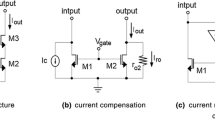
Abstract
This paper presents a high-voltage tolerant power driver for integrated power applications in standard low-cost CMOS processes. The design employs a complementary stacked-MOSFET structure to achieve reliable, n× scalable high-voltage switching. In addition, the power driver enhances the current drivability, thereby improving the switching speed of the power switches in modern power conversion systems. By exploiting the availability of the rated power supply, it uses fewer on-chip biasing capacitors and diodes, which considerably reduces silicon area and cost. A hardware prototype of the proposed power driver is fabricated using the TSMC 0.25-μm CMOS process. It is capable of switching at 7.5 V, using 2.5-V rated transistors. The design improves the rise and fall times by 26.0 and 21.1 % at 1 MHz while driving a load of 70 pF, when compared to the prior art. In addition, the proposed design achieves 16.8 % silicon area savings due to the reduction of on-chip biasing capacitors and diodes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandyopadhyay, S., Ramadass, Y. K., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2011). 20 μA to 100 mA DC–DC converter with 2.8–4.2 V battery supply for portable applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 12(46), 2807–2820.
Chung, J. W., Lee, J.-K., Piner, E. L., & Palacios, T. (2009). Seamless on-wafer integration of Si(100) MOSFETs and GaN HEMTs. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 10(30), 1015–1017.
Rahman, A., Agostinelli, M., Bai, P., et al. (2011). Reliability studies of a 32 nm System-on-Chip (SoC) platform technology with 2nd generation high-k/metal gate transistors. In IEEE international symposium on reliability physics (pp. 3.1–3.6).
Li, Y. M., Wen, C.-B., Yuan, B., Wen, L.-M., & Ye, Q. (2010). A high speed and power-efficient level shifter for high voltage buck converter drivers. In IEEE International conference on solid-state and integrated circuit technology (pp. 309–311).
Lee, T. J., Chang, T.-Y., & Wang, C.-C. (2009). Wide-range 5.0/3.3/1.8-V I/O buffer using 0.35-μm 3.3-V CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions Circuits Systems I: Regular Papers, 4(56), 763–772.
Hess, H., & Baker, R. J. (2000). Transformerless capacitive coupling of gate signals for series operation of power MOS devices. IEEE Transaction on Power Electronics, 5(15), 923–930.
Mentze, E. J., Hess, H. L., Buck, K. M., & Windley, T. G. (2006). A scalable high-voltage output driver for low-voltage CMOS technologies. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 12(14), 1347–1353.
Serneels, B., Geukens, E., De Muer, B., & Piessens, T. (2012). A 1.5 W 10 V-output class-D amplifier using a boosted supply from a single 3.3 V input in standard 1.8 V/3.3 V 0.18 μm CMOS. In IEEE ISSCC digest of technology papers (pp. 94–96).
Geng, Y., & Ma, D. (2013). Design of reliable 2 × V DD and 3 × V DD series-parallel charge pumps in nanoscale CMOS. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 705–708).
Annema, A.-J., Geelen, G. J. G. M., & de Jong, P. C. (2001). 5.5-V I/O in a 2.5-V 0.25-μm CMOS technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(3), 528–538.
Ker, M.-D., & Chen, S.-L. (2006). Design of mixed-voltage I/O buffer by using NMOS-blocking technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 10(41), 2324–2333.
Wu, C. C., Leung, Y. K., Chang, C. S., et al. (2002). A 90-nm CMOS device technology with high-speed, general-purpose, and low-leakage transistors for system on chip applications. In International electron devices meeting (pp. 65–68).
Chang, C. S., Chao, C. P., Leung, Y. K., et al. (2002). Extended 0.13 μm CMOS technology for the ultra high-speed and MS/RF application segments. In symposium on VLSI technology (pp. 68–69).
Wang, Y., & Ma, D. (2012). A 450-mV single-fuel-cell power management unit with switch-mode quasi-V2 hysteretic control and automatic startup on 0.35-μm standard CMOS process. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 9(47), 2216–2226.
Tan, S. C., & Sun, X. W. (2002). Low power CMOS level shifters by bootstrapping technique. Electronics Letters, 16(38), 876–878.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, Y., Bondade, R. & Ma, D. High-voltage tolerant power driver with enhanced current drivability for integrated power applications. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 79, 469–477 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0288-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0288-y