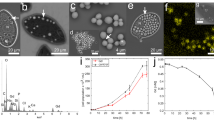
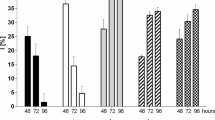
Abstract
Trace metals are required for many cellular processes. The acquisition of trace elements from the environment includes a rapid adsorption of metals to the cell surface, followed by a slower internalization. We investigated the uptake of the trace elements Co2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ and the non-essential divalent cation Cd2+ in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme. For each metal, a dose response study based on cell viability showed that the highest non-toxic concentrations were: 0.5 μM Cd2+, 2 μM Co2+, 0.5 μM Cu2+, 500 μM Mn2+, 1 μM Ni2+, and 18 μM Zn2+. Cells exposed to these non-toxic concentrations with combinations of Zn2+ and Cd2+, Zn2+ and Co2+, Zn2+ and Cu2+ or Zn2+ and Ni2+, had reduced growth in comparison to controls. Cells exposed to metal combinations with the addition of 500 μM Mn2+ showed similar growth compared to the untreated controls. Metal levels were measured after one and 72 h for whole cells and absorbed (EDTA-resistant) fractions and used to calculate differential uptake rates for each metal. The differences in binding and internalisation between different metals indicate different uptake processes exist for each metal. For each metal, competitive uptake experiments using 65Zn showed that after 72 h of exposure Zn2+ uptake was reduced by most metals particularly 0.5 μM Cd2+, while 2 μM Co2+ increased Zn2+ uptake. This study demonstrates that N. punctiforme discriminates between different metals and favourably substitutes their uptake to avoid the toxic effects of particular metals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackland ML, McArdle HJ (1996) Cation-dependant uptake of Zn2+ in human fibroblasts. Biometals 9:29–37
Anderson DC, Campbell EL, Meeks JC (2006) A soluble 3D LC/MS/MS proteome of the filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme. J Proteome Res 5:3096–3104
Asayama M, Imamura S, Yoshihara S, Miyazaki A, Yoshida N, Sazuka T, Kaneko T, Ohara O, Tabata S, Osanai T, Tanaka K, Takahashi H, Shirai M (2004) SigC, the group 2 sigma factor of RNA polymerase, contributes to the late-stage gene expression and nitrogen promoter recognition in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:477–487
Awasthi M, Rai LC (2006) Interactions between Zn2+ and Cd2+ uptake by free and immobilized cells of Scenedesums quadricauda (Turp.) Breb. Acta Hydroch Hydrob 34:20–26
Azeez PA, Banerjee DK (1991) Ni2+ uptake and toxicity in cyanobacteria. Toxicol Environ Chem 30:43–50
Backor M, Fashelt D (2008) Lichen photobionts and metal toxicity. Symbiosis 46:1–10
Baptista MS, Vasconcelos TM (2006) Cyanobacteria metal interactions: requirements, toxicity, and ecological implications. Crit Rev Microbiol 32:127–137
Bartsevich VV, Pakrasi HB (1996) Mn2+transport in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. J Biol Chem 271:26057–26061
Bender J, Gould JP, Vatcharapijarn Y, Young JS, Phillips P (1994) Removal of Zn2+ and Mn2+ from contaminated water with cyanobacteria mats. Water Environ Res 66:679–683
Blindauer CA (2008) Zn2+-handling in cyanobacteria: an update. Chem Biodivers 5:1990–2013
Cavet JS, Borrelly GPM, Robinson NJ (2003) Zn, Cu and Co in cyanobacteria: selective control of metal availability. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:165–181
Chong KH, Volesky B (1996) Metal biosorption equilibria in a ternary system. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:629–638
Choudhary M, Jetly UK, Khan MA, Zutshi S, Fatma T (2006) Effect of heavy metal stress on proline, malondialdehyde and super dismutase activity in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis S5. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 66:204–209
Daday A, Mackerras H, Smith GD (1988) A role for Ni2+ in cyanobacterial nitrogen fixation and growth via cyanophycin metabolism. J Gen Micro 134:2659–2663
Dohnalkova A, Marshall MJ, Kennedy DW, Gorby YA, Shi L, Beliaev A, Apkarian R, Fredrickson JK (2005) The role of bacterial exopolymers in metal sorption and reduction. Microsc Microanal 11:116–117
Dupont CL, Butcher A, Valas RE, Bourne PE, Caetano-Anolles G (2010) History of biological metal utilization inferred through phylogenomic analysis of protein structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:10567–10572
