Abstract
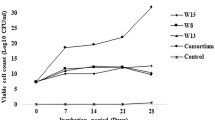
BTEX biodegradation by a mixed community of micro-organisms offers a promising approach in terms of cost-effectiveness and elimination of secondary pollution. Two bacterial strains, Pseudomonas putida F1 and Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 were chosen to formulate synthetic consortia based on their ability to biodegrade the mono-aromatic compounds. Benzene and toluene supported the growth of both the strains; while ethyl benzene and o-xylene were only utilized as growth substrates by P. putida F1 and P. stutzeri OX1, respectively. In a mixed substrate system, P. putida F1 exhibited incomplete removal of o-xylene while P. stutzeri OX1 displayed cometabolic removal of ethyl benzene with dark coloration of the growth medium. The biodegradation potential of the two Pseudomonas species complemented each other and offered opportunities to explore their performance as a co-culture for enhanced BTEX biodegradation. Several microbial formulations were concocted and their BTEX biodegradation characteristics were evaluated. Mixed culture biodegradation ascertained the advantages of the co-culture over the individual Pseudomonas species. This study also emphasized the significance of inoculum density and species proportion while concocting preselected micro-organisms for enhanced BTEX biodegradation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuhamed T, Bayraktar E, Mehmetoğlu T, Mehmetoğlu Ü (2004) Kinetics model for growth of Pseudomonas putida F1 during benzene, toluene and phenol degradation. Process Biochem 39:983–988
Arafa MA (2003) Biodegradation of some aromatic hydrocarbons (BTEXs) by a bacterial consortium isolated from polluted site in Saudi Arabia. Pak J Biol Sci 6:1482–1486
Attaway HH, Schmidt MG (2002) Tandem biodegradation of BTEX components by two Pseudomonas sp. Curr Microbiol 45:30–36
Baggi G, Barbieri P, Galli E, Tollari S (1987) Isolation of a Pseudomonas stutzeri strain that degrades o-xylene. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2129–2132
Barbieri P, Arenghi FLG, Bertoni G, Bolognese F, Galli E (2001) Evolution of catabolic pathways and metabolic versatility in Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 79:135–140
Barbieri P, Solera D, Galli E, Vidal-Aroca F, Bertoni G (2007) Degradation of o-xylene by Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 (Pseudomonas sp. OX1). In: Ramos J-L, Filloux A (eds) Pseudomonas A model system in biology, vol 2. Springer, New York, pp 89–105
Bielefeldt AR, Stensel HD (1999) Modeling competitive inhibition effects during biodegradation of BTEX mixtures. Water Res 33:704–714
Chakraborty R, Coates JD (2004) Anaerobic degradation of monoaromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:437–446
Chang M-K, Voice TC, Criddle CS (1993) Kinetics of competitive inhibition and cometabolism in the biodegradation of benzene, toluene and p-xylene by two Pseudomonas isolates. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:1057–1065
Deeb RA, Alvarez-Cohen L (1999) Temperature and substrate interactions during the aerobic biotransformation of BTEX mixtures by toluene-enriched consortia and Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:526–536
Díaz E (2004) Bacterial degradation of aromatic pollutants: a paradigm of metabolic versatility. Int Microbiol 7:173–180
Dou J, Liu X, Hu Z (2008) Anaerobic BTEX degradation in soil biaugmented with mixed consortia under nitrate reducing conditions. J Environ Sci 20:585–592
Duetz WA, Wind B, van Andel JG, Barnes MR, Williams PA, Rutgers M (1998) Biodegradation kinetics of toluene, m-xylene, p-xylene and their intermediates through the upper TOL pathway in Pseudomonas putida (PWWO). Microbiology 144:1669–1675
Fries MR, Zhou J, Chee-Sanford J, Tiedje JM (1994) Isolation, characterization, and distribution of denitrifying toluene degraders from a variety of habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2802–2810
Gilbert ES, Walker AW, Keasling JD (2003) A constructed microbial consortium for biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide parathion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:77–80
Jo MS, Rene ER, Kim SH, Park HS (2008) An analysis of synergistic and antagonistic behavior during BTEX removal in batch system using response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 152:1276–1284
Jung I-G, Park C-H (2004) Characteristics of Rhodococcus pyridinovorans PYJ-1 for the biodegradation of benzene, toluene, m-xylene (BTX), and their mixtures. J Biosci Bioeng 97:429–431
