Abstract
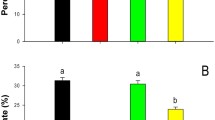
Two endophytic strains of the entomopathogenic fungus Tolypocladium cylindrosporum, originally isolated from the grass Festuca rubra, were artificially inoculated in tomato and bean plants. Strains 11-1L and 11-0BR were isolated from asymptomatic leaf fragments of both plant species at 3, 7, 14, 21, and 35 days after their inoculation. The percentage of leaf fragments infected by the fungus in inoculated leaves decreased at each sampling time, and no systemic colonization of the plants occurred. The two T. cylindrosporum strains tested were isogenic, differing in the infection by the victorivirus TcV1, harboured by strain 11-1L, but not by 11-0BR. The percentage of infected leaf fragments in leaves inoculated with the virus infected strain was greater in bean than in tomato plants, while the virus-free strain was more successful in tomato than in bean plants. This result suggests that the mycovirus infection can affect the adaptation of T. cylindrosporum to particular host plants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akello JT, Dubois T, Gold CS, Coyne D, Nakavuma J, Paparu P (2007) Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin as an endophyte in tissue culture banana (Musa spp.). J Invertebr Pathol 96:34–42
Anderson CMT, McGee PA, Nehl DB, Mensah RK (2007) The fungus Lecanicillium lecanii colonises the plant Gossypium hirsutum and the aphid Aphis gossypii. Australas Mycol 26:65–70
Arnold AE (2007) Understanding the diversity of foliar endophytic fungi: progress, challenges, and frontiers. Fungal Biol Rev 21:51–66
Bills GF (1996) Isolation and analysis of endophytic fungal communities from woody plants. In: Erdlin SC, Carris LM (eds) Endophytic fungi in grasses and woody plants. APS Press, St Paul, USA, pp 31–65
Bills GF, Polishook JD (1991) Microfungi from Carpinus caroliniana. Can J Bot 69:1477–1482
Bing LA, Lewis LC (1991) Suppression of Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) by endophytic Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin. Environ Entomol 20:1207–1211
Biswas C, Dey P, Satpathy S, Satya P (2012) Establishment of the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana as a season long endophyte in jute (Corchorus olitorius) and its rapid detection using SCAR marker. BioControl 57:565–571
Cherry AJ, Lomer CJ, Djegui D, Schulthess F (1999) Pathogen incidence and their potential as microbial control agents in IPM of maize stem borers in West Africa. BioControl 44:301–327
Clay K, Schardl C (2002) Evolutionary origins and ecological consequences of endophyte symbiosis with grasses. Am Nat 160:99–127
Cory JS, Ericsson JD (2010) Fungal entomopathogens in a tritrophic context. BioControl 55:75–88
Ghabrial SA, Suzuki N (2010) Fungal viruses. In: Mahy BWJ, Van Regenmortel MHV (eds) Desk encyclopedia of plant and fungal virology. Elsevier, Oxford, UK, pp 517–524
Gómez-Vidal S, López-Llorca LV, Jansson HB, Salinas J (2006) Endophytic colonization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) leaves by entomopathogenic fungi. Micron 37:624–632
Gurulingappa P, Sword GA, Murdoch G, McGee PA (2010) Colonization of crop plants by fungal entomopathogens and their effects on two insect pests when in planta. Biol Control 55:34–41
Gurulingappa P, McGee PA, Sword G (2011) Endophytic Lecanicillium lecanii and Beauveria bassiana reduce the survival and fecundity of Aphis gossypii following contact with conidia and secondary metabolites. Crop Prot 30:349–353
Hanada RE, Pomella AWV, Costa HS, Bezerra JL, Loguercio LL, Pereira JO (2010) Endophytic fungal diversity in Theobroma cacao (cacao) and T. grandiflorum (cupuaçu) trees and their potential for growth promotion and biocontrol of black-pod disease. Fungal Biol 114:901–910
Herrero N (2011) Micovirus asociados a los hongos endofíticos y entomopatógenos Tolypocladium cylindrosporum y Beauveria bassiana. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad de Salamanca, Spain
Herrero N, Zabalgogeazcoa I (2011) Mycoviruses infecting the endophytic and entomopathogenic fungus Tolypocladium cylindrosporum. Virus Res 160:409–413
Herrero N, Pérez R, Oleaga A, Zabalgogeazcoa I (2011) Tick pathogenicity, thermal tolerance and virus infection in Tolypocladium cylindrosporum. Ann Appl Biol 159:192–201
Hyde KD, Soytong K (2008) The fungal endophyte dilemma. Fungal Divers 33:163–173
Lam TNC, Goettel MS, Soares GG (1988) Host records for the entomopathogenic hyphomycete Tolypocladium cylindrosporum. Fla Entomol 71:86–89
