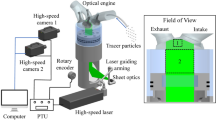
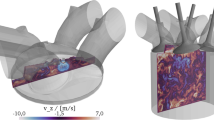
Abstract
Cycle-to-cycle variations (CCVs) limit the extension of the operating range by inducing load variations and even misfire and/or knock for direct injection spark ignition (DISI) engines and hence need to be controlled. One of the effective and flexible ways to reduce CCV is to employ a charge motion control valve. This study is aimed to analyze the flow characteristics and CCV using large eddy simulation (LES) and fast Fourier transform (FFT) in a non-reacting, DISI engine equipped with a tumble flap (i.e., a specific type of charge motion control valve) inside the intake port. The in-cylinder flow characteristics are analyzed in detail, and the possible effects of multi-scale structures of the fluid field on the subsequent ignition and combustion processes are also discussed. Computational results indicate that closing the tumble flap helps enhance the intensity of the coherent structures and increase the total integral length scale (ILS) while decreasing the Kolmogorov scale and stabilizing the flow field by suppressing the CCV of tumble ratio and tumble center. Furthermore, based on a newly developed FFT triple decomposition, each instantaneous flow field is decomposed into three subfields, termed ensemble mean part and low- and high-spatial frequency parts, respectively. It is found that switching the tumble flap position greatly affects the first two subfields, but it has negligible effect on the last part. With the closed tumble flap, the energy portion of the mean part increases, the rate of energy decay reduces, and the CCV of the low- and high-spatial frequency parts decreases.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heywood, J.B.: Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals. McGraw-Hill, New York (1988)
Young, M.B.: Cyclic dispersion in the homogeneous-charge spark-ignition engine—a literature survey. SAE Technical Paper 810020 (1981)
Ozdor, N., Dulger, M., Sher, E.: Cyclic variability in spark ignition engines a literature survey. SAE Technical Paper 940987 (1994)
Berkooz, G., Holmes, P., Lumley, J.L.: Low dimensional models of the wall region in a turbulent boundary layer: new results. Physica D 58(1), 402–406 (1992)
Wang, T.Y., Liu, D.M., Tan, B.Q., Wang, G.D., Peng, Z.J.: An investigation into in-cylinder tumble flow characteristics with variable valve lift in a gasoline engine. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 94(2), 285–304 (2015)
Liu, S.L., Li, Y.F., Lu, M.: Prediction of tumble speed in the cylinder of the 4-valve spark ignition engines. SAE Technical Paper 2000-01-0247 (2000)
Liou, T.M., Santavicca, D.A.: Cycle resolved LDV measurements in a motored IC engine. J. Fluid. Eng-t. Asme. 107(2), 232–240 (1985)
Fraser, R.A., Bracco, F.V.: Cycle-resolved LDV integral length scale measurements in an IC Engine. SAE Technical Paper 880381 (1988)
Fan, L., Reitz, R.D., Trigui, N.: Intake flow simulation and comparison with PTV measurements. SAE Technical Paper 1999-01-0176 (1999)
Heim, D., Ghandhi, J.: A detailed study of in-cylinder flow and turbulence using PIV. SAE Technical Paper 2011-01-1287 (2011)
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Leach, B., Ma, T., Ladommatos, N.: Characterization of an in-cylinder flow structure in a high-tumble SI engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 5(5), 375–400 (2004)
Baumann, M., Mare, F., Janicka, J.: On the validation of large eddy simulation applied to internal combustion engine flows. Part II: numerical analysis. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 92(1-2), 299–317 (2014)
Vermorel, O., Richard, S., Colin, O., Angelberger, C., Benkenida, A., Veynante, D.: Towards the understanding of cyclic variability in a spark ignited engine using multi-cycle LES. Combust. Flame. 156(8), 1525–1541 (2009)
Funk, C., Sick, V., Reuss, D.L., Dahm, W.: Turbulence properties of high and low swirl in-cylinder flows. SAE Technical Paper 2002-01-2841 (2002)
