Abstract
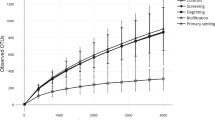
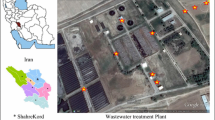
The emission of the airborne bacteria and fungi from an indoor wastewater treatment station adopting an integrated oxidation ditch with a vertical circle was investigated. Microbial samples were collected by the six-stage viable Andersen cascade impactor, and the samples were collected in triplicate in each sampling site per season. Culture-based method was applied to determine the concentrations of the airborne bacteria and fungi, while the cloning/sequencing method was used to characterize the genetic structure and community diversity of airborne bacteria. The highest concentrations of airborne bacteria (4155 ± 550 CFU/m3) and fungi (883 ± 150 CFU/m3) were obtained in June (summer). The lowest concentration of bacteria (1458 ± 434 CFU/m3) was determined in January (winter), and the lowest concentration of fungi (169 ± 40 CFU/m3) was found in March (spring), respectively. The particle size distribution analysis showed that most culturable bacteria obtained in all the sampling sites were in the particle size range of 1.1–4.7 µm. Most culturable fungi had particle sizes in the range 1.1–3.3 µm. Microbial population analysis showed that Bacillus sp., Acinetobacter sp., and Lysinibacillus were the main groups obtained in S1. Enterobacter was the dominant group in sampling site S2. Both the concentrations and particle size distribution of the bioaerosols in the enclosed space presented a seasonal and site-related variation. Concentration and richness of microorganisms in bioaerosols in June were higher than in September and January. The particle size distribution varied between the sampling sites, and proportion of large particles was higher in S2 than in S1 because of the settlement of large particles. Pathogenic species, such as Acinetobacter lwoffii, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, and Enterobacter sp., were isolated from the bioaerosols, which could pose serious latent danger to sewage workers’ health.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, A. A. (1958). New sampler for the collection, sizing, and enumeration of viable airborne particles. Journal of Bacteriology, 76(5), 471–484.
Bauer, H., Fuerhacker, M., Zibuschka, F., Schmid, H., & Puxbaum, H. (2002). Bacteria and fungi in aerosols generated by two different types of wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 36(16), 3965–3970.
Brandi, G., Sisti, M., & Amagliani, G. (2000). Evaluation of the environmental impact of microbial aerosols generated by wastewater treatment plants utilizing different aeration systems. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 88(5), 845–852.
Brodka, K., Kozajda, A., Buczynska, A., & Szadkowska-Stanczyk, I. (2012). The variability of bacterial aerosol in poultry houses depending on selected factors. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 25(3), 281–293.
Conrad, M. L., Ferstl, R., Teich, R., Brand, S., Blumer, N., Yildirim, A. O., et al. (2009). Maternal TLR signaling is required for prenatal asthma protection by the nonpathogenic microbe Acinetobacter lwoffii F78. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 206(13), 2869–2877.
De Luca, G., Zanetti, F., Perari, A. C., & Stampi, S. (2001). Airborne coagulase negative staphylococci produced by a sewage treatment plant. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 204(4), 231–238.
Ding, Y., Wu, W. X., Han, Z. Y., & Chen, Y. X. (2008). Correlation of reactor performance and bacterial community composition during the removal of trimethylamine in three-stage biofilters. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 38(2), 248–258.
Douwes, J., Thorne, P., Pearce, N., & Heederik, D. (2003). Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment: Progress and prospects. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 47(3), 187–200.
Fahlgren, C., Bratbak, G., Sandaa, R. A., Thyrhaug, R., & Zweifel, U. L. (2011). Diversity of airborne bacteria in samples collected using different devices for aerosol collection. Aerobiologia, 27(2), 107–120.
Filipkowska, Z. (2003). Sanitary and bacteriological aspects of sewage treatment. Acta Microbiologica Polonica, 52, 57–66.
