Abstract
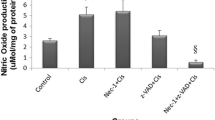
We previously reported that necrosis occurs predominantly in porcine renal tubular LLC-PK1 cells, when the cells were exposed transiently to a high concentration of cisplatin. Moreover, we demonstrated that generation of reactive oxygen species and subsequent production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) through phosphorylation of p38 MAPK are implicated in the pathogenesis of cisplatin-induced renal cell injury. However, some TUNEL-positive cells appeared in renal proximal tubules of rats after systemic injection of cisplatin, suggesting an involvement of apoptosis. In the present study, we found in LLC-PK1 cells that both apoptosis and necrosis were elicited when the cells were exposed to 200 μM cisplatin for 1 h followed by incubation for 24 h in the presence of 20 μM cisplatin. The cisplatin-induced necrosis was largely attenuated by the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine, while apoptosis was prevented by the specific inhibitors for caspases-2, -8, and -3 and a p53 inhibitor pifithrin-α but not by the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580. On the other hand, SB203580 attenuated the cisplatin-induced increase in TNF-α production. These findings suggest that p53-mediated activations of caspases-2, -8 and -3 play a key role in cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis, while oxidative stress-induced TNF-α synthesis via p38 MAPK phosphorylation contributed to the necrosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonard BJ, Eccleston E, Jones D, Todd P, Walpole A (1971) Antileukaemic and nephtotoxic properties of platinum compounds. Nature 234:43–45
Anand AJ, Bashey B (1993) Newer insights into cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother 27:1519–1525
Lieberthal W, Triaca V, Levine J (1996) Mechanisms of death induced by cisplatin in proximal tubular epithelial cells: apoptosis vs. necrosis. Am J Physiol 270:F700–F708
Lau AH (1999) Apoptosis induced by cisplatin nephrotoxic injury. Kidney Int 56:1295–1298
Cummings BS, Schnellmann RG (2002) Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: caspase 3-dependent and -independent pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:8–17
Park MS, De Leon M, Devarajan P (2002) Cisplatin induces apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells via activation of mitochondrial pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:858–865
Sueishi K, Mishima K, Makino K et al (2002) Protection by a radical scavenger edaravone against cisplatin-induced ephrotoxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 451:203–208
Shino Y, Itoh Y, Kubota T, Yano T, Sendo T, Oishi R (2003) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in cisplatin-induced injury in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 35:966–977
Mishima K, Baba A, Matsuo M, Itoh Y, Oishi R (2006) Protective effect of cyclic AMP against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1564–1577
Isobe I, Michikawa M, Yanagisawa K (1999) Enhancement of MTT, a tetrazolium salt, exocytosis by amyloid beta-protein and chloroquine in cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci Lett 266:129–132
Yano T, Itoh Y, Sendo T, Kubota T, Oishi R (2003) Cyclic AMP reverses radiocontrast media-induced apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells by activating A kinase/PI3 kinase. Kidney Int 64:2052–2063
Takahashi M, Shibatam M., Niki E (2001) Estimation of lipid peroxidation of live cells using a fluorescent probe, diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine. Free Radic Biol Med 31:164–174
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Akasaka K, Suzuki T, Ohrui H, Meguro H (1987) Study on aromatic phosphines for novel fluorometry of hydroperoxides (II)—the determination of lipid ydroperoxides with diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine. Anal Lett 20:797–807
Akasaka K, Ijichi S, Watanabe K, Ohrui H, Meguro H (1992) High performance liquid chromatography and postcolumn derivatization with diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine for fluorometric determination of triacylglycerol hydroperoxides. J Chromatogr 596:197–202
Ramesh G, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS, Reeves WB (2007) Endotoxin and cisplatin synergistically stimulate TNF-alpha production by renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F812–F819
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2002) TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 110:835–842
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2003) TNFR2-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F610–618
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2005) p38 MAP kinase inhibition ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F166–174
Gregoli PA, Bondurant MC (1999) Function of caspases in regulating apoptosis caused by erythropoietin deprivation in erythroid progenitors. J Cell Physiol 178:133–143
Wolf BB, Green DR (1999) Suicidal tendencies: apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J Biol Chem 274:20049–20052
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1997) Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell 91:443–446
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Seth R, Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV, Kaushal GP (2005) p53-dependent caspase-2 activation in mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor and its role in renal tubular epithelial cell injury. J Biol Chem 280:31230–31239
Yu J, Wang Z, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Zhang L (2003) PUMA mediates the apoptotic response to p53 in colorectal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1931–1936
Jiang M, Wei Q, Pabla N et al (2007) Effects of hydroxyl radical scavenging on cisplatin-induced p53 activation, tubular cell apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 73:1499–1510
Jiang M, Wei Q, Wang J et al (2006) Regulation of PUMA-alpha by p53 in cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis. Oncogene 25:4056–4066
Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Nardacci R et al (2005) Essential role of p53 phosphorylation by p38 MAPK in apoptosis induction by the HIV-1 envelope. J Exp Med 201:279–289
Sanchez-Prieto R, Rojas JM, Taya Y, Gutkind JS (2000) A role for the p38 mitogen-acitvated protein kinase pathway in the transcriptional activation of p53 on genotoxic stress by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res 60:2464–2472
Bulavin DV, Saito S, Hollander MC et al (1999) Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation. Embo J 18:6845–6854
Acknowledgement
This research was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C17590129) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sport and Culture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yano, T., Itoh, Y., Matsuo, M. et al. Involvement of both tumor necrosis factor-α-induced necrosis and p53-mediated caspase-dependent apoptosis in nephrotoxicity of cisplatin. Apoptosis 12, 1901–1909 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0110-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0110-8