Abstract
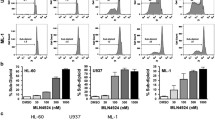
We investigated the relevance of signaling mechanisms regulated by the Ras-homologous GTPase Rac1 for survival of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells harbouring the MLL-AF9 oncogene due to t(9;11)(p21;q23) translocation. Monocytic MLL-AF9 expressing cells (MM6, THP-1) were hypersensitive to both small-molecule inhibitors targeting Rac1 (EHT 1864, NSC 23766) (IC50EHT ~12.5 μM) and lipid lowering drugs (lovastatin, atorvastatin) (IC50Lova ~7.5 μM) as compared to acute myelocytic leukemia (NOMO-1, HL60) and T cell leukemia (Jurkat) cells (IC50EHT >30 μM; IC50Lova >25 μM). Hypersensitivity of monocytic cells following Rac1 inhibition resulted from caspase-driven apoptosis as shown by profound activation of caspase-8,-9,-7,-3 and substantial (~90 %) decrease in protein expression of pro-survival factors (survivin, XIAP, p-Akt). Apoptotic death was preceded by S139-posphorylation of histone H2AX (γH2AX), a prototypical surrogate marker of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Taken together, abrogation of Rac1 signaling causes DSBs in acute monocytic leukemia cells harbouring the MLL-AF9 oncogene, which, together with downregulation of survivin, XIAP and p-Akt, results in massive induction of caspase-driven apoptotic death. Apparently, Rac1 signaling is required for maintaining genetic stability and maintaining survival in specific subtypes of AML. Hence, targeting of Rac1 is considered a promising novel strategy to induce lethality in MLL-AF9 expressing AML.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- ALL:
-
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- AML:
-
Acute myeloid leukemia
- ATM:
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated
- ATR:
-
ATM and Rad3-related
- BER:
-
Base excision repair
- BRCA:
-
Breast cancer susceptibility protein
- Chk:
-
Checkpoint kinase
- CRIB:
-
Cdc42/Rac interactive binding region
- DDR:
-
DNA damage response
- DSBs:
-
DNA double-strand breaks
- GEF:
-
Guanine exchange factor
- IC50 :
-
Inhibitory concentration 50 %
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- HMG-CoA:
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A
- H2AX:
-
Histone H2AX
- γH2AX:
-
S139 phosphorylated H2AX
- IC50 :
-
Inhibitory concentration 50 %
- IC50EHT :
-
IC50 after EHT 1864 treatment
- IC50Lova :
-
IC50 after lovastatin treatment
- MLL:
-
Mixed lineage leukemia
- MLLT3 (=AF9):
-
Mixed lineage leukemia, tanslocated to, 3
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- Rac1:
-
Ras-related C3 botulinum substrate 1
- Rho:
-
Ras-homologous
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
References
Bokoch GM (2000) Regulation of cell function by Rho family GTPases. Immunol Res 21:139–148
Hall A (1998) Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279:509–514
Villalonga P, Ridley AJ (2006) Rho GTPases and cell cycle control. Growth Factors 24(3):159–164
Coniglio SJ, Jou TS, Symons M (2001) Rac1 protects epithelial cells against anoikis. J Biol Chem 276:28113–28120
Minden A, Lin A, Claret FX, Abo A, Karin M (1995) Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell 81:1147–1157
Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu JC, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N et al (1995) The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81:1137–1146
Canman CE, Kastan MB (1996) Three paths to stress relief. Nature 384:213–214
Schmitz AA, Govek EE, Bottner B, Van Aelst L (2000) Rho GTPases: signaling, migration, and invasion. Exp Cell Res 261:1–12
Aznar S, Fernandez-Valeron P, Espina C, Lacal JC (2004) Rho GTPases: potential candidates for anticancer therapy. Cancer Lett 206:181–191
Ellenbroek SI, Collard JG (2007) Rho GTPases: functions and association with cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 24:657–672
Liao JK, Laufs U (2005) Pleiotropic effects of statins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:89–118
Zhou Q, Liao JK (2010) Pleiotropic effects of statins—Basic research and clinical perspectives. Circ J 74:818–826
Rao S, Lowe M, Herliczek TW, Keyomarsi K (1998) Lovastatin mediated G1 arrest in normal and tumor breast cells is through inhibition of CDK2 activity and redistribution of p21 and p27, independent of p53. Oncogene 17:2393–2402
Matar P, Rozados VR, Binda MM, Roggero EA, Bonfil RD, Scharovsky OG (1999) Inhibitory effect of lovastatin on spontaneous metastases derived from a rat lymphoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 17:19–25
Cafforio P, Dammacco F, Gernone A, Silvestris F (2005) Statins activate the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in human lymphoblasts and myeloma cells. Carcinogenesis 26:883–891
Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, Moss SF, Ramey WG, Holt PR (1999) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:2223–2229
Super HJ, McCabe NR, Thirman MJ, Larson RA, Le Beau MM, Pedersen-Bjergaard J et al (1993) Rearrangements of the MLL gene in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia in patients previously treated with agents targeting DNA-topoisomerase II. Blood 82:3705–3711
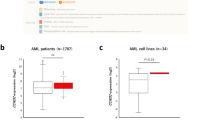
Schoch C, Schnittger S, Klaus M, Kern W, Hiddemann W, Haferlach T (2003) AML with 11q23/MLL abnormalities as defined by the WHO classification: incidence, partner chromosomes, FAB subtype, age distribution, and prognostic impact in an unselected series of 1897 cytogenetically analyzed AML cases. Blood 102:2395–2402
Dobson CL, Warren AJ, Pannell R, Forster A, Lavenir I, Corral J et al (1999) The mll-AF9 gene fusion in mice controls myeloproliferation and specifies acute myeloid leukaemogenesis. EMBO J 18:3564–3574
Muntean AG, Tan J, Sitwala K, Huang Y, Bronstein J, Connelly JA et al (2010) The PAF complex synergizes with MLL fusion proteins at HOX loci to promote leukemogenesis. Cancer Cell 17:609–621
Monroe SC, Jo SY, Sanders DS, Basrur V, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Slany RK et al (2011) MLL-AF9 and MLL-ENL alter the dynamic association of transcriptional regulators with genes critical for leukemia. Exp Hematol 39(77–86):e71–e75
Liu H, Takeda S, Kumar R, Westergard TD, Brown EJ, Pandita TK et al (2010) Phosphorylation of MLL by ATR is required for execution of mammalian S-phase checkpoint. Nature 467:343–346
Paulsen RD, Cimprich KA (2007) The ATR pathway: fine-tuning the fork. DNA Repair (Amst) 6:953–966
Harper JW, Elledge SJ (2007) The DNA damage response: ten years after. Mol Cell 28:739–745
Cortez D, Guntuku S, Qin J, Elledge SJ (2001) ATR and ATRIP: partners in checkpoint signaling. Science 294:1713–1716
Shutes A, Onesto C, Picard V, Leblond B, Schweighoffer F, Der CJ (2007) Specificity and mechanism of action of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases. J Biol Chem 282:35666–35678
Gao Y, Dickerson JB, Guo F, Zheng J, Zheng Y (2004) Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7618–7623
Onesto C, Shutes A, Picard V, Schweighoffer F, Der CJ (2008) Characterization of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases. Methods Enzymol 439:111–129
Kinner A, Wu W, Staudt C, Iliakis G (2008) Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res 36:5678–5694
Olive PL (2004) Detection of DNA damage in individual cells by analysis of histone H2AX phosphorylation. Methods Cell Biol 75:355–373
Wong WW, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD, Penn LZ (2002) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis. Leukemia 16:508–519
Roboz GJ (2012) Current treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Opin Oncol 24:711–719
Burnett A, Wetzler M, Lowenberg B (2011) Therapeutic advances in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 29:487–494
Yoshida T, Zhang Y, Rivera Rosado LA, Chen J, Khan T, Moon SY et al (2010) Blockade of Rac1 activity induces G1 cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in breast cancer cells through downregulation of cyclin D1, survivin, and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Mol Cancer Ther 9:1657–1668
Li W, Wang H, Kuang CY, Zhu JK, Yu Y, Qin ZX et al (2012) An essential role for the Id1/PI3K/Akt/NFkB/survivin signalling pathway in promoting the proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem 363:135–145
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Stiff T, O’Driscoll M, Rief N, Iwabuchi K, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA (2004) ATM and DNA-PK function redundantly to phosphorylate H2AX after exposure to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 64:2390–2396
Rothkamm K, Lobrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low X-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5057–5062
Roos WP, Kaina B (2006) DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol Med 12:440–450
Graaf MR, Richel DJ, van Noorden CJ, Guchelaar HJ (2004) Effects of statins and farnesyltransferase inhibitors on the development and progression of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30:609–641
Agarwal B, Halmos B, Feoktistov AS, Protiva P, Ramey WG, Chen M et al (2002) Mechanism of lovastatin-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis 23:521–528
Xia Z, Tan MM, Wong WW, Dimitroulakos J, Minden MD, Penn LZ (2001) Blocking protein geranylgeranylation is essential for lovastatin-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 15:1398–1407