Filipkowska, Z., Janczukowicz, W., Krzemieniewski, M., & Pesta, J. (2000). Microbiological air pollution in the surroundings of the wastewater treatment plant with activated-sludge tanks aerated by horizontal rotors. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 9(4), 273–280.
Fracchia, L., Pietronave, S., Rinaldia, M., & Martinotti, M. G. (2006). Site-related airborne biological hazard and seasonal variations in two wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 40(10), 1985–1994.
Gangamma, S., Patil, R. S., & Mukherji, S. (2011). Characterization and proinflammatory response of airborne biological particles from wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(8), 3282–3287.
GB/T18883-2002. (2002). Standards for indoor air quality. Beijing: Standards press of China.
Go, J., Lee, K. M., Park, Y., & Yoon, S. S. (2014). Extended longevity and robust early-stage development of Caenorhabditis elegans by a soil microbe, Lysinibacillus sphaericus. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 6(6), 730–737.
Good, I. J. (1953). The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika, 40, 237–264.
Guo, X. S., Wu, P. P., Ding, W. J., Zhang, W. Y., & Li, L. (2014). Reduction and characterization of bioaerosols in a wastewater treatment station via ventilation. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 26(8), 1575–1583.
Haas, D., Unteregger, M., Habib, J., Galler, H., Marth, E., & Reinthaler, F. F. (2010). Exposure to bioaerosol from sewage systems. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 207(1–4), 49–56.
Han, Y. P., Li, L., Liu, J. X., & Zhang, M. Z. (2012). Microbial structure and chemical components of aerosols caused by rotating brushes in a wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(9), 4097–4108.
Handley, B. A., & Webster, A. J. F. (1995). Some factors affecting the airborne survival of bacteria outdoors. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 79(4), 368–378.
Heinonen-Tanski, H., Reponen, T., & Koivunen, J. (2009). Airborne enteric coliphages and bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Research, 43(9), 2558–2566.
Horner, W. E., Helbling, A., Salvaggio, J. E., & Lehrer, S. B. (1995). Fungal allergens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 8(2), 161–179.
Huang, C. Y., Lee, C. C., Li, F. C., Ma, Y. P., & Su, H. J. J. (2002). The seasonal distribution of bioaerosols in municipal landfill sites: A 3-yr study. Atmospheric Environment, 36(27), 4385–4395.
Jones, A. M., & Harrison, R. M. (2004). The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 326(1–3), 151–180.
Kay, D., Crowther, J., Stapleton, C. M., Wyer, M. D., Fewtrell, L., Edwards, A., et al. (2008). Faecal indicator organism concentrations in sewage and treated effluents. Water Research, 42(1–2), 442–454.
Korzeniewska, E., Filipkowska, Z., Gotkowska-Plachta, A., Janczukowicz, W., Dixon, B., & Czulowska, M. (2009). Determination of emitted airborne microorganisms from a BIO-PAK wastewater treatment plant. Water Research, 43(11), 2841–2851.
Korzeniewska, E., & Harnisz, M. (2012). Culture-dependent and culture-independent methods in evaluation of emission of enterobacteriaceae from sewage to the air and surface water. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 223(7), 4039–4046.
Kuroda, M., Yamashita, A., Hirakawa, H., Kumano, M., Morikawa, K., Higashide, M., et al. (2005). Whole genome sequence of Staphylococcus saprophyticus reveals the pathogenesis of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(37), 13272–13277.
Li, L., Gao, M., & Liu, J. X. (2011). Distribution characterization of microbial aerosols emitted from a wastewater treatment plant using the Orbal oxidation ditch process. Process Biochemistry, 46(4), 910–915.
Li, L., Han, Y. P., & Liu, J. X. (2013). Assessing genetic structure, diversity of bacterial aerosol from aeration system in an oxidation ditch wastewater treatment plant by culture methods and bio-molecular tools. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 603–613.
Liu, J. W., & Ma, W. L. (2010). Characteristics of microbial aerosol pollution in pig house. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2, 41–44.
