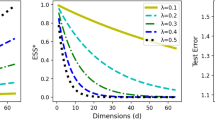
Abstract
A situation where training and test samples follow different input distributions is called covariate shift. Under covariate shift, standard learning methods such as maximum likelihood estimation are no longer consistent—weighted variants according to the ratio of test and training input densities are consistent. Therefore, accurately estimating the density ratio, called the importance, is one of the key issues in covariate shift adaptation. A naive approach to this task is to first estimate training and test input densities separately and then estimate the importance by taking the ratio of the estimated densities. However, this naive approach tends to perform poorly since density estimation is a hard task particularly in high dimensional cases. In this paper, we propose a direct importance estimation method that does not involve density estimation. Our method is equipped with a natural cross validation procedure and hence tuning parameters such as the kernel width can be objectively optimized. Furthermore, we give rigorous mathematical proofs for the convergence of the proposed algorithm. Simulations illustrate the usefulness of our approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldi P., Brunak S. (1998) Bioinformatics: The machine learning approach. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bartlett P., Bousquet O., Mendelson S. (2005) Local Rademacher complexities. Annals of Statistics 33: 1487–1537
Bickel S., Scheffer T. (2007) Dirichlet-enhanced spam filtering based on biased samples. In: Schölkopf B., Platt J., Hoffman T.(eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, Vol. 19. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bickel, S., Brückner, M., Scheffer, T. (2007). Discriminative learning for differing training and test distributions. In Proceedings of the 24th international conference on machine learning.
Borgwardt K.M., Gretton A., Rasch M.J., Kriegel H.-P., Schölkopf B., Smola A.J. (2006) Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14): e49–e57
Bousquet O. (2002) A Bennett concentration inequality and its application to suprema of empirical process. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Série I. Mathématique, 334: 495–500
Boyd S., Vandenberghe L. (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fukumizu, K., Kuriki, T., Takeuchi, K., Akahira, M. (2004). Statistics of singular models. The Frontier of Statistical Science 7. Iwanami Syoten. in Japanese.
Ghosal S., van der Vaart A.W. (2001) Entropies and rates of convergence for maximum likelihood and Bayes estimation for mixtures of normal densities. Annals of Statistics 29: 1233–1263
Hachiya, H., Akiyama, T., Sugiyama, M., Peters, J. (2008). Adaptive importance sampling with automatic model selection in value function approximation. In Proceedings of the twenty-third AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI-08), Chicago, USA.
Hall P. (1987) On Kullback-Leibler loss and density estimation. The Annals of Statistics 15(4): 1491–1519
Härdle W., Müller M., Sperlich S., Werwatz A. (2004) Nonparametric and Semiparametric Models. Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, Berlin
Heckman J.J. (1979) Sample selection bias as a specification error. Econometrica 47(1): 153–162
Huang J., Smola A., Gretton A., Borgwardt K.M., Schölkopf B. (2007) Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data. In: Schölkopf B., Platt J., Hoffman T.(eds) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 19. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 601–608
Koltchinskii V. (2006) Local Rademacher complexities and oracle inequalities in risk minimization. Annals of Statistics 34: 2593–2656
Lin, C.-J., Weng, R. C., Keerthi, S. S. (2007). Trust region Newton method for large-scale logistic regression. Technical report, Department of Computer Science, National Taiwan University.
Mendelson S. (2002) Improving the sample complexity using global data. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 48: 1977–1991
Minka, T. P. (2007). A comparison of numerical optimizers for logistic regression. Technical report, Microsoft Research.
Nguyen, X., Wainwright, M. J., Jordan, M. I. (2007). Estimating divergence functions and the likelihood ratio by penalized convex risk minimization. In Advances in neural information processing systems, Vol. 20.
Rasmussen, C. E., Neal, R. M., Hinton, G. E., van Camp, D., Revow, M., Ghahramani, Z., Kustra, R., Tibshirani, R. (1996). The DELVE manual.
Rätsch G., Onoda T., Müller K.-R. (2001) Soft margins for adaboost. Machine Learning 42(3): 287–320
Schuster E., Gregory C. (1982) On the non-consistency of maximum likelihood nonparametric density estimators. In: Eddy W.F.(eds) In Computer science and statistics: proceedings of the 13th symposium on the interface, New York, NY, USA: Springer pp 295–298
Self S.G., Liang K.Y. (1987) Asymptotic properties of maximum likelihood estimators and likelihood ratio tests under nonstandard conditions. Journal of the American Statistical Association 82: 605–610
Shelton, C. R. (2001). Importance sampling for reinforcement learning with multiple objectives. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Shimodaira H. (2000) Improving predictive inference under covariate shift by weighting the log-likelihood function. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 90(2): 227–244
Steinwart I. (2001) On the influence of the kernel on the consistency of support vector machines. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2: 67–93
Sugiyama M., Müller K.-R. (2005) Input-dependent estimation of generalization error under covariate shift. Statistics and Decisions 23(4): 249–279
Sugiyama M., Kawanabe M., Müller K.-R. (2004) Trading variance reduction with unbiasedness: The regularized subspace information criterion for robust model selection in kernel regression. Neural Computation 16(5): 1077–1104
Sugiyama M., Krauledat M., Müller K.-R. (2007) Covariate shift adaptation by importance weighted cross validation. Journal of Machine Learning Research 8: 985–1005
Sugiyama, M., Nakajima, S., Kashima, H., von Bünau, P., Kawanabe, M. (2008). Direct importance estimation with model selection and its application to covariate shift adaptation. In Advances in neural information processing systems, Vol. 20. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Sutton R.S., Barto G.A. (1998) Reinforcement learning: An introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge
Talagrand M. (1994) Sharper bounds for Gaussian and empirical processes. Annals of Probability 22: 28–76
Talagrand M. (1996a) New concentration inequalities in product spaces. Inventiones Mathematicae 126: 505–563
Talagrand M. (1996b) A new look at independence. Annals of Statistics 24: 1–34
Tsuboi Y., Kashima H., Hido S., Bickel S., Sugiyama M. (2008) Direct density ratio estimation for large-scale covariate shift adaptation. In: In:Zaki M.J., Wang K., Apte C., Park H.(eds) Proceedings of the eighth SIAM international conference on data mining (SDM2008). Atlanta, Georgia, USA, pp 443–454
van de Geer S. (2000) Empirical processes in M-Estimation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
van der Vaart A.W., Wellner J.A. (1996) Weak convergence and empirical processes. With applications to statistics. Springer, New York
Wolpaw J.R., Birbaumer N., McFarland D.J., Pfurtscheller G., Vaughan T.M. (2002) Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clinical Neurophysiology 113(6): 767–791
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, M., Suzuki, T., Nakajima, S. et al. Direct importance estimation for covariate shift adaptation. Ann Inst Stat Math 60, 699–746 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-008-0197-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-008-0197-x