Abstract
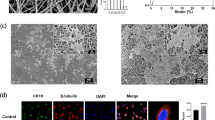
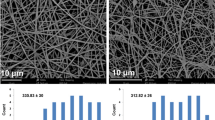
Nanomaterials with stem cells have evolved as a promising therapeutic strategy to regenerate various tissues. Tissue engineered grafts with bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) can offer a cell-based therapeutic strategy for deep wounds like burns and traumatic ulcers. In this study, we have fabricated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) nanofibers through electrospinning. The adhesion, proliferation and epidermal differentiation of BM-MSCs on PHBV nanofibers were investigated. Epidermal differentiation media containing epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin, 3,3′,5-triiodo-l-thyronine (T3), Hydrocortisone and 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin (D3) were used to trigger differentiation of BM-MSCs on PHBV. The proliferation of BM-MSCs on PHBV was significantly higher than the tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) control (p < 0.05). Live/dead staining of BM-MSCs on PHBV nanofibers confirmed the change in morphology of BM-MSCs from spindle to polygonal shape indicating their differentiation into keratinocytes. The expression levels of the genes keratin (early), filaggrin (intermediate) and involucrin (late) that are involved in epidermal differentiation were upregulated in a stage-specific manner. Our results demonstrate the potential of PHBV nanofibers in promoting adhesion and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. This novel cellular nanofiber construct can be a better alternative to the existing therapies for skin tissue engineering.
Graphical Abstract
(1) PHBV nanofibrous scaffold promotes adhesion of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. (2) Nano geometry of the scaffold favors the epidermal differentiation of stem cells. (3) This novel scaffold-stem cells construct could be used as dermal substitute.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertrand-Vallery, V., E. Boilan, N. Ninane, C. Demazy, B. Friguet, O. Toussaint, Y. Poumay, and F. Debacq-Chainiaux. Repeated exposures to UVB induce differentiation rather than senescence of human keratinocytes lacking p16INK-4A. Biogerontology 11:167–181, 2010.
Biazar, E., and S. H. Keshel. Chitosan-cross-linked nanofibrous PHBV nerve guide for rat sciatic nerve regeneration across a defect bridge. ASAIO J. 59:651–659, 2013.
Cai, Y. Z., L. L. Wang, H. X. Cai, Y. Y. Qi, X. H. Zou, and H. W. Ouyang. Electrospun nanofibrous matrix improves the regeneration of dense cortical bone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 95:49–57, 2010.
Candi, E., R. Schmidt, and G. Melino. The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:328–340, 2005.
Dornseifer, U., D. Lonic, T. I. Gerstung, F. Herter, A. M. Fichter, C. Holm, T. Schuster, and M. Ninkovic. The ideal split-thickness skin graft donor-site dressing: a clinical comparative trial of a modified polyurethane dressing and aquacel. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 128:918–924, 2011.
Hu, Y. J., X. Wei, W. Zhao, Y. S. Liu, and G. Q. Chen. Biocompatibility of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 5:1115–1125, 2009.
Jensen, J.-M., R. Fölster-Holst, A. Baranowsky, M. Schunck, S. Winoto-Morbach, C. Neumann, S. Schütze, and E. Proksch. Impaired sphingomyelinase activity and epidermal differentiation in atopic dermatitis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 122:1423–1431, 2004.
Jin, G., M. P. Prabhakaran, and S. Ramakrishna. Stem cell differentiation to epidermal lineages on electrospun nanofibrous substrates for skin tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 7:3113–3122, 2011.
Kazemnejad, S., A. Allameh, M. Soleimani, A. Gharehbaghian, Y. Mohammadi, N. Amirizadeh, S. Kaviani, M. Jazayeri, and M. Amani. Development of a novel three-dimensional biocompatible nanofibrous scaffold for the expansion and hepatogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Iran J. Biotechnol. 5:201–211, 2007.
Krause, D. S., N. D. Theise, M. I. Collector, O. Henegariu, S. Hwang, R. Gardner, S. Neutzel, and S. J. Sharkis. Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone marrow-derived stem cell. Cell 105:369–377, 2001.
Kuppan, P., S. Sethuraman, and U. M. Krishnan. PCL and PCL-gelatin nanofibers as esophageal tissue scaffolds: optimization, characterization and cell–matrix interactions. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9:1540–1555, 2013.
Kuppan, P., K. S. Vasanthan, D. Sundaramurthi, U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Development of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibers for skin tissue engineering: effects of topography, mechanical, and chemical stimuli. Biomacromolecules 12:3156–3165, 2011.
Lakshmanan, R., U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Living cardiac patch: the elixir for cardiac regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 12:1623–1640, 2012.
Li, W. J., R. Tuli, X. Huang, P. Laquerriere, and R. S. Tuan. Multilineage differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold. Biomaterials 26:5158–5166, 2005.
Lü, L. X., Y. Y. Wang, X. Mao, Z. D. Xiao, and N. P. Huang. The effects of PHBV electrospun fibers with different diameters and orientations on growth behavior of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Mater. 7:015002, 2012.
Ma, K., F. Laco, S. Ramakrishna, S. Liao, and C. K. Chan. Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into multi-layered epidermis-like cells in 3D organotypic coculture. Biomaterials 30:3251–3258, 2009.
Ma, K., S. Liao, L. He, J. Lu, S. Ramakrishna, and C. K. Chan. Effects of nanofiber/stem cell composite on wound healing in acute full-thickness skin wounds. Tissue Eng. A 17:1413–1424, 2011.
