Abstract
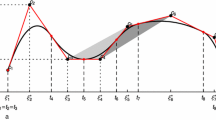
In the common nonparametric regression model we consider the problem of constructing optimal designs, if the unknown curve is estimated by a smoothing spline. A special basis for the space of natural splines is introduced and the local minimax property for these splines is used to derive two optimality criteria for the construction of optimal designs. The first criterion determines the design for a most precise estimation of the coefficients in the spline representation and corresponds to D-optimality, while the second criterion is the G-optimality criterion and corresponds to an accurate prediction of the curve. Several properties of the optimal designs are derived. In general, D- and G-optimal designs are not equivalent. Optimal designs are determined numerically and compared with the uniform design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler N.A. (2001) Properties of optimal polynomial designs under smoothing spline models. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 92: 259–266
De Boor, C. (1978). A practical guide to splines. In Applied mathematical sciences (Vol. 27, XXIV). New York: Springer-Verlag.
Dette H., Melas V.B., Pepelyshev A.N. (2008) Optimal designs for free knot least squares splines. Statistica Sinica 18: 1047–1062
Dierckx, P. (1995). Curve and surface fitting with splines. In Monographs on numerical analysis. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Efromovich S. (1999) Nonparametric curve estimation: Methods, theory and applications. Springer, New York
Eubank, R. L. (1999). Nonparametric regression and spline smoothing (2nd ed.). In Statistics: Textbooks and monographs (Vol. 157). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Fan J., Gijbels I. (1996) Local polynomial modelling and its applications. Chapman and Hall, London
Gantmacher F.R. (1998) The theory of matrices. Providence, Chelsea
Green P., Silverman B. (1994) Nonparametric regression and generalized linear models. Chapman and Hall, London
Heiligers B. (1998) E-optimal designs for polynomial spline regression. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 75: 159–172
Heiligers B. (1999) Experimental design for polynomial spline regression. Tatra Mountains Mathematical Publications 17: 157–165
Jupp D.L.B. (1978) Approximation to data by splines with free knots. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 15: 328–343
Kaishev V.K. (1989) Optimal experimental designs for the B-spline regression. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis 8: 39–47
Karlin S., Studden W.J. (1966) Tchebycheff systems: With applications in analysis and statistics. Wiley, New York
Kiefer J. (1974) General equivalence theory for optimum designs (approximate theory). Annals of statistics 2: 849–879
Kiefer J., Wolfowitz J. (1960) The equivalence of two extremum problems. Canadian Journal of Mathematics 12: 363–366
Kuks J., Olman W. (1971) Minimaxnaja linejnaja ozenka coefficientov regressii II. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk Ehstonskoj SSR 21: 66–72
Mao W., Zhao L.H. (2003) Free-knot polynomial splines with confidence intervals. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B 65(4): 901–919
Murty V.N. (1971a) Optimal designs with a Tchebycheffian spline regression function. Annals of Mathematical Statistics 42: 643–649
Murty V.N. (1971b) Optimal designs with a polynomial spline regression with a single multiple knot at the center. Annals of Mathematical Statistics 42: 952–960
Park S.H. (1978) Experimental designs for fitting segmented polynomial regression models. Technometrics 20: 151–154
Pukelsheim F. (1993) Optimal design of experiments. Wiley, New York
Reinsch C. (1967) Smoothing by spline functions. Numerische Mathematik 10: 177–183
Schoenberg I.J. (1964) Spline functions and the problem of graduation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 52: 947–950
Silverman B.W. (1985) Some aspects of the spline smoothing approach to non-parametric regression curve fitting. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B 47: 1–52
Silvey S.D. (1980) Optimal design. Chapman and Hall, London
Studden, W. J. (1971). Optimal designs and spline regression. Optimizing methods in statistics. In Proceedings of the Symposium, Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio (pp. 63–76). New York: Academic Press.
Studden W.J., VanArman D.J. (1969) Admissible designs for polynomial spline regression. Annals of Mathematical Statistics 40: 1557–1569
Toutenburg H. (1982) Prior information in linear models. Wiley, New York
Wahba, G. (1990). Spline models for observational data. In CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics (Vol. 59). Philadelphia: SIAM.
Whittaker E.T. (1923) On a new method of graduation. Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society 41: 63–75
Woods D.C. (2005) Designing experiments under random contamination with application to polynomial spline regression. Statistica Sinica 15: 619–635
Woods D., Lewis S. (2006) All-bias designs for polynomial spline regression models. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Statistics 48: 49–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Dette, H., Melas, V.B. & Pepelyshev, A. Optimal design for smoothing splines. Ann Inst Stat Math 63, 981–1003 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-009-0265-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-009-0265-x