Leckie BM, Ownley BH, Pereira RM, Klingeman WE, Jones CJ, Gwinn KD (2008) Mycelia and spent fermentation broth of Beauveria bassiana incorporated into synthetic diets affect mortality, growth and development of larval Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 18:697–710
Marquez LM, Redman RS, Rodriguez RJ, Roossinck MJ (2007) A virus in a fungus in a plant: three-way symbiosis required for thermal tolerance. Science 315:513–515
Miles LA, Lopera CA, González S, Cepero de García MC, Franco AE, Restrepo S (2012) Exploring the biocontrol potential of fungal endophytes from an Andean Colombian Paramo ecosystem. BioControl. doi:10.1007/s10526-012-9442-6
Nuss DL (2005) Hypovirulence: mycoviruses at the fungal-plant interface. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:632–642
Ownley BH, Griffin MR, Klingeman WE, Gwinn KD, Moulton JK, Pereira RM (2008) Beauveria bassiana: endophytic colonization and plant disease control. J Invertebr Pathol 98:267–270
Ownley BH, Gwinn KD, Vega FE (2010) Endophytic fungal entomopathogens with activity against plant pathogens: ecology and evolution. BioControl 55:113–128
Posada F, Vega FE (2005) Establishment of the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) as an endophyte in cocoa seedlings (Theobroma cacao). Mycologia 97:1195–1200
Posada F, Vega FE (2006) Inoculation and colonization of coffee seedlings (Coffea arabica L.) with the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Mycoscience 47:284–289
Posada F, Aime MC, Peterson SW, Rehner SA, Vega FE (2007) Inoculation of coffee plants with the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Mycol Res 111:749–758
Quesada-Moraga E, Landa BB, Muñoz-Ledesma J, Jiménez-Díaz RM, Santiago-Álvarez C (2006) Endophytic colonisation of opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, by an entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana strain. Mycopathologia 161:323–329
Quesada-Moraga E, Muñoz-Ledesma FJ, Santiago-Álvarez C (2009) Systemic protection of Papaver somniferum L. against Iraella luteipes (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) by an endophytic strain of Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Environ Entomol 38:723–730
Rodríguez RJ, White JF Jr, Arnold AE, Redman RS (2009) Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol 182:314–330
Romaine CP, Goodin MM (2002) Unraveling the viral complex associated with La France disease of the cultivated mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. In: Tavantzis SM (ed) dsRNA genetic elements. Concepts and applications in agriculture, forestry, and medicine. CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, pp 237–257
Roy HE, Brodie EL, Chandler D, Goettel MS, Pell JK, Wajnberg E, Vega FE (2010) Deep space and hidden depths: understanding the evolution and ecology of fungal entomopathogens. BioControl 55:1–6
Sánchez Márquez S, Bills G, Herrero N, Zabalgogeazcoa I (2012) Non-systemic fungal endophytes of grasses. Fungal Ecol 5:289–297
Schulz B, Boyle C (2005) The endophytic continuum. Mycol Res 109:661–686
Schulz B, Guske S, Dammann U, Boyle C (1998) Endophyte-host interactions II. Defining symbiosis of the endophyte-host interaction. Simbiosis 25:213–227
Tefera T, Vidal S (2009) Effect of inoculation method and plant growth medium on endophytic colonization of sorghum by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. BioControl 54:663–669
Vega FE, Posada F, Aime MC, Pava-Ripoll M, Infante F, Rehner SA (2008) Entomopathogenic fungal endophytes. Biol Control 46:72–82
Vega FE, Goettel MS, Blackwell M, Chandler D, Jackson MA, Keller S, Koike M, Maniania NK, Monzón A, Ownley BH, Pell JK, Rangel DEN, Roy HE (2009) Fungal entomopathogens: new insights on their ecology. Fungal Ecol 2:149–159
Wagner BL, Lewis LC (2000) Colonization of corn, Zea mays, by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3468–3473
Zabalgogeazcoa I (2008) Fungal endophytes and their interaction with plant pathogens. Span J Agric Res 6:138–146
Acknowledgments
This work was financed with research grant AGL2008-01159, awarded by the Spanish Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Helen Roy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrero Asensio, N., Sánchez Márquez, S. & Zabalgogeazcoa, I. Mycovirus effect on the endophytic establishment of the entomopathogenic fungus Tolypocladium cylindrosporum in tomato and bean plants. BioControl 58, 225–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9476-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9476-9