Abstract
Objectives
To prepare fluorescent carbon dots for loading cationic anticancer drug through donor-quenched nanosurface energy transfer in visible sensing of drug release.
Results
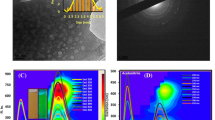
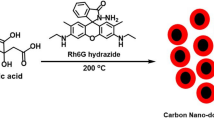
Highly fluorescent carbon dots (CDs) were prepared by a facile hydrothermal approach from citric acid and o-phenylenediamine. The obtained CDs showed a high quantum yield of 46 % and exhibited good cytocompatibility even at 1 mg/ml. The cationic anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) can be loaded onto the negatively charged CDs through electrostatic interactions. Additionally, the fluorescent CDs feature reversible donor-quenched mode nanosurface energy transfer. When loading the energy receptor DOX, the donor CDs’ fluorescence was switched “off”, while it turned “on” again after DOX release from the surface through endocytic uptake.
Conclusions
Most DOX molecules were released from the CDs after 6 h incubation and entered cell nuclear region after 8 h, suggesting the drug delivery system may have potential for visible sensing in drug release.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49:6726–6744
Costas-Mora I, Romero V, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2014) In situ building of a nanoprobe based on fluorescent carbon dots for methylmercury detection. Anal Chem 86:4536–4543
Gao X, Ding C, Zhu A, Tian Y (2014) Carbon-dot-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for imaging and biosensing of superoxide anion in live cells. Anal Chem 86:7071–7078
Griffin J, Singh AK, Senapati D, Rhodes P, Mitchell K, Robinson B, Yu E, Ray PC (2009) Size- and distance-dependent nanoparticle surface-energy transfer (NSET) method for selective sensing of hepatitis C virus RNA. Chemistry 15:342–351
Hsu PC, Chang HT (2012) Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots from hydrophilic compounds: role of functional groups. Chem Commun 48:3984–3986
Huang JJ, Zheng ZF, Rong MZ, Zhou X, Chen XD, Zhang MQ (2014) An easy approach of preparing strongly luminescent carbon dots and their polymer based composites for enhancing solar cell efficiency. Carbon 70:190–198
Jia X, Li J, Wang E (2012) One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 4:5572–5575
Kong B, Zhu A, Ding C, Zhao X, Li B, Tian Y (2012) Carbon dot-based inorganic-organic nanosystem for two-photon imaging and biosensing of pH variation in living cells and tissues. Adv Mater 24:5844–5848
Lin LP, Wang XX, Lin SQ, Zhang LH, Lin CQ, Li ZM, Liu JM (2012) Research on the spectral properties of luminescent carbon dots. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 95:555–561
Liu H, Ye T, Mao C (2007) Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:6473–6475
Liu Z, Fan AC, Rakhra K, Sherlock S, Goodwin A, Chen X, Yang Q, Felsher DW, Dai H (2009) Supramolecular stacking of doxorubicin on carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:7668–7672
Liu Y, Li CY, Zhang ZY (2012) Synthesis of highly luminescent graphitized carbon dots and the application in the Hg2+ detection. Appl Surf Sci 263:481–485
Mewada A, Pandey S, Thakur M, Jadhav D, Sharon M (2014) Swarming carbon dots for folic acid mediated delivery of doxorubicin and biological imaging. J Mater Chem B 2:698–705
Posthuma-Trumpie GA, Wichers JH, Koets M, Berendsen LB, Van Amerongen A (2012) Amorphous carbon nanoparticles: a versatile label for rapid diagnostic (immuno)assays. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:593–600
Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti TK, Mohapatra S (2012) Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem Commun 48:8835–8837
Tao H, Yang K, Ma Z, Wan J, Zhang Y, Kang Z, Liu Z (2011) In vivo NIR fluorescence imaging, biodistribution, and toxicology of photoluminescent carbon dots produced from carbon nanotubes and graphite. Small 8:281–290
Wang C, Wu X, Li X, Wang W, Wang L, Gu M, Li Q (2012) Upconversion fluorescent carbon nanodots enriched with nitrogen for light harvesting. J Mater Chem 22:15522–15525
Wang B, Wang Y, Wu H, Song X, Guo X, Zhang D, Ma X, Tan M (2014a) A mitochondria-targeted fluorescent probe based on TPP-conjugated carbon dots for both one- and two-photon fluorescence cell imaging. RSC Adv 4:49960–49963
Wang J, Zhang Z, Zha S, Zhu Y, Wu P, Ehrenberg B, Chen JY (2014b) Carbon nanodots featuring efficient FRET for two-photon photodynamic cancer therapy with a low fs laser power density. Biomaterials 35:9372–9381
Yang Y, Cui J, Zheng M, Hu C, Tan S, Xiao Y, Yang Q, Liu Y (2012) One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan. Chem Commun 48:380–382
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (91227126), the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of China (2013YQ17046307) and the Nature Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (2013020177).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Wang, S., Wang, Y. et al. Highly fluorescent carbon dots for visible sensing of doxorubicin release based on efficient nanosurface energy transfer. Biotechnol Lett 38, 191–201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1965-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1965-3