Abstract
Objective
To characterize Moloney murine leukemia virus (MMLV) reverse transcriptases (RTs) expressed in a cell-free system and in Escherichia coli.
Results
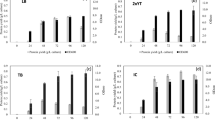
We previously expressed MMLV RT using an E. coli expression system and generated a highly thermostable quadruple variant MM4 (E286R/E302K/L435R/D524A) by site-directed mutagenesis. In this study, we expressed the wild-type MMLV RT (WT) and MM4 using a cell-free protein expression system from insect cells. WT exhibited DNA polymerase and RNase H activities, while MM4, in which the catalytic residue for RNase H activity, Asp524 is changed into Ala, exhibited only DNA polymerase activity. MM4, when held at 60 °C for 10 min, retained DNA polymerase activity, while WT, held at 54 °C for 10 min, lost this activity. In the cDNA synthesis reaction (0.5 μl) in which WT or MM4 were exposed to various temperatures and amounts of target RNA in a microarray chip, MM4 exhibited higher thermostability than WT.
Conclusion
MMLV RT expressed in the cell-free system is indistinguishable from that expressed in E. coli.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arezi B, Hogrefe H (2009) Novel mutations in Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase increase thermostability through tighter binding to template-primer. Nucleic Acid Res 37:473–481
Baase WA, Liu L, Tronrud DF, Matthews BW (2010) Lessons from the lysozyme of phage T4. Protein Sci 19:631–641
Baranauskas A, Paliksa S, Alzbutas G, Vaitkevicius M, Lubiene J, Letukiene V, Burinskas S, Sasnauskas G, Skirgaila R (2012) Generation and characterization of new highly thermostable and processive M-MuLV reverse transcriptase variants. Protein Eng Des Sel 25:657–668
Das D, Georgiadis MM (2004) The crystal structure of the monomeric reverse transcriptase from Moloney murine leukemia virus. Structure 12:819–829
Ezure T, Suzuki T, Shikata M, Ito M, Ando E (2010) A cell-free protein synthesis system from insect cells. Method Mol Biol 607:31–42
Gerard GF, Potter RJ, Smith MD, Rosenthal K, Dhariwal G, Lee J, Chatterjee DK (2002) The role of template-primer in protection of reverse transcriptase from thermal inactivation. Nucleic Acid Res 30:3118–3129
Hodgman CE, Jewett MC (2012) Cell-free synthetic biology: thinking outside the cell. Metab Eng 14:261–269
Kanno T, Tozawa Y (2010) Protein engineering accelerated by cell-free technology. Method Mol Biol 607:85–99
Kinoshita Y, Tayama T, Kitamura K, Salimullah M, Uchida H, Suzuki M, Husimi Y, Nishigaki K (2010) Novel concept microarray enabling PCR and multistep reactions through pipette-free aperture-to-aperture parallel transfer. BMC Biotechnol 10:71
Konishi A, Yasukawa K, Inouye K (2012) Improving the thermal stability of avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase α subunit by site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechnol Lett 34:1209–1215
Konishi A, Ma X, Yasukawa K (2014) Stabilization of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase by site-directed mutagenesis of the surface residue Val433. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 78:147–150
Kotewicz ML, D’Alessio JM, Driftmier KM, Blodgett KP, Gerard GF (1985) Cloning and overexpression of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Gene 35:249–258
Lu M, Ngo W, Mei Y, Munshi V, Burlein C, Loughran MH, Williams PD, Hazuda DJ, Miller MD, Grobler JA, Diamond TL, Lai MT (2010) Purification of untagged HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by affinity chromatography. Protein Expr Purif 71:231–239
Mizuno M, Yasukawa K, Inouye K (2010) Insight into the mechanism of the stabilization of Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase by eliminating RNase H activity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:440–442
Nishimura K, Yokokawa K, Hisayoshi T, Fukatsu K, Kuze I, Konishi A, Mikami B, Kojima K, Yasukawa K (2015) Preparation and characterization of the RNase H domain of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase. Protein Expr Purif 113:44–50
Parniak MA, Min KL, Budihas SR, Le Grice SFJ, Beutler JA (2003) A fluorescence-based high throughput screening assay for inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity. Anal Biochem 322:33–39
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO (1995) Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science 270:467–470
Schulze A, Downward J (2001) Navigating gene expression using microarrays—a technology review. Nat Cell Biol 3:E190–E195
Sharma H, Kinoshita Y, Fujiu S et al (2014) Establishment of a reborn MMV-microarray technology: realization of microbionme analysis and other hitherto inaccessible technologies. BMC Biotechnol 14:78
Suzuki T, Ezure T, Ito M, Shikata M, Ando E (2009) An insect cell-free system for recombinant protein expression using cDNA resources. Method Mol Biol 577:97–108
Whittaker JW (2013) Cell-free protein systhesis: the state of the art. Biotechnol Lett 35:143–152
Yasukawa K, Nemoto D, Inouye K (2008) Comparison of the thermal stabilities of reverse transcriptases from avian myeloblastosis virus and Moloney murine leukaemia virus. J Biochem 143:261–268
Yasukawa K, Mizuno M, Inouye K (2009) Characterization of Moloney murine leukaemia virus/avian myeloblastosis virus chimeric reverse transcriptases. J Biochem 145:315–324
Yasukawa K, Agata N, Inouye K (2010a) Detection of cesA mRNA from Bacillus cereus by RNA-specific amplification. Enz Microb Technol 46:391–396
Yasukawa K, Mizuno M, Konishi A, Inouye K (2010b) Increase in thermal stability of Moloney murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biotechnol 150:299–306
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by SENTAN, Japan Science and Technology Agency and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 21580110) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Nakatani Foundation for Advancement of Measuring Technologies in Biomedical Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katano, Y., Hisayoshi, T., Kuze, I. et al. Expression of moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase in a cell-free protein expression system. Biotechnol Lett 38, 1203–1211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2097-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2097-0