El-Enany AE, Issa AA (2000) Cyanobacteria. as a biosorbent of heavy metals in sewage water. Environ Toxicol Phar 8:95–101
Gardea-Torresdeya JL, Arenasb JL, Franciscob NMC, Tiemanna KJ, Webbb R (1998) Ability of immobilized cyanobacteria to remove metal ions from solution and demonstration of the presence of metallothionein genes in various strains. J Hazard Sub Res 1:2–18
Hameed MSA, Ebrahim OH (2007) Biotechnological potential uses of immobilized algae. Int J Agri Biol 9:183–192
Hantke K (2005) Bacterial Zn2+ uptake and regulators. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:196–202
Hoiczyk E, Hansel A (2000) Cyanobacterial cell walls: news from an unusual prokaryotic envelope. J Bacteriol 182:1191–1199
Hudek L, Rai LC, Freestone DF, Michalczyk A, Gibson M, Song YF, Ackland ML (2009) Bioinformatic and expression analyses of genes mediating Zn2+ homeostasis in Nostoc punctiforme. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:784–791
Loaec M, Olier R, Guenzennec J (1997) Uptake of lead, Cd2+ and Zn2+ by a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide. Wat Res 31:1171–1179
Ma Z, Jacobsen FE, Giedroc DP (2009) Coordination chemistry of bacterial metal transport and sensing. Chem Rev 109:4644–4681
Meeks JC, Elhai J, Thiel T, Potts M, Larimer F, Lamerdin J, Predki P, Atlas R (2001) An overview of the genome of Nostoc punctiforme, a multicellular, symbiotic cyanobacterium. Photosynth Res 70:85–106
Mehta SK, Gaur JP (2005) Use of algae for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: progress and prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol 25:113–152
Miccadei S, Floridi A (1993) Sites of inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport by Cd2+. Chem Biol Interact 89:159–167
Mullen MD, Wolf DC, Ferris FG, Beveridge TJ, Flemming CA, Bailey GW (1989) Bacterial sorption of heavy metals. Appl Environ Microb 55:3143–3149
Nies DH (2007) How cells control Zn2+ homeostasis. Science 317:1695–1696
Pradhan SP, Conrada JR, Paterek JR, Srivastava VJ (1998) Potential of phytoremediation for treatment of PAHs in soil at MGP sites. Soil Sediment Contam 7:467–480
Qiu A, Hogstrand C (2005) Functional expression of a low-affinity Zn2+ uptake transporter (Fr ZIP2) from pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) in MDCK cells. Biochem J 390:777–786
Ran L, Huang F, Ekman M, Klint J, Bergman B (2007) Proteomic analyses of the photoauto- and diazotrophically grown cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. PCC73102. Microbiology 153:608–618
Scholnick S, Keren N (2006) Metal homeostasis in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. Balancing benefits and risks to the photosynthetic apparatus. Plant Physiol 141:805–810
Sharma M, Kaushik A, Kiran Bala S, Kamra A (2008) Sequestration of chromium by exopolysaccharides of Nostoc and Gleocapsa from dilute aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 157:315–318
Singh AL, Asthana RK, Srivastava SC, Singh SP (1992) Ni2+ uptake and its localization in a cyanobacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 99:165–168
Singh S (1989) Co2+-induced inhibition of growth in the cyanobacteria Anabaena doliolum and Anacystis nidulans: interaction with sulphur containing amino acids. J Exp Biol 12:1092–1093
Tanioka Y, Yabuta Y, Yamaji R, Shigeoka S, Nakano Y, Watanabe F, Inui H (2009) Occurrence of psuedovitamin B12 and its possible function as the cofactor of cobalamin-dependant methionine synthase in a cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 55:518–521
Wu CH, Wood TK, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2006) Engineering plant–microbe symbiosis for rhizoremediation of heavy metals. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1129–1134
Ybarra GR, Webbb R (1999) Effects of divalent metal cations and resistance mechanisms of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC7942. J Hazard Sub Res 2:1–9
Yee N, Benning LG, Phoenix VR, Ferris FG (2004) Characterization of metal–cyanobacteria sorption reactions: a combined macroscopic investigation. Environ Sci Technol 38:775–782
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor John C. Meeks for technical assistance and helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hudek, L., Rai, S., Michalczyk, A. et al. Physiological metal uptake by Nostoc punctiforme . Biometals 25, 893–903 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9556-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9556-4