Akkerman, V., Ivanov, M., Bychkov, V.: Turbulent flow produced by piston motion in a spark-ignition engine. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 82(3), 317–337 (2009)
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Peng, Z., Ladommatos, N.: Particle image velocimetry measurement of in-cylinder flow in internal combustion engines-experiment and flow structure analysis. P. I. Mech. Eng. D-j. Aut 216(1), 65–81 (2002)
Jebamani, R.D., Kumar, T. M. N.: Studies on variable swirl intake system for DI diesel engine using computational fluid dynamics. Therm. Sci. 12(1), 25–32 (2008)
Dembinski, H., Ångström, H.: An experimental study of the influence of variable in-cylinder flow, caused by active valve train, on combustion and emissions in a diesel engine at low lambda operation. SAE Technical Paper 2011-01-1830 (2011)
Fischer, J., Velji, A., Spicher, U.: Investigation of cycle-to-cycle variations of in-cylinder processes in gasoline direct injection engines operating with variable tumble systems. SAE Technical Paper 2004-01-0044 (2004)
Adomeit, P., Jakob, M., Pischinger, S., Brunn, A., Ewald, J.: Effect of intake port design on the flow field stability of a gasoline DI engine. SAE Technical Paper 2011-01-1284 (2011)
Berntsson, A.W., Josefsson, G., Ekdahl, R., Ogink, R., Grandin, B.: The effect of tumble flow on efficiency for a direct injected turbocharged downsized gasoline engine. SAE Technical Paper 2011-24-0054 (2011)
Ramajo, D., Zanotti, A., Nigro, N.: In-cylinder flow control in a four-valve spark ignition engine: numerical and experimental steady rig tests. P. I. Mech. Eng. D-j. Aut 225(6), 813–828 (2011)
Vu, T.T., Guibert, P.: Proper orthogonal decomposition analysis for cycle-to-cycle variations of engine flow. Effect of a control device in an inlet pipe. Exp. Fluids. 52(6), 1519–1532 (2012)
Barlow, R.S.: Laser diagnostics and their interplay with computations to understand turbulent combustion. P. Combust. Inst. 31(1), 49–75 (2007)
Jiang, X., Siamas, G., Jagus, K., Karayiannis, T.: Physical modelling and advanced simulations of gas–liquid two-phase jet flows in atomization and sprays. Prog. Energ. Combust. 36(2), 131–167 (2010)
Jagus, K., Jiang, X.: Large eddy simulation of diesel fuel injection and mixing in a HSDI engine. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 87(2-3), 473–491 (2011)
Bottone, F., Kronenburg, A., Gosman, D., Marquis, A.: Large eddy simulation of diesel engine in-cylinder flow. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 88(1-2), 233–253 (2011)
Bottone, F., Kronenburg, A., Gosman, D., Marquis, A.: The numerical simulation of diesel spray combustion with LES-CMC. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 4, 651–673 (2012)
Enaux, B., Granet, V., Vermorel, O., Lacour, C., Thobois, L., Dugué, V., Poinsot, T.: Large eddy simulation of a motored single-cylinder piston engine: numerical strategies and validation. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 86(2), 153–177 (2010)
Reuss, D.L.: Cyclic variability of large-scale turbulent structures in directed and undirected IC engine flows. SAE Technical Paper 2000-01-0246 (2000)
Joo, S., Srinivasan, K., Lee, K., Bell, S.: The behaviourt of small-and large-scale variations of in-cylinder flow during intake and compression strokes in a motored four-valve spark ignition engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 5(4), 317–328 (2004)
Liu, D., Wang, T., Jia, M., Wang, G.: Cycle-to-cycle variation analysis of in-cylinder flow in a gasoline engine with variable valve lift. Exp. Fluids. 53(3), 585–602 (2012)
Lumley, J.L.: The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows. Atmospheric turbulence and radio wave propagation, pp. 166–178 (1967)
Liu, K., Haworth, D.C., Yang, X., Gopalakrishnan, V.: Large-eddy simulation of motored flow in a two-valve piston engine: POD analysis and cycle-to-cycle variations. Flow. Turbul. Combust. 91(2), 373–403 (2013)
Abraham, P., Liu, K., Haworth, D., Reuss, D., Sick, V.: Evaluating large-eddy simulation (LES) and high-speed particle image velocimetry (PIV) with phase-invariant proper orthogonal decomposition (POD). Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. (2013)
