Abstract
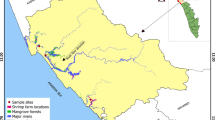
This study analyzed water and soil quality and environmental impacts of shrimp farming in the southwestern coastal region of Bangladesh. Shrimp farming in the region is very traditional in nature where two culture systems viz. shrimp–rice and shrimp-only are being practiced, which are characterized by lower production, repeated stocking, irregular feeding, and fertilizing. Water quality in both farming systems was found suitable for optimum growth and survival of shrimp (Penaeus spp.). The level of 5-day biological oxygen demand (BOD5) in both systems even in canal water was within the recommended level provided by the Government of Bangladesh which is less than 5 mg/l. Therefore, effluents of shrimp farms in the study area did not show any nutrient pollution on the surrounding environment. However, saltwater intrusion has caused many problems like loss of agricultural production, reduced availability of fodder for livestock, and fresh water for domestic uses in the coastal region. The findings of this study confirmed that shrimp farming using saline water have long-term effect of soil salinization. As a result, it poses a real threat toward sustainability of coastal shrimp farming as well as coastal development in Bangladesh.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SMN, Pokrant B, Yakupitiyage A, Phillips MJ (2007) Economic returns of disease-affected extensive shrimp farming in southwest Bangladesh. Aquac Int 15(5):363–370
Ali AMS (2006) Rice to shrimp: land use/land cover changes and soil degradation in southwestern Bangladesh. Land Use Policy 23(4):421–435
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1980) Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater, 15th edn. APHA, Washington, p 1134
Azad AK, Jensen KR, Lin CK (2009) Coastal aquaculture development in Bangladesh: unsustainable and sustainable experiences. Environ Manag 44:800–809
Bandyopadhay BK (1998) Submergence of coastal lands under brackish water aquaculture—effect on soil properties and ecology of coastal region. J Ind Soc Coastal Agric Resour 16(2):73–79
Barg UC (1992) Guidelines for the promotion of environmental management of coastal aquaculture development. FAO fisheries Technical paper 328. The United Nations, Rome, p 122
Boyd CE (2003) Guidelines for aquaculture effluent management at the farm-level. Aquaculture 226(1–4):101–112
Boyd CE, Green BW (2002) Coastal water quality monitoring in shrimp farming areas, an example from honduras. Report prepared under the World Bank, NACA, WWF and FAO Consortium Program on Shrimp Farming and the Environment. Work in Progress for Public Discussion. Published by the Consortium, p 29
Boyd CE, Massaut L, Wedding LJ (1998) Towards reducing environmental impacts of pond aquaculture. INFOFISH Int 2(98):27–33
Braaten RO, Flaherty M (2001) Salt balance of inland shrimp ponds in Thailand: implications for land and water stabilization. Environ Conserv 28(4):357–367
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci 59:39–45
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Total nitrogen. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 595–624
Chanratchakool P, Turnbull JF, Limsuwan C (1994) Health management in shrimp ponds. Kasetsart University, Bangkok
Chowdhury MA (2006) The sustainability assessment of shrimp farming: a case study of the present farming systems in Bangladesh. Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand Ph.D Dissertation no. AQ-06-5
Chowdhury MA, Shivakoti GP, Salequzzaman M (2006) A conceptual framework for the sustainability assessment procedures of the shrimp aquaculture industry in coastal Bangladesh. Int J Agric Resour Gov Ecol 5(2/3):162–184
Dierberg FE, Kiattisimkul W (1996) Issues, impacts, and implications of shrimp aquaculture in Thailand. Environ Manag 20(5):649–666
DoE (Department of Environment) (1999) Environmental guidelines. Published by Department of Environment, Ministry of Forestry and Environment, Bangladesh
FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization) (2010) FISSTATE-plus, Fisheries Production Database, software (in CD) collected by personal communication
Ham D, Nandy S (1990) Equity aspects of shrimp cultivation practices in Khulna region. Paper presented in a seminar on “Environmental and Policy Aspects of Shrimp Cultivation”. Dhaka, Bangladesh, p 15
Hambrey J (1996) The sustainability of shrimp farming. Seminar on aquaculture industry: Prospects and issues. Organized by Confederation of Indian Industry, Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India, 22–23 Aug1996
Hesse PR (1971) Preparation of soil samples for analysis. In A textbook of soil chemical analysis, Chapter 2, 10–17. Chemical Publishing Co Inc., USA
Hossain MS (2001) Biological aspects of the coastal and marine environment of Bangladesh. Ocean Coast Manag 44:261–282