Kahraman H, Geckil H (2005) Degradation of benzene, toluene and xylene by Pseudomonas aeruginosa engineered with the Vitreoscilla Hemoglobin gene. Eng Life Sci 5:363–368
Kim D-J, Choi J-W, Choi N-C, Mahendran B, Lee C-E (2005) Modeling of growth kinetics for Pseudomonas spp. during benzene degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:456–462
Lee E, Cho KS (2009) Effect of substrate interaction on the degradation of methyl tert-butyl ether, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene by Rhodococcus sp. J Hazard Mater 167:669–674
Lee S-K, Lee SB (2001) Isolation and characterization of a thermotolerant bacterium Ralstonia sp. strain PHS1 that degrades benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and o-xylene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:270–275
Lee J-Y, Roh JR, Kim H-S (1994) Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for the simultaneous biodegradation of benzene, toluene, and p-xylene mixture. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:1146–1152
Lee J-Y, Jung K-H, Choi SH, Kim H-S (1995) Combination of the tod and the tol pathways in redesigning a metabolic route of Pseudomonas putida for the mineralization of a benzene, toluene, and p-xylene mixture. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2211–2217
Littlejohns JV, Daugulis AJ (2008) Kinetics and interactions of BTEX compounds during degradation by a bacterial consortium. Process Biochem 43:1068–1076
Mathur AK, Majumder CB (2010) Kinetics modelling of the biodegradation of benzene, toluene and phenol as single substrate and mixed substrate by using Pseudomonas putida. Chem Biochem Eng Q 24:101–109
Mazzeo DEC, Levy CE, de Angelis DDF, Marin-Morales MA (2010) BTEX biodegradation by bacteria from effluents of petroleum refinery. Sci Total Environ 408:4334–4340
Muñoz R, Díaz LF, Bordel S, Villaverde S (2007) Inhibitory effects of catechol accumulation on benzene biodegradation in Pseudomonas putida F1 cultures. Chemosphere 68:244–252
Oh Y-S, Bartha R (1997) Construction of a bacterial consortium for the biofiltration of benzene, toluene and xylene emissions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:627–632
Oh Y-S, Choi SC (1997) Characterization of BTX-degrading bacteria and identification of substrate interactions during their degradation. J Microbiol 35:193–199
Oh Y-S, Shareefdeen Z, Baltzis BC, Bartha R (1994) Interactions between benzene, toluene and p-xylene (BTX) during their biodegradation. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:533–538
Otenio MH, Da Silva MTL, Marques MLO, Roseiro JC, Bidoia ED (2005) Benzene, toluene and xylene biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida CCMI 852. Braz J Microbiol 36:258–261
Prenafeta-Boldú FX, Vervoot J, Grotenhuis JTC, Van Groenestijn JW (2002) Substrate interactions during the biodegradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX) hydrocarbons by the fungus Cladophialophora sp. strain T1. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2660–2665
Reardon KF, Mosteller DC, Rogers JB (2000) Biodegradation kinetics of toluene and phenol as single and mixed substrates for Pseudomonas putida F1. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:385–400
Rogers JB, Reardon KF (2000) Modelling substrate interactions during the biodegradation of mixtures of toluene and phenol by Burkholderia species JS150. Biotechnol Bioeng 70:428–435
Tsao C-W, Song H-G, Bartha R (1998) Metabolism of benzene, toluene and xylene hydrocarbons in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4924–4929
Yu H, Kim BJ, Rittmann BE (2001) The role of intermediates in biodegradation of benzene, toluene and p-xylene by Pseudomonas putida F1. Biodegradation 12:455–463
Zylstra GJ (1994) Molecular analysis of aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. In: Garte SJ (ed) Molecular environmental biology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Zylstra GJ, McCombie WR, Gibson DT, Finette BA (1988) Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1: genetic organization of the tod operon. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1498–1503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarajan, K., Loh, KC. Formulation of microbial cocktails for BTEX biodegradation. Biodegradation 26, 51–63 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9715-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9715-0