Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether RNA interference suppressor P19 derived from tombusvirus can enhance baculovirus yield and transgene expression.
Results
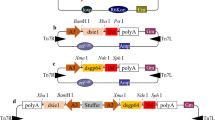
A number of recombinant baculoviruses with P19 under the control of white spot syndrome virus immediate-early promoter, baculovirus early-to-late promoter, or P10 late promoter were constructed The budded virus titer and the expression levels of eGFP and luciferase were determined. P19 was clearly functional in Sf9 cells and could enhance baculovirus yield, eGFP and luciferase expression levels up to 6.8-, 1.8-, and 2.1-fold respectively, at 72 h post infection.
Conclusion
P19 enhanced baculovirus production and transgene expression, and thus has potential applications in baculovirus-based gene therapy and vaccine studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger I, Fitzgerald DJ, Richmond TJ (2004) Baculovirus expression system for heterologous multiprotein complexes. Nat Biotechnol 22:1583–1587
Crawford AM, Miller LK (1988) Characterization of an early gene accelerating expression of late genes of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol 62:2773–2781
Gao H, Wang Y, Li N, Peng WP, Sun Y, Tong GZ et al (2007) Efficient gene delivery into mammalian cells mediated by a recombinant baculovirus containing a whispovirus ie1 promoter, a novel shuttle promoter between insect cells and mammalian cells. J Biotechnol 131:138–143
Jayachandran B, Hussain M, Asgari S (2012) RNA interference as a cellular defense mechanism against the DNA virus baculovirus. J Virol 86:13729–13734
Kuzio J, Rohel DZ, Curry CJ, Krebs A, Carstens EB, Faulkner P (1984) Nucleotide sequence of the p10 polypeptide gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology 139:414–418
Lakatos L, Szittya G, Silhavy D, Burgyan J (2004) Molecular mechanism of RNA silencing suppression mediated by p19 protein of tombusviruses. EMBO J 23:876–884
Li WX, Li H, Lu R, Li F, Dus M, Atkinson P et al (2004) Interferon antagonist proteins of influenza and vaccinia viruses are suppressors of RNA silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1350–1355
Mena JA, Kamen AA (2011) Insect cell technology is a versatile and robust vaccine manufacturing platform. Expert Rev Vaccines 10:1063–1081
Oliveiraa VC, Bartassona L, Castrob ME, Corrêaa JR, Ribeiroa BM, Resendea RO (2011) A silencing suppressor protein (NSs) of a tospovirus enhances baculovirus replication in permissive and semipermissive insect cell lines. Virus Res 155:259–267
Qu F, Morris TJ (2002) Efficient infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by tomato bushy stunt virus is facilitated by the coat protein and maintained by p19 through suppression of gene silencing. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:193–202
Rauschhuber C, Mueck-Haeusl M, Zhang WL, Nettelbeck DM, Ehrhardt A (2013) RNAi suppressor P19 can be broadly exploited for enhanced adenovirus replication and microRNA knock-down experiments. Sci Rep 3:1363
Siddiqui SA, Sarmiento C, Truve E, Lehto H, Lehto K (2008) Phenotypes and functional effects caused by various viral RNA silencing suppressors in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana and N. tabacum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:178–187
van Rij RP, Saleh MC, Berry B, Foo C, Houk A, Antoniewski C, Andino R (2006) The RNA silencing endonuclease Argonaute 2 mediates specific antiviral immunity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev 20:2985–2995
Wang Y, Gao H, Chen C, Zhao HP, Li M, Sun Y et al (2008) Promoter activity of different promoters in recombinant Baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells. Chin J Biotechnol 24:598–603
Wang W, Cheng T, Ma K, Xia D, Wang Y, Liu J et al (2013) Development of a novel baculovirus titration method using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISPOT) assay. J Virol Methods 188:114–120
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Starting Foundation for Dr. Enqi Du, Harbin Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Grant No. SKLVBF201405) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31201939), China.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Primers used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yangkun Liu and Lei Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y. et al. Functional analysis of RNAi suppressor P19 on improving baculovirus yield and transgene expression in Sf9 cells. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2159–2166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1910-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1910-5