Abstract
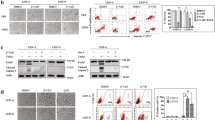
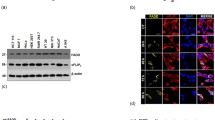
Axin is a multifunctional protein that participates in many cellular events including Wnt signaling and cell fate determination. Aurora kinase inhibitor (AKI)-induced cell death and cell membrane rupture is facilitated in L929 cells expressing axin (L-axin cells) through the activation of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP). We observed that caspase-2 activity is required for AKI-induced cell death. Inhibition of caspase-2 activity suppressed AKI-induced PARP activation and mitochondrial dysfunction, resulting in a decrease in AKI-induced cell death. When an axin mutant deleted for the glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β)-binding domain was expressed in L929 cells (L-ΔGSK cells), AKI-induced caspase-2 activation and cell death decreased. AKI treatment reduced the expression of a 32-kDa caspase-2 splicing variant (caspase-2S) in most L-axin cells, but not in L-ΔGSK cells. These results suggest that AKI-induced caspase-2 activation in L-axin cells might be due to a decrease in the expression of caspase-2S, which inhibits caspase-2 activity. In addition, AKI treatment failed to activate caspase-8 and treatment with necrostatin inhibited AKI-induced cell death in L-axin cells, suggesting that the absence of caspase-8 activation might favor necrotic cell death. Axin expression may facilitate AKI-induced caspase-2 activation followed by activation of PARP and initiation of the necrotic cell death pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmena M, Ruchaud S, Earnshaw WC (2009) Making the Auroras glow: regulation of Aurora A and B kinase function by interacting proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:796–805
Katayama H, Brinkley WR, Sen S (2003) The Aurora kinases: role in cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:451–464
Katayama H, Sen S (2010) Aurora kinase inhibitors as anticancer molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:829–839
Li M, Jung A, Ganswindt U et al (2010) Aurora kinase inhibitor ZM447439 induces apoptosis via mitochondrial pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 79:122–129
Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C et al (2007) AZD1152, a novel and selective aurora B kinase inhibitor, induces growth arrest, apoptosis, and sensitization for tubulin depolymerizing agent or topoisomerase II inhibitor in human acute leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 110:2034–2040
Zhou N, Singh K, Mir MC et al (2013) The investigational aurora kinase A inhibitor MLN8237 induces defects in cell viability and cell cycle progression in bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 19(7):1717–1728
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127:469–480
Kim SM, Choi EJ, Song KJ et al (2009) Axin localizes to mitotic spindles and centrosomes in mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res 315:943–954
Ruan K, Ye F, Li C, Liou YC, Lin SC, Lin SY (2012) PLK1 interacts and phosphorylates Axin that is essential for proper centrosome formation. PLoS One 7(11):e49184
Salahshor S, Woodgett JR (2005) The links between axin and carcinogenesis. J Clin Pathol 58:225–236
Neo SY, Zhang Y, Yaw LP, Li P, Lin SC (2000) Axin-induced apoptosis depends on the extent of its JNK activation and its ability to down-regulate beta-catenin levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272:144–150
Rui Y, Xu Z, Lin S et al (2004) Axin stimulates p53 functions by activation of HIPK2 kinase through multimeric complex formation. EMBO J 23:4583–4594
Li Q, Wang X, Wu X et al (2007) Daxx cooperates with the Axin/HIPK2/p53 complex to induce cell death. Cancer Res 67:66–74
Li Q, Lin S, Wang X et al (2009) Axin determines cell fate by controlling the p53 activation threshold after DNA damage. Nat Cell Biol 11:1128–1134
Dupont P, Besson MT, Devaux J, Lievens JC (2012) Reducing canonical Wingless/Wnt signaling pathway confers protection against mutant Huntingtin toxicity in Drosophila. Neurobiol Dis 47:237–247
Shin JH, Kim HW, Rhyu IJ, Song KJ, Kee SH (2012) Axin expression reduces staurosporine-induced mitochondria-mediated cell death in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res 318:2022–2033
Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P (2007) Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 14:44–55
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA et al (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H, Zhivotovsky B (2010) The unpredictable caspase-2: what can it do? Trends Cell Biol 20:150–159
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G et al (1998) Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 12:1304–1314
Harvey NL, Butt AJ, Kumar S (1997) Functional activation of Nedd2/ICH-1 (caspase-2) is an early process in apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:13134–13139
Wang L, Miura M, Bergeron L, Zhu H, Yuan J (1994) Ich-1, an Ice/ced-3-related gene, encodes both positive and negative regulators of programmed cell death. Cell 78:739–750
Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2006) Functional connection between p53 and caspase-2 is essential for apoptosis induced by DNA damage. Oncogene 25:5683–5692
Tu S, McStay GP, Boucher LM, Mak T, Beere HM, Green DR (2006) In situ trapping of activated initiator caspases reveals a role for caspase-2 in heat shock-induced apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 8:72–77
