Abstract
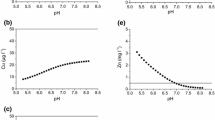
The influence of Zn speciation on Zn transport by drainage from different soils to surface water is examined in a stream catchment in an agricultural area. Drainage waters were collected from two types of soils, a mineral soil (MS) and a soil rich in organic matter (OS) by means of artificial drainage pipes. The speciation of dissolved Zn in the stream and the drainage waters was determined using ligand-exchange and voltammetry. About 50–95% of dissolved Zn is bound in strong complexes, and the free Zn2+ ion concentration is in the range of 1–16% of dissolved Zn. A substantial part of Zn is present in weaker organic or inorganic complexes. The simulated Zn speciation using the WHAM VI model is compared to the determined speciation. Free Zn2+ concentrations predicted by the WHAM VI model are generally higher than the analytically determined free Zn2+, but are mostly within the same order of magnitude. Effects of different soil organic matter content on Zn speciation and transport are discussed. Zn speciation in the drainage at the OS site is influenced by the distribution of organic matter between the solid and solution phase. The abundant organic Zn complexes in solution contribute to facilitate Zn transport from soil into surface waters, through the drainage at the OS site. Drainage from the OS site contributes about twice as much Zn input to the receiving water as the MS soil, as related to specific area. The mineral soil contains much lower organic matter, and a part of Zn bound with inorganic phases can hardly be released by dissolved organic ligands, leading to much higher Zn retention at the MS site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. P. Aldrich D. Kistler L. Sigg (2002) ArticleTitleSpeciation of Cu and Zn in drainage water from agricultural soils Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 4824–4830 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es025813x
D. Buerge-Weirich R. Hari H. B. Xue P. Behra L. Sigg (2002) ArticleTitleAdsorption of Cu, Cd and Ni on goethite in the presence of natural ground water ligands Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 328–336 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es010892i
R. Gächter J. M. Ngatia C. Stamm (1998) ArticleTitleTransport of phosphate from soil to surface water by preferential flow Environ. Sci. Technol. 32 1865–1869
G. D. Kinnburgh W. H. V. Riemsdijk L. K. Koopal M. Borkovec M. F. Benedetti M. J. Avena (1999) ArticleTitleIon binding to natural organic matter: competition, heterogeneity, stoichiometry and thermodynamic consistency J. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 151 147–166
H. Menzi E. Lermann J. Kessler (1999) ArticleTitleAnfall und Zusammensetzung von Hofdünger aus der Rindviehmast Agrarforschung 6 417–420
F. A. Nicholson B. J. Chambers J. R. Willians R. J. Unwin (1999) ArticleTitleHeavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales Bioresource Technol. 70 23–31 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00017-6
E. Tipping (1998) ArticleTitleHumic ion-binding Model VI: An improved description of the interractions of protons and metal ions with humic substances Aquat. Geochem. 4 3–48 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009627214459
L. Weng E. J. M. Temminghof S. Lofts E. Tipping W. H. V. Riemsdijk (2002) ArticleTitleComplexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil Environ. Sci. Technol. 36 4804–4810
L. Weng E. J. M. Temminghoff W. H. Riemsdijk Particlevan (2001) ArticleTitleComplexation of individual sorbents to the control of heavy metal activity in sandy soil Environ. Sci. Technol. 35 4436–4443 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es010085j
H. B. Xue D. Kistler L. Sigg (1995a) ArticleTitleCompetition of copper and zinc for strong ligands in a eutrophic lake Limnol. Oceanogr. 40 1142–1152 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1995.40.6.1142
H. B. Xue P. H. Nhat R. Gaechter P. S. Hooda (2003) ArticleTitleThe transport of Cu and Zn from agricultural soils to surface water in a small catchment Advances Environ. Res. 8 69–76
H. B. Xue L. Sigg (1994) ArticleTitleZn Speciation in lake waters and its determination by ligand exchange with EDTA and differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry Anal. Chim. Acta 284 505–515 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2670(94)85057-7
H. B. Xue L. Sigg R. Gaechter (2000) ArticleTitleTransport of Cu, Zn and Cd in a small agricultural catchment Water Res. 34 2558–2568 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00015-4
H. B. Xue L. Sigg F. G. Kari (1995b) ArticleTitleSpeciation of EDTA in natural waters: Exchange kinetics of Fe-EDTA in River Water Environ. Sci. Technol. 29 59–68 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es00001a007
J. M. Zachara S. C. Smith C. T. Resch C. E. Cowan (1992) ArticleTitleCadmium sorption to soil separates containing layer silicates and iron and aluminum-oxides Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 56 1074–1084 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1992.03615995005600040012x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, H., Nhat, P.H. & Sigg, L. Effects of Soil Composition on Zn Speciation in Drainage Waters from Agricultural Soils. Aquat Geochem 11, 303–318 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-005-4682-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-005-4682-z