EJ, Lee JS, Choi KS (2005a) Sodium butyrate sensitizes human glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through inhibition of Cdc2 and the subsequent downregulation of survivin and XIAP. Oncogene 24(46):6877–6889
Kim EH, Kim SU, Choi KS (2005b) Rottlerin sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibition of Cdc2 and the subsequent downregulation of survivin and XIAP. Oncogene 24(5):838–849
Kim H, Kim EH, Eom YW, Kim WH, Kwon TK, Lee SJ et al (2006) Sulforaphane sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-resistant hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated up-regulation of DR5. Cancer Res 66(3):1740–1750
Kuntzen C, Sonuc N, De Toni EN, Opelz C, Mucha SR, Gerbes AL et al (2005) Inhibition of c-Jun-N-terminal-kinase sensitizes tumor cells to CD95-induced apoptosis and induces G2/M cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 65(15):6780–6788
Liao X, Zhang L, Thrasher JB, Du J, Li B (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta suppression eliminates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2(11):1215–1222
Liedtke C, Plumpe J, Kubicka S, Bradham CA, Manns MP, Brenner DA et al (2002) Jun kinase modulates tumor necrosis factor-dependent apoptosis in liver cells. Hepatology 36(2):315–325
Liu Q, Hilsenbeck S, Gazitt Y (2003) Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent G1 or G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of caspase-8 or caspase-9, and synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood 101(10):4078–4087
Matsebatlela T, Gallicchio V, Becker R (2012) Lithium modulates cancer cell growth, apoptosis, gene expression and cytokine production in HL-60 promyelocytic leukaemia cells and their drug-resistant sub-clones. Biol Trace Elem Res 149(3):323–330
Moon DO, Kim MO, Kang CH, Lee JD, Choi YH, Kim GY (2009) JNK inhibitor SP600125 promotes the formation of polymerized tubulin, leading to G2/M phase arrest, endoreduplication, and delayed apoptosis. Exp Mol Med 41(9):665–677
Nielsen J, Hoffer JD, Knepper MA, Agre P, Nielsen S, Fenton RA (2008) Proteomic analysis of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: mechanisms for aquaporin 2 down-regulation and cellular proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(9):3634–3639
Noh KT, Park YM, Cho SG, Choi EJ (2011) GSK-3 beta-induced ASK1 stabilization is crucial in LPS-induced endotoxin shock. Exp Cell Res 317(12):1663–1668
Nordenberg J, Panet C, Wasserman L, Malik Z, Fuchs A, Stenzel KH et al (1987) The anti-proliferative effect of lithium chloride on melanoma cells and its reversion by myo-inositol. Br J Cancer 55(1):41–46
Pampori N, Eason PD, Schaefer LK, Ly JT, Leta BG, Leffel SM et al (2004) MAPK cascade as a signaling convergence point in cancer therapy: simultaneous detection of activated p38, Erk and Jnk. Mol Biol Cell 15S:247A
Penso J, Beitner R (2003) Lithium detaches hexokinase from mitochondria and inhibits proliferation of B16 melanoma cells. Mol Genet Metab 78(1):74–78
Phiel CJ, Klein PS (2001) Molecular targets of lithium action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:789–813
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Kannappan R, Aggarwal BB (2011) Ursolic acid, a pentacyclin triterpene, potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis through p53-independent up-regulation of death receptors: evidence for the role of reactive oxygen species and JNK. J Biol Chem 286(7):5546–5557
Qiu Y, Liu X, Zou W, Yue P, Lonial S, Khuri FR et al (2007) The farnesyltransferase inhibitor R115777 up-regulates the expression of death receptor 5 and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 67(10):4973–4980
Riadh N, Allagui MS, Bourogaa E, Vincent C, Croute F, Elfeki A (2011) Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of long term lithium treatment in mouse brain. Biometals 24(4):747–757
Sanchez-Perez T, Ortiz-Ferron G, Lopez-Rivas A (2010) Mitotic arrest and JNK-induced proteasomal degradation of FLIP and Mcl-1 are key events in the sensitization of breast tumor cells to TRAIL by antimicrotubule agents. Cell Death Differ 17(5):883–894
Schotte P, Van Loo G, Carpentier I, Vandenabeele P, Beyaert R (2001) Lithium sensitizes tumor cells in an NF-kappa B-independent way to caspase activation and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Evidence for a role of the TNF receptor-associated death domain protein. J Biol Chem 276(28):25939–25945
Schraube P, Kimmig B, Zum WK (1984) Lithium as an adjuvant in the radioiodine therapy of thyroid cancer. Nuklearmedizin 23(3):151–154
Stolovich M, Lerer T, Bolkier Y, Cohen H, Meyuhas O (2005) Lithium can relieve translational repression of TOP mRNAs elicited by various blocks along the cell cycle in a glycogen synthase kinase-3- and S6-kinase-independent manner. J Biol Chem 280(7):5336–5342
Sun A, Shanmugam I, Song J, Terranova PF, Thrasher JB, Li B (2007) Lithium suppresses cell proliferation by interrupting E2F-DNA interaction and subsequently reducing S-phase gene expression in prostate cancer. Prostate 67(9):976–988
Thill PG, Goswami P, Berchem G, Domon B (2011) Lung cancer statistics in Luxembourg from 1981 to 2008. Bull Soc Sci Med Grand Duche Luxemb (2):43–55
Thorburn A, Behbakht K, Ford H (2008) TRAIL receptor-targeted therapeutics: resistance mechanisms and strategies to avoid them. Drug Resist Updat 11(1–2):17–24
Thornton TM, Pedraza-Alva G, Deng B, Wood CD, Aronshtam A, Clements JL et al (2008) Phosphorylation by p38 MAPK as an alternative pathway for GSK3 beta inactivation. Science 320(5876):667–670
Tran SE, Holmstrom TH, Ahonen M, Kahari VM, Eriksson JE (2001) MAPK/ERK overrides the apoptotic signaling from Fas, TNF, and TRAIL receptors. J Biol Chem 276(19):16484–16490
Wang JS, Wang CL, Wen JF, Wang YJ, Hu YB, Ren HZ (2008a) Lithium inhibits proliferation of human esophageal cancer cell line Eca-109 by inducing a G2/M cell cycle arrest. World J Gastroenterol 14(25):3982–3989
Wang XM, Li J, Feng XC, Wang Q, Guan DY, Shen ZH (2008b) Involvement of the role of Chk1 in lithium-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem 104(4):1181–1191
Xie ZH, Quan MF, Liu F, Cao JG, Zhang JS (2011) 5-allyl-7-gen-difluoromethoxychrysin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. BMC Cancer 11:322
Zhang L, Fang B (2005) Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 12(3):228–237
Zhang A, Huang X, Luo P, Jiang X (1998) Study on inhibition and prevention of tumor and antioxidative effects of lithium carbonate in tumor bearing mice. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 27(2):77–80
Zhu H, Liu XW, Ding WJ, Xu DQ, Zhao YC, Lu W et al (2010) Up-regulation of death receptor 4 and 5 by celastrol enhances the anti-cancer activity of TRAIL/Apo-2L. Cancer Lett 297(2):155–164
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to grants from National Key Basic Research Program from Ministry of Science and Technology (2012CB967004), the Jiangsu Provincial Nature Science Foundation (BK2011228, BZ2011048, BZ2010074, BZ2012050), the Chinese National Nature Sciences Foundation (81121062, 50973046, 31071196, 31070706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, R. et al. Lithium enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Biometals 26, 241–254 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9607-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9607-x