Dimitroulakos J, Nohynek D, Backway KL, Hedley DW, Yeger H, Freedman MH et al (1999) Increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemias to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: a potential therapeutic approach. Blood 93:1308–1318
Wu J, Wong WW, Khosravi F, Minden MD, Penn LZ (2004) Blocking the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway sensitizes acute myelogenous leukemia cells to lovastatin-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 64:6461–6468
Huelsenbeck J, Henninger C, Schad A, Lackner KJ, Kaina B, Fritz G (2011) Inhibition of Rac1 signaling by lovastatin protects against anthracycline-induced cardiac toxicity. Cell Death Dis 2:e190. doi:110.1038/cddis.2011.1065
Rashid M, Tawara S, Fukumoto Y, Seto M, Yano K, Shimokawa H (2009) Importance of Rac1 signaling pathway inhibition in the pleiotropic effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Circ J 73:361–370
Mizukawa B, Wei J, Shrestha M, Wunderlich M, Chou FS, Griesinger A et al (2011) Inhibition of Rac GTPase signaling and downstream prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins as combination targeted therapy in MLL-AF9 leukemia. Blood 118:5235–5245
Mulloy JC, Wunderlich M, Zheng Y, Wei J (2008) Transforming human blood stem and progenitor cells: a new way forward in leukemia modeling. Cell Cycle 7:3314–3319
Wei J, Wunderlich M, Fox C, Alvarez S, Cigudosa JC, Wilhelm JS et al (2008) Microenvironment determines lineage fate in a human model of MLL-AF9 leukemia. Cancer Cell 13:483–495
Somervaille TC, Cleary ML (2006) Identification and characterization of leukemia stem cells in murine MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 10:257–268
Perona R, Montaner S, Saniger L, Sanchez-Perez I, Bravo R, Lacal JC (1997) Activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB by Rho, CDC42, and Rac-1 proteins. Genes Dev 11:463–475
Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Nishio Y, Hayasaka T, Kimura A, Ohta T et al (2004) Inhibition of NFkappaB increases the efficacy of cisplatin in in vitro and in vivo ovarian cancer models. J Biol Chem 279:23477–23485
Sandrock K, Bielek H, Schradi K, Schmidt G, Klugbauer N (2010) The nuclear import of the small GTPase Rac1 is mediated by the direct interaction with karyopherin alpha2. Traffic 11:198–209
Maroto B, Ye MB, von Lohneysen K, Schnelzer A, Knaus UG (2008) P21-activated kinase is required for mitotic progression and regulates Plk1. Oncogene 27:4900–4908
Halet G, Carroll J (2007) Rac activity is polarized and regulates meiotic spindle stability and anchoring in mammalian oocytes. Dev Cell 12:309–317
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Kopinski PK, Ray R, Hoser G, Ngaba D, Flis S et al (2012) Rac2-MRC-cIII-generated ROS cause genomic instability in chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells and primitive progenitors. Blood 119:4253–4263
Patel KJ, Joenje H (2007) Fanconi anemia and DNA replication repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 6:885–890
Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, Tutt AN, Johnson DA, Richardson TB et al (2005) Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 434:917–921
Helleday T (2011) The underlying mechanism for the PARP and BRCA synthetic lethality: clearing up the misunderstandings. Mol Oncol 5:387–393
Sallmyr A, Fan J, Datta K, Kim KT, Grosu D, Shapiro P et al (2008) Internal tandem duplication of FLT3 (FLT3/ITD) induces increased ROS production, DNA damage, and misrepair: implications for poor prognosis in AML. Blood 111:3173–3182
Muller LU, Schore RJ, Zheng Y, Thomas EK, Kim MO, Cancelas JA et al (2008) Rac guanosine triphosphatases represent a potential target in AML. Leukemia 22:1803–1806
Thomas EK, Cancelas JA, Chae HD, Cox AD, Keller PJ, Perrotti D et al (2007) Rac guanosine triphosphatases represent integrating molecular therapeutic targets for BCR-ABL-induced myeloproliferative disease. Cancer Cell 12:467–478
Thomas EK, Cancelas JA, Zheng Y, Williams DA (2008) Rac GTPases as key regulators of p210-BCR-ABL-dependent leukemogenesis. Leukemia 22:898–904
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank C. Brachetti for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the José Carreras Leukämie Stiftung (SP 10/07) and the Deutsche Krebshilfe (109188).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinterleitner, C., Huelsenbeck, J., Henninger, C. et al. Rac1 signaling protects monocytic AML cells expressing the MLL-AF9 oncogene from caspase-mediated apoptotic death. Apoptosis 18, 963–979 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0842-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0842-6