MacNeil, S. Progress and opportunities for tissue-engineered skin. Nature 445:874–880, 2007.
Metcalfe, A. D., and M. W. Ferguson. Tissue engineering of replacement skin: the crossroads of biomaterials, wound healing, embryonic development, stem cells and regeneration. J. R. Soc. Interface 4:413–437, 2007.
Micallef, L., F. Belaubre, A. Pinon, C. Jayat-Vignoles, C. Delage, M. Charveron, and A. Simon. Effects of extracellular calcium on the growth-differentiation switch in immortalized keratinocyte HaCaT cells compared with normal human keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 18:143–151, 2009.
Pascu, E. I., J. Stokes, and G. B. McGuinness. Electrospun composites of PHBV, silk fibroin and nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33:4905–4916, 2013.
Păunescu, V., E. Deak, D. Herman, I. R. Siska, C. Bunu, S. Anghel, C. A. Tatu, T. I. Oprea, R. Henschler, and B. Rüster. In vitro differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to epithelial lineage. J. Cell Mol. Med. 11:502–508, 2007.
Prelle, K., N. Zink, and E. Wolf. Pluripotent stem cells–model of embryonic development, tool for gene targeting, and basis of cell therapy. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 31:169–186, 2002.
Ravichandran, R., S. Gandhi, D. Sundaramurthi, S. Sethuraman, and U. M. Krishnan. Hierarchical mesoporous silica nanofibers as multifunctional scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 24:1988–2005, 2013.
Ravichandran, R., D. Sundaramurthi, S. Gandhi, S. Sethuraman, and U. M. Krishnan. Bioinspired hybrid mesoporous silica–gelatin sandwich construct for bone tissue engineering. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 187:53–62, 2014.
Rochefort, G. Y., B. Delorme, A. Lopez, O. Herault, P. Bonnet, P. Charbord, V. Eder, and J. Domenech. Multipotential mesenchymal stem cells are mobilized into peripheral blood by hypoxia. Stem Cells 24:2202–2208, 2006.
Sasaki, M., R. Abe, Y. Fujita, S. Ando, D. Inokuma, and H. Shimizu. Mesenchymal stem cells are recruited into wounded skin and contribute to wound repair by transdifferentiation into multiple skin cell type. J. Immunol. 180:2581–2587, 2008.
Sethuraman, S., L. S. Nair, S. El-Amin, M. T. N. Nguyen, Y. E. Greish, J. D. Bender, P. W. Brown, H. R. Allcock, and C. T. Laurencin. Novel low temperature setting nanocrystalline calcium phosphate cements for bone repair: osteoblast cellular response and gene expression studies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 82:884–891, 2007.
Sethuraman, S., L. S. Nair, S. El-Amin, M.-T. Nguyen, A. Singh, Y. E. Greish, H. R. Allcock, P. W. Brown, and C. T. Laurencin. Development and characterization of biodegradable nanocomposite injectables for orthopaedic applications based on polyphosphazenes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 22:733–752, 2011.
Sethuraman, S., L. S. Nair, S. El-Amin, M.-T. Nguyen, A. Singh, N. Krogman, Y. E. Greish, H. R. Allcock, P. W. Brown, and C. T. Laurencin. Mechanical properties and osteocompatibility of novel biodegradable alanine based polyphosphazenes: side group effects. Acta Biomater. 6:1931–1937, 2010.
Smith Callahan, L. A., S. Xie, I. A. Barker, J. Zheng, D. H. Reneker, A. P. Dove, and M. L. Becker. Directed differentiation and neurite extension of mouse embryonic stem cell on aligned poly (lactide) nanofibers functionalized with YIGSR peptide. Biomaterials 34:9089–9095, 2013.
Steinert, P. M., and L. N. Marekov. Direct evidence that involucrin is a major early isopeptide cross-linked component of the keratinocyte cornified cell envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 272:2021–2030, 1997.
Subramanian, A., U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Fabrication of uniaxially aligned 3D electrospun scaffolds for neural regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 6:025004, 2011.
Sundaramurthi, D., U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Biocompatibility of Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co3-hydroxyvalerate)(PHBV) Nanofibers for Skin Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9:1383–1392, 2013.
Sundaramurthi, D., U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Electrospun nanofibers as scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Polym. Rev. 54:348–376, 2014.
Sundaramurthi, D., K. S. Vasanthan, P. Kuppan, U. M. Krishnan, and S. Sethuraman. Electrospun nanostructured chitosan–poly (vinyl alcohol) scaffolds: a biomimetic extracellular matrix as dermal substitute. Biomed. Mater. 7:045005, 2012.
Xing, Z. C., W. P. Chae, J. Y. Baek, M. J. Choi, Y. Jung, and I. K. Kang. In vitro assessment of antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of silver-containing PHBV nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 11:1248–1253, 2010.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the Nano Mission (SR/S5/NM-07/2006 and SR/NM/PG-16/2007) and FIST (SR/FST/LSI-327/2007 & SR/FST/LSI-058/2010), Department of Science & Technology, India. We also acknowledge the financial support from Prof. T. R. Rajagopalan R&D Cell of SASTRA University. The first author acknowledges the SRF support from the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (09/1095/(0002)/2013/EMR-I).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jane Grande-Allen oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaramurthi, D., Krishnan, U.M. & Sethuraman, S. Epidermal Differentiation of Stem Cells on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) Nanofibers. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 2589–2599 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1124-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1124-3