Abstract
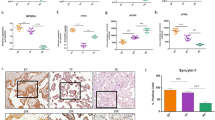
During pregnancy, apoptosis is a physiological event critical in the remodeling and aging of the placenta. Increasing evidence has pointed towards the relevance of endocannabinoids (ECs) and hypoxia as modulators of trophoblast cell death. However, the relation between these factors is still unknown. In this report, we evaluated the participation of ECs in placental apoptosis induced by cobalt chloride (CoCl2), a hypoxia mimicking agent that stabilizes the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α). We found that HIF-1α stabilization decreased FAAH mRNA and protein levels, suggesting an increase in ECs tone. Additionally, CoCl2 incubation and Met-AEA treatment reduced cell viability and increased TUNEL-positive staining in syncytiotrophoblast layer. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated Bax and Bcl-2 protein expression in the cytoplasm of syncytiotrophoblast. Finally, HIF-1α stabilization produced an increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, activation of caspase 3 and PARP cleavage. All these changes in apoptotic parameters were reversed with AM251, a CB1 antagonist. These results demonstrate that HIF-1α may induce apoptosis in human placenta via intrinsic pathway by a mechanism that involves activation of CB1 receptor suggesting a role of the ECs in this process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habayeb OM, Taylor AH, Evans MD, Cooke MS, Taylor DJ, Bell SC, Konje JC (2004) Plasma levels of the endocannabinoid anandamide in women–a potential role in pregnancy maintenance and labor? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(11):5482–5487
Di Marzo V, Fontana A, Cadas H, Schinelli S, Cimino G, Schwartz JC, Piomelli D (1994) Formation and inactivation of endogenous cannabinoid anandamide in central neurons. Nature 372(6507):686–691
Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2002) The enzymatic inactivation of the fatty acid amide class of signaling lipids. Chem Phys Lipids 121(1–2):135–148
Park B, Gibbons HM, Mitchell MD, Glass M (2003) Identification of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in the human placenta. Placenta 24(10):990–995
Marczylo TH, Lam PM, Amoako AA, Konje JC (2010) Anandamide levels in human female reproductive tissues: solid-phase extraction and measurement by ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 400(2):155–162
Aban C, Leguizamon GF, Cella M, Damiano A, Franchi AM, Farina MG (2013) Differential expression of endocannabinoid system in normal and preeclamptic placentas: effects on nitric oxide synthesis. Placenta 34(1):67–74
Heazell AE, Crocker IP (2008) Live and let die—regulation of villous trophoblast apoptosis in normal and abnormal pregnancies. Placenta 29(9):772–783
Smith SC, Baker PN, Symonds EM (1997) Increased placental apoptosis in intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177(6):1395–1401
Leung DN, Smith SC, To KF, Sahota DS, Baker PN (2001) Increased placental apoptosis in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 184(6):1249–1250
Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia–a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2(1):38–47
Pringle KG, Kind KL, Sferruzzi-Perri AN, Thompson JG, Roberts CT (2010) Beyond oxygen: complex regulation and activity of hypoxia inducible factors in pregnancy. Hum Reprod Update 16(4):415–431
Déry MA, Michaud MD, Richard DE (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(3):535–540
Rajakumar A, Conrad KP (2000) Expression, ontogeny, and regulation of hypoxia inducible transcription factors in the human placenta. Biol Reprod 63(2):559–569
Rajakumar A, Michael HM, Daftary A, Jeyabalan A, Gilmour A, Conrad KP (2008) Proteasomal activity in placentas from women with preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction: implications for expression of HIF-alpha proteins. Placenta 29(3):290–299
Costa MA (2016) The endocannabinoid system: a novel player in human placentation. Reprod Toxicol 61:58–67
Castro-Parodi M, Szpilbarg N, Dietrich V, Sordelli M, Reca A, Aban C, Maskin B, Farina MG, Damiano AE (2013) Oxygen tension modulates AQP9 expression in human placenta. Placenta 34(8):690–698
Miller RK, Genbacev O, Turner MA, Aplin JD, Caniggia I, Huppertz B (2005) Human placental explants in culture: approaches and assessments. Placenta 26(6):439–448
Lee JH, Choi SH, Baek MW, Kim MH, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Oh SJ, Park HJ, Kim WJ, Jung JY (2013) CoCl2 induces apoptosis through the mitochondria- and death receptor-mediated pathway in the mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem 379(1–2):133–140
Maccarrone M, Bisogno T, Valensise H, Lazzarin N, Fezza F, Manna C, Di Marzo V, Finazzi-Agro A (2002) Low fatty acid amide hydrolase and high anandamide levels are associated with failure to achieve an ongoing pregnancy after IVF and embryo transfer. Mol Hum Reprod 8(2):188–195