Droin N, Rebe C, Bichat F, Hammann A, Bertrand R, Solary E (2001) Modulation of apoptosis by procaspase-2 short isoform: selective inhibition of chromatin condensation, apoptotic body formation and phosphatidylserine externalization. Oncogene 20:260–269
Parent N, Sane AT, Droin N, Bertrand R (2005) Procaspase-2S inhibits procaspase-3 processing and activation, preventing ROCK-1-mediated apoptotic blebbing and body formation in human B lymphoma Namalwa cells. Apoptosis 10:313–322
Choi EJ, Kim SM, Song KJ, Lee JM, Kee SH (2011) Axin1 expression facilitates cell death induced by aurora kinase inhibition through PARP activation. J Cell Biochem 112:2392–2402
Yoo BH, Wang Y, Erdogan M et al (2011) Oncogenic ras-induced down-regulation of pro-apoptotic protease caspase-2 is required for malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 286:38894–38903
Carlile GW, Smith DH, Wiedmann M (2004) Caspase-3 has a nonapoptotic function in erythroid maturation. Blood 103:4310–4316
Li H, Bergeron L, Cryns V et al (1997) Activation of caspase-2 in apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:21010–21017
Droin N, Beauchemin M, Solary E, Bertrand R (2000) Identification of a caspase-2 isoform that behaves as an endogenous inhibitor of the caspase cascade. Cancer Res 60:7039–7047
Shin S, Lee Y, Kim W, Ko H, Choi H, Kim K (2005) Caspase-2 primes cancer cells for TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by processing procaspase-8. EMBO J 24:3532–3542
Green DR, Oberst A, Dillon CP, Weinlich R, Salvesen GS (2011) RIPK-dependent necrosis and its regulation by caspases: a mystery in five acts. Mol Cell 44:9–16
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M et al (2005) Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 1:112–119
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S et al (2009) Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 461:614–620
Choi EJ, Kim S, Jho EH, Song KJ, Kee SH (2013) Axin expression enhances herpes simplex virus type 1 replication by inhibiting virus-mediated cell death in L929 cells. J Gen Virol 94(Pt 7):1636–1646
Vercammen D, Brouckaert G, Denecker G et al (1998) Dual signaling of the Fas receptor: initiation of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways. J Exp Med 188:919–930
Vercammen D, Beyaert R, Denecker G et al (1998) Inhibition of caspases increases the sensitivity of L929 cells to necrosis mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 187:1477–1485
Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Kropotov A, Vakifahmetoglu H, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2004) Processed caspase-2 can induce mitochondria-mediated apoptosis independently of its enzymatic activity. EMBO Rep 5:643–648
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2002) Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem 277:13430–13437
Upton JP, Austgen K, Nishino M et al (2008) Caspase-2 cleavage of BID is a critical apoptotic signal downstream of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol 28:3943–3951
Logette E, Wotawa A, Solier S, Desoche L, Solary E, Corcos L (2003) The human caspase-2 gene: alternative promoters, pre-mRNA splicing and AUG usage direct isoform-specific expression. Oncogene 22:935–946
Toh WH, Logette E, Corcos L, Sabapathy K (2008) TAp73beta and DNp73beta activate the expression of the pro-survival caspase-2S. Nucleic Acids Res 36:4498–4509
Moll UM, Slade N (2004) p63 and p73: roles in development and tumor formation11 National Cancer Institute. Mol Cancer Res 2:371–386
Ozaki T, Nakagawara A (2005) p73, a sophisticated p53 family member in the cancer world. Cancer Sci 96:729–737
Ando K, Ozaki T, Yamamoto H et al (2004) Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) Inhibits p53 function by physical interaction and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 279:25549–25561
Koida N, Ozaki T, Yamamoto H et al (2008) Inhibitory role of Plk1 in the regulation of p73-dependent apoptosis through physical Interaction and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 283:8555–8563
Grimes CA, Jope RS (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Forde JE, Dale TC (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1930–1944
Lin CF, Chen CL, Chang WT et al (2004) Sequential caspase-2 and caspase-8 activation upstream of mitochondria during ceramide and etoposide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:40755–40761
Yu L, Alva A, Su H et al (2004) Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 304:1500–1502
Ch’en IL, Beisner DR, Degterev A et al (2008) Antigen-mediated T cell expansion regulated by parallel pathways of death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17463–17468
Kikuchi M, Kuroki S, Kayama M, Sakaguchi S, Lee KK, Yonehara S (2012) Protease activity of procaspase-8 is essential for cell survival by inhibiting both apoptotic and nonapoptotic cell death dependent on receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3. J Biol Chem 287:41165–41173
Pugacheva EN, Jablonski SA, Hartman TR, Henske EP, Golemis EA (2007) HEF1-dependent aurora A activation induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell 129:1351–1363
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0022963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, EJ., Kim, SM., Shin, JH. et al. Involvement of caspase-2 activation in aurora kinase inhibitor-induced cell death in axin-expressing L929 cells. Apoptosis 19, 657–667 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0951-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0951-2