Abstract
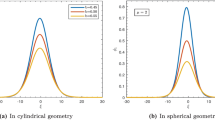
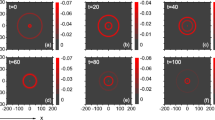
Interaction of nonplanar ion acoustic solitary waves is an important source of information to study the nature and characteristics of ion acoustic solitary waves (IASWs) structures. The head-on collision between two cylindrical/spherical IASWs in un-magnetized plasmas comprising with inertial ions, superthermal electrons and positrons is investigated by using the extended version of Poincaré-Lighthill-Kuo (PLK) perturbation method. It has been shown numerically that how the interactions are taking place in cylindrical and spherical geometry. The nonplanar geometry modified analytical phase shifts following the head-on collision are derived. The effects of the superthermal electrons and positrons on the phase shift are studied. It is shown that the properties of the interaction IASWs in different geometry are very different.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham-Shrauner, B., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C.: J. Geophys. Res. 84, 553 (1979)
Armstrong, T.P., Paonessa, M.T., Bell, E.V. II, Krimigis, S.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 88, 8893 (1983)
Chatterjee, P., Ghosh, U.N.: Eur. Phys. J. D 64, 413 (2011)
Chatterjee, P., Ghosh, U.N., Roy, K., Muniandy, S.V., Wong, C.S., Sahu, B.: Phys. Plasmas 17, 122314 (2010)
El-Bedwehy, N.A., Moslem, W.M.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 335, 435 (2011)
Eslami, P., Mottaghizadeh, M., Pakzad, H.R.: Phys. Plasmas 18, 072305 (2011)
Formisano, V., Moreno, G., Palmiotto, F.: J. Geophys. Res. 78, 3714 (1973)
Gardner, C.S., Greener, J.M., Kruskal, M.D., Miura, R.M.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 19, 1095 (1967)
Ghosh, S., Bharuthram, R.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 314, 121 (2008)
Ghosh, U.N., Roy, K., Chatterjee, P.: Phys. Plasmas 18, 103703 (2011)
Ghosh, U.N., Chatterjee, P., Kundu, S.K.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 339, 255 (2012c)
Ghosh, U.N., Chatterjee, P., Roychoudhury, R.: Phys. Plasmas 19, 012113 (2012b)
Ghosh, D.K., Chatterjee, P., Sahu, B.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 341, 559 (2012a)
Greaves, R.G., Surko, C.M.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3846 (1995)
Greaves, R.G., Tinkle, M.D., Surko, C.M.: Phys. Plasmas 1, 1439 (1994)
Han, J.N., Du, S.L., Duan, W.S.: Phys. Plasmas 15, 112104 (2008)
Hansen, E.T., Emshie, A.G.: The Physics of Solar Flares, p. 124. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1988)
Helander, P., Ward, D.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 135004 (2003)
Hershkowitz, N., Romesser, T.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 32, 581 (1974)
Huang, G., Velarde, M.G.: Phys. Rev. E 53, 2988 (1996)
Kundu, S.K., Chatterjee, P., Ghosh, U.N.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 340, 87 (2012)
Lazar, M., Schlickeiser, R., Poedts, S., Tautz, R.C.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 168, 390 (2008)
Leubner, M.P.: J. Geophys. Res. 87, 6335 (1982)
Leubner, M.P.: Phys. Plasmas 11, 1308 (2004)
Li, S.-C.: Phys. Plasmas 17, 082307 (2010)
Lightman, A.P.: Astrophys. J. 253, 842 (1982)
Lui, A.T.Y., Krimigis, S.M.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 527 (1987)
Mamun, A.A., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Lett. A 290, 173 (2001)
Mamun, A.A., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Plasmas 9, 1468 (2002)
Marsch, E., Muhlhauser, K.H., Schwenn, R., Rosenbauer, H., Pillip, W., Neubauer, F.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 87, 52 (1982)
Maxon, S., Viecelli, J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 32, 4 (1974)
Mendis, D.A., Rosenberg, M.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 32, 419 (1994)
Michel, F.C.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 54, 1 (1982)
Michel, F.C.: Theory of Neutron Star Magnetosphere. Chicago University Press, Chicago (1991)
Miller, H.R., Witta, P.J.: Active Galactic Nuclei, p. 202. Springer, Berlin (1987)
Pakzad, H.R.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 326, 77 (2009)
Pakzad, H.R.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 331, 169 (2011)
Popel, S.I., Vladimirov, S.V., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Plasmas 2, 716 (1995)
Rees, M.J.: In: Gibbons, G.W., Hawking, S.W., Siklas, S. (eds.) The Very Early Universe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1983)
Sahu, B., Roychoudhury, R.: Phys. Plasmas 11, 104871 (2004)
Sarby, R., Moslem, W.M., Shukla, P.K.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 333, 203 (2011)
Scudder, J.D., Sittler, E.C., Bridge, H.S.: J. Geophys. Res. 86, 8157 (1981)
Shukla, P.K., Rao, N.N., Yu, M.Y., Tsintsa, N.L.: Phys. Rep. 135, 1 (1986)
Su, C.H., Mirie, R.M.: J. Fluid Mech. 98, 509 (1980)
Surko, C.M., Murphy, T.J.: Phys. Fluids B 2, 1372 (1990)
Surko, C.M., Leventhal, M., Passner, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 901 (1989)
Trivelpiece, A.W.: Comments Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 1, 57 (1972)
Tsytovich, V., Wharton, C.B.: Comments Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 4, 91 (1978)
Vasyliunas, V.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 73, 2839 (1968)
Wesson, J.A., et al.: Nucl. Fusion 29, 641 (1989)
Xue, J.K.: Phys. Plasmas 10, 3430 (2003)
Xue, J.K.: Europhys. Lett. 68, 645 (2004)
Zabusky, N.J., Kruskal, M.D.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 15, 240 (1965)
Zdziarski, A.A.: Astrophys. J. 335, 786 (1988)
Acknowledgements
This present work is supported by SAP-DRS Phase-II for research equipments and grants. Reviewer’s comments and constructive suggestions are gratefully acknowledged by the authors, without which this paper would not have been in the present form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, U.N., Chatterjee, P. Interaction of cylindrical and spherical ion acoustic solitary waves with superthermal electrons and positrons. Astrophys Space Sci 344, 127–133 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-012-1307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-012-1307-z