Chamley LW, Bhalla A, Stone PR, Liddell H, O’Carroll S, Kearn C, Glass M (2008) Nuclear localization of the endocannabinoid metabolizing enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in invasive trophoblasts and an association with recurrent miscarriage. Placenta 29(11):970–975
Habayeb OM, Taylor AH, Finney M, Evans MD, Konje JC (2008) Plasma anandamide concentration and pregnancy outcome in women with threatened miscarriage. JAMA 299(10):1135–1136
Endsley MP, Thill R, Choudhry I, Williams CL, Kajdacsy-Balla A, Campbell WB, Nithipatikom K (2008) Expression and function of fatty acid amide hydrolase in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 123(6):1318–1326
Cippitelli A, Cannella N, Braconi S, Duranti A, Tontini A, Bilbao A, Defonseca FR, Piomelli D, Ciccocioppo R (2008) Increase of brain endocannabinoid anandamide levels by FAAH inhibition and alcohol abuse behaviours in the rat. Psychopharmacology 198(4):449–460
Jian H, Liu B, Zhang J (2014) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 repress SEMA4B expression to promote non-small cell lung cancer invasion. Tumour Biol 35(5):4949–4955
Zheng J, Sun X, Wang W, Lu S (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha modulates the down-regulation of the homeodomain protein CDX2 in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 24(1):97–104
Costa MA, Fonseca BM, Keating E, Teixeira NA, Correia-da-Silva G (2014) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 is expressed in human cytotrophoblasts: induction of cell apoptosis and impairment of syncytialization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 57:177–185
Costa MA, Fonseca BM, Teixeira NA, Correia-da-Silva G (2015) The endocannabinoid anandamide induces apoptosis in cytotrophoblast cells: involvement of both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Placenta 36(1):69–76
Roh CR, Lee JW, Kang BH, Yang SH, Kim BG, Bae DS, Kim JH, Lee JH (2002) Differential expressions of Fas and Fas ligand in human placenta. J Korean Med Sci 17(2):213–216
Pongcharoen S, Searle RF, Bulmer JN (2004) Placental Fas and Fas ligand expression in normal early, term and molar pregnancy. Placenta 25(4):321–330
Ishihara N, Matsuo H, Murakoshi H, Laoag-Fernandez JB, Samoto T, Maruo T (2002) Increased apoptosis in the syncytiotrophoblast in human term placentas complicated by either preeclampsia or intrauterine growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186(1):158–166
De Falco M, Penta R, Laforgia V, Cobellis L, De Luca A (2005) Apoptosis and human placenta: expression of proteins belonging to different apoptotic pathways during pregnancy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 24(1):25–33
Ratts VS, Tao XJ, Webster CB, Swanson PE, Smith SD, Brownbill P, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Tilly JL, Nelson DM (2000) Expression of BCL-2, BAX and BAK in the trophoblast layer of the term human placenta: a unique model of apoptosis within a syncytium. Placenta 21(4):361–366
Huppertz B, Frank HG, Kingdom JC, Reister F, Kaufmann P (1998) Villous cytotrophoblast regulation of the syncytial apoptotic cascade in the human placenta. Histochem Cell Biol 110(5):495–508
Abumaree MH, Stone PR, Chamley LW (2012) Changes in the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in the life cycle of human villous trophoblast. Reprod Sci 19(6):597–606
Huppertz B, Kingdom J, Caniggia I, Desoye G, Black S, Korr H, Kaufmann P (2003) Hypoxia favours necrotic versus apoptotic shedding of placental syncytiotrophoblast into the maternal circulation. Placenta 24(2–3):181–190
Tomiyama K, Funada M (2014) Cytotoxicity of synthetic cannabinoids on primary neuronal cells of the forebrain: the involvement of cannabinoid CB1 receptors and apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274(1):17–23
Fonseca BM, Correia-da-Silva G, Teixeira NA (2009) Anandamide-induced cell death: dual effects in primary rat decidual cell cultures. Placenta 30(8):686–692
Huppertz B, Kadyrov M, Kingdom JC (2006) Apoptosis and its role in the trophoblast. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195(1):29–39
Sharp AN, Heazell AE, Crocker IP, Mor G (2010) Placental apoptosis in health and disease. Am J Reprod Immunol 64(3):159–169
Caniggia I, Winter JL (2002) Adriana and Luisa Castellucci Award lecture 2001 Hypoxia inducible factor-1: oxygen regulation of trophoblast differentiation in normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies–a review. Placenta 23(Suppl A):S47–S57
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs. Ramona Morales and Ph.D. Maximiliano Cella for technical assistance and Mrs. Rossana Santarelli for English corrections.
Funding
This work was supported by PICT 2010 N 1974 (CONICET), Fundación Florencio Fiorini and Fundación Roemmers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abán, C., Martinez, N., Carou, C. et al. Endocannabinoids participate in placental apoptosis induced by hypoxia inducible factor-1. Apoptosis 21, 1094–1105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1274-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1274-x