Chen, H., Reuss, D.L., Hung, D.L., Sick, V.: A practical guide for using proper orthogonal decomposition in engine research. Int. J. Engine Res. 14(4), 307–319 (2012)
Chen, H., Reuss, D.L., Sick, V.: On the use and interpretation of proper orthogonal decomposition of in-cylinder engine flows. Meas. Sci. Technol. 23(8), 085302 (2012)
Roudnitzky, S., Druault, P., Guibert, P.: Proper orthogonal decomposition of in-cylinder engine flow into mean component, coherent structures and random Gaussian fluctuations. J. Turbul. N70 (2006)
Wang, T., Li, W., Jia, M., Liu, D., Qin, W., Zhang, X.: Large-eddy simulation of in-cylinder flow in a DISI engine with charge motion control valve: proper orthogonal decomposition analysis and cyclic variation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 75, 561–574 ((2015) )
CONVERGE™: A three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics program for transient flows with complex geometries. Convergent Science Inc, Middleton (2009)
Speziale, C.: Analytical methods for the development of Reynolds-stress closures in turbulence. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 23(1), 107–157 (1991)
Werner, H., Wengle, H.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over and around a cube in a plate channel. In: Durst, F., Friedrich, R., Launder, B.E., Schmidt, F.W., Schumann, U. (eds.) Turbulent shear flows 8, pp 155–168. Springer, Heidelberg (1993)
Goryntsev, D., Sadiki, A., Klein, M., Janicka, J.: Large eddy simulation based analysis of the effects of cycle-to-cycle variations on air-fuel mixing in realistic DISI IC-engines. P. Combust. Inst. 32(2), 2759–2766 (2009)
Yang, X., Gupta, S., Kuo, T.-W., Gopalakrishnan, V.: RANS and large eddy simulation of internal combustion engine flows—a comparative study. J. Eng. Gas. Turb. Power 136(5), 051507 (2014)
Kuo, T.-W., Yang, X., Gopalakrishnan, V., Chen, Z.: Large eddy simulation (LES) for IC engine flows. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 69(1), 61–81 (2014)
Fansler, T., French, D.: Cycle-resolved laser-velocimetry measurements in a reentrant-bowl-in-piston engine. SAE Technical Paper 880377 (1988)
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Ladommatos, N.: Analysis of large-scale flow characteristics in a four-valve spark ignition engine. P. I. Mech. Eng. C-j. Mec 216(9), 923–938 (2002)
Reuss, D., Adrian, R., Landreth, C., French, D., Fansler, T.: Instantaneous planar measurements of velocity and large-scale vorticity and strain rate in an engine using particle-image velocimetry. SAE Technical Paper 890616 (1989)
Liu, K., Haworth, D.C.: Development and assessment of POD for analysis of turbulent flow in piston engines. SAE Technical Paper 2011-01-0830 (2011)
di Mare, F., Knappstein, R., Baumann, M.: Application of LES-quality criteria to internal combustion engine flows. Comput. Fluids. 89, 200–213 (2014)
Hunt, J.C.R., Wray, A.A., Moin, P.: Eddies, streams, and convergence zones in turbulent flows. Center for Turbulence Research 1, 193–208 (1988)
Pope, S.B.: Turbulent Flow. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Khalighi, B.: Study of the intake tumble motion by flow visualization and particle tracking velocimetry. Exp. Fluids. 10(4), 230–236 (1991)
Vollmers, H.: Detection of vortices and quantitative evaluation of their main parameters from experimental velocity data. Meas. Sci. Technol. 12(8), 1199–1207 (2001)
Rouland, E., Trinite, M.: Particle image velocimetry measurements in a high tumble engine for in-cylinder flow structure analysis. SAE technical paper 972831 (1997)
Acknowledgments
The financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 91441111 and 51476151) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Li, Y., Wang, T. et al. Investigation of the Effect of the In-Cylinder Tumble Motion on Cycle-to-Cycle Variations in a Direct Injection Spark Ignition (DISI) Engine Using Large Eddy Simulation (LES). Flow Turbulence Combust 98, 601–631 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-016-9773-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-016-9773-y