Macher, J. M. (1989). Positive-hole correction of multiple-jet impactors for collecting viable microorganisms. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 50(11), 561–568.
Malakootian, M., Radhakrishna, N., Mazandarany, M. P., & Hossaini, H. (2013). Bacterial-aerosol emission from wastewater treatment plant. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(22–24), 4478–4488.
Maron, P. A., Lejon, D. P. H., Carvalho, E., Bizet, K., Lemanceau, P., Ranjard, L., & Mougel, C. (2005). Assessing genetic structure and diversity of airborne bacterial communities by DNA fingerprinting and 16S rDNA clone library. Atmospheric Environment, 39(20), 3687–3695.
Marthi, B., Fieland, V. P., Walter, M., & Seidler, R. J. (1990). Survival of bacteria during aerosolization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56(11), 3463–3467.
O’Gorman, C. M., & Fuller, H. T. (2008). Prevalence of culturable airborne spores of selected allergenic and pathogenic fungi in outdoor air. Atmospheric Environment, 42(18), 4355–4368.
Peccia, J., Werth, H. M., Miller, S., & Hernandez, M. (2001). Effects of relative humidity on the ultraviolet induced inactivation of airborne bacteria. Aerosol Science and Technology, 35(3), 728–740.
Pillai, S. D., & Ricke, S. C. (2002). Bioaerosols from municipal and animal wastes: Background and contemporary issues. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 48(8), 681–696.
Polymenakou, P. N., Mandalakis, M., Stephanou, E. G., & Tselepides, A. (2008). Particle size distribution of airborne microorganisms and pathogens during an intense African dust event in the eastern Mediterranean. Environmental Health Perspectives, 116(3), 292–296.
Remoroza, C., Wagenknecht, M., Buchholt, H. C., Moerschbacher, B. M., Gruppen, H., & Schols, H. A. (2015). Mode of action of Bacillus licheniformis pectin methylesterase on highly methylesterified and acetylated pectins. Carbohydrate Polymers, 115, 540–550.
Sanchez-Monedero, M. A., Aguilar, M. I., Fenoll, R., & Roig, A. (2008). Effect of the aeration system on the levels of airborne microorganisms generated at wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 42(14), 3739–3744.
Shokrollahzadeh, S., Azizmohseni, F., Golmohammad, F., Shokouhi, H., & Khademhaghighat, F. (2008). Biodegradation potential and bacterial diversity of a petrochemical wastewater treatment plant in Iran. Bioresource technology, 99(14), 6127–6133.
Tsai, M. Y., & Liu, H. M. (2009). Exposure to culturable airborne bioaerosols during noodle manufacturing in central Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 407(5), 1536–1546.
Wan, S. G., Li, G. Y., An, T. C., Guo, B., Sun, L., Zu, L., & Ren, A. L. (2010). Biodegradation of ethanethiol in aqueous medium by a new Lysinibacillus sphaericus strain RG-1 isolated from activated sludge. Biodegradation, 21(6), 1057–1066.
Xia, S. B., & Liu, J. X. (2004). An innovative integrated oxidation ditch with vertical circle for domestic wastewater treatment. Process Biochemistry, 39(9), 1111–1117.
Zulkifly, A. H., Roslan, D. D., Hamid, A. A. A., Hamdan, S., & Huyop, F. (2010). Biodegradation of low concentration of monochloroacetic acid-degrading Bacillus sp. TW1 isolated from terengganu water treatment and distribution plant. Journal of Applied Sciences, 10(22), 2940–2944.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere acknowledgements to Dr. John for the English revision of the manuscript. The work was financially supported by the Young Scientists Fund of Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. RCEES-QN-20130006F), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51478456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, W., Li, L., Han, Y. et al. Site-related and seasonal variation of bioaerosol emission in an indoor wastewater treatment station: level, characteristics of particle size, and microbial structure. Aerobiologia 32, 211–224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-015-9391-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-015-9391-5