Islam MS (2003) Socioeconomic impacts of alternate shrimp-shrimp-crop farming in Bangladesh. In: Wahab MA (ed) Environmental and socioeconomic impacts of shrimp aquaculture in Bangladesh. Technical proc., BAU—NORAD Workshop, BRAC Centre, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh, 5 March 2002, pp 61–78
James DW, Wells KI (1990) Soil sample collection and handling: technique based on source and degree of field variability. In: Westerman RL (ed) Soil testing and plant analysis, 3rd edn. SSSA Book Series 3, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsis, pp 25–44
Knudsen D, Peterson GA, Pratit PF (1982) Lithium, sodium and potassium. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2, chemical and microbiological properties edition. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 225–245
Lertpaitoonpan W (2000) Water quality assessment in shrimp ponds: a case study in renong, Thailand. M.S. Thesis, Asian Institute of Technology, EV-00-18
Liu CI (1989) Shrimp disease prevention and treatment. In: Akiyama DM (ed). Proceedings of the Southeast Asia Shrimp farm Management Workshop Philippines, Indonesia, and Thailand, 26 July–11 Aug 1989
McIntosh D, Fitzsimmons K (2003) Characterization of effluent from an inland low-salinity shrimp farm: what contribution could this water make if used for irrigation. Aquac Eng 27:147–156
McLean EO (1982) Soil pH and lime requirement. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy Inc., Madison, pp 199–224
Naylor LR, Goldburg RJ, Primavera JH, Kautsky N, Beveridge MCM, Clay J, Folks C, Lubchenco J, Mooney H, Troell M (2000) Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 405:1017–1024
Nissapa A, Boromthanarat S, Chaijaroenwatana B, Chareonkunanond W (2002) Shrimp farming in Thailand: a review of issues. individual partner report for the project: policy research for sustainable shrimp farming in Asia. European Commission INCO-DEV Project PORESSFA No.IC4-2001-10042, CEMARE University of Portsmouth UK and CORIN, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand. p 73
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy Inc., Madison, pp 403–430
Petersen L (2002) Analytical methods: soil, water, plant material, fertilizer. Soil resource management and analytical services. Soil Resource Development Institute, DANIDA, KAMPSAX, Dhaka, p 125
Phillips MJ (1998) Tropical mariculture and coastal environmental integrity. In: De Silva SS (ed) Tropical mariculture. Academic press, California 92101-4495, USA, pp 17–59
Primavera JH (1994) Shrimp farming in the Asia-Pacific: Environmental and trade issues and regional cooperation. Aquaculture Department. Southeast Asian Fisheries development Center. Tigbaun, Iloilo, Philippines 5021. Present at the national institute workshop on trade and environment in Asia-Pacific: Prospect of regional cooperation 23–25 September. East-West Center, Honolulu
Primavera JH (2006) Overcoming the impacts of aquaculture on coastal zone. Ocean Coast Manag 49:531–545
Rasul G, Thapa GB (2004) Sustainability analysis of ecological and conventional agricultural systems in Bangladesh. World Development doi:10.1016/S0305-750X(03)00137-2:1721-1741
Rhoades JD (1982) Soluble salts. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Inc., Madison, pp 167–179
Salequzzaman M (2001) Sustainability of shrimp aquaculture in coastal Bangladesh. MEDCOAST 01, the fifth international conference on the mediterranean coastal environment, Hamammet, Tunisia, 23–27 Oct 2001
Samantray P, Mishra BK, Panda CR, Rout SP (2009) Assessment of water quality index in Mahanadi and Atharabanki Rivers and Taldanda Canal in Paradip area. Indian J Hum Ecol 26(3):153–161
SRDI (Soil Resource Development Institute) (2003) Soil salinity in Bangladesh. Ministry of Agriculture, Dhaka 1215
Tanavud C, Yongchalermchai C, Bennui A, Densrisereekul O (2001) The eexpansion of inland shrimp farming and its environmental impacts in Songkla lake basin. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 35(3):326–343
Thakur DP, Lin CK (2003) Water quality and nutrient budget in coastal shrimp (Penaeus monodon) culture systems. Aquac Eng 27(3):159–176
Wahab MA (2003) Environmental impacts of shrimp farming in the coastal areas of Bangladesh. In: Wahab MA (ed) Environmental and socioeconomic impacts of shrimp farming in Bangladesh. Technical proc. BAU—NORAD Workshop, BRAC Centre, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh, 5 March 2002, pp 19–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, M.A., Khairun, Y., Salequzzaman, M. et al. Effect of combined shrimp and rice farming on water and soil quality in Bangladesh. Aquacult Int 19, 1193–1206 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9433-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9433-0