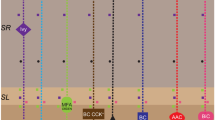
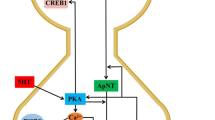
Microinjection of kainic acid into rat hippocampus causes excitotoxic neuronal damage predominantly in the CA3 and CA1 fields. These lesions can be significantly reduced by simultaneous administration of MPEP, a negative allosteric modulator of type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptors, and LY354740, an agonist of type 2 metabotropic glutamate receptors. The decrease in neuronal death in the hippocampus during pharmacological modulation was paralleled by adaptive changes in gene expression. In the hippocampus, gene expression of type 5 postsynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor was close to the control level, and in the frontal cortex expression of the gene of α1-subunit of the GABAA receptor returned to normal. In the frontal cortex, a reciprocal relationship was observed for type 2 metabotropic glutamate receptor: expression of the corresponding gene decreased in response to pharmacological activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkhipov VI, Kapralova MV. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as targets for new drug development. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2011;74(10):46-52. Russian.
Arkhipov VI, Kapralova MV. Expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors after hippocampal injury. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014;156(4):457-460.
Arkhipov VI, Kapralova MV, Pershina EV. Excitotoxicity and experimental approaches to neuroprotection. Sovremen. Problemy Nauki Obrazovaniya. 2013;(5):486. Russian.
Gordon RYa, Shubina LV, Kapralova MV, Pershina EB, Khutzian SS, Arhipov VI. Peculiarities of neurodegeneration in hippocampus fields after kainic acid action in rats. Tsitologiya. 2014;56(12):919-925. Russian.
Lebedev DS, Arkhipov VI. Expression of mGluR5 and synaptophysin genes after injury to the dorsal Hippocampus, inflicted by cainic acid. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009;147(2):236-239.
Lebedev DS, Arkhipov VI. Expression of mitochondrial uncoupling protein UCP2 in the brain of rats after hippocampal injury inflicted by kainic acid. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010;150(2):185-187.
Arkhipov V, Kapralova M, Pershina E, Gordon R. Delayed treatments with pharmacological modulators of pre- and postsynaptic mGlu receptors rescue the hippocampus from kainateinduced neurodegeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 2014;570:5-9.
Gerin CG, Madueke IC, Perkins T, Hill S, Smith K, Haley B, Allen SA, Garcia RP, Paunesku T, Woloschak G. Combination strategies for repair, plasticity, and regeneration using regulation of gene expression during the chronic phase after spinal cord injury. Synapse. 2011;65(12):1255-1281.
Grabenstatter HL, Russek SJ, Brooks-Kayal AR. Molecular pathways controlling inhibitory receptor expression. Epilepsia. 2012;53(Suppl. 9):71-78.
Mehta A, Prabhakar M, Kumar P, Deshmukh R, Sharma PL. Excitotoxicity: bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. Eur. J. Pharm. 2013;698(1-3):6-18.
Motti D, Le Duigou C, Eugène E, Chemaly N, Wittner L, Lazarevic D, Krmac H, Marstrand T, Valen E, Sanges R, Stupka E, Sandelin A, Cherubini E, Gustincich S, Miles R. Gene expression analysis of the emergence of epileptiform activity after focal injection of kainic acid into mouse hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010;32(8):1364-1379.
Niswender CM, Conn PJ. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;50:295-322.
Pershina EV, Arkhipov VI. Subacute activation of mGlu4 receptors causes the feedback inhibition of its gene expression in rat brain. Life Sci. 2016;153:50-54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 12, pp. 756-759, December, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pershina, E.V., Kapralova, M.V. & Arkhipov, V.I. Effect of Pharmacological Modulation of Activity of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors on Their Gene Expression after Excitotoxic Damage in Hippocampal Neurons. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 784–787 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3713-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3713-2