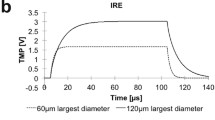
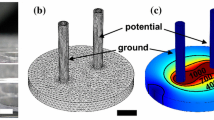
Abstract
Irreversible electroporation (IRE) achieves targeted volume non-thermal focal ablation using a series of brief electric pulses to kill cells by disrupting membrane integrity. Electrochemotherapy (ECT) uses lower numbers of sub-lethal electric pulses to disrupt membranes for improved drug uptake. Malignant glioma (MG) brain tumors are difficult to treat due to diffuse peripheral margins into healthy neural tissue. Here, in vitro experimental data and numerical simulations investigate the feasibility for IRE-relevant pulse protocols with adjuvant ECT drugs to enhance MG treatment. Cytotoxicity curves were produced on two glioma cell lines in vitro at multiple pulse strengths and drug doses with Bleomycin or Carboplatin. Pulses alone increased cytotoxicity with higher pulse numbers and strengths, reaching >90% by 800 V/cm with 90 pulses. Chemotherapeutic addition increased cytotoxicity by >50% for 1 ng/mL concentrations of either drug relative to 80 pulses alone with J3T cells at electric fields ≥400 V/cm. In addition to necrosis, transmission electron microscopy visualizes apoptotic morphological changes and Hoescht 33342 staining shows apoptotic cell fractions varying with electric field and drug dose relative to controls. Numerically simulated treatment volumes in a canine brain show IRE combined with ECT expands therapeutic volume by 2.1–3.2 times compared to IRE alone.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IRE:
-
Irreversible electroporation
- ECT:
-
Electrochemotherapy
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain-barrier
References
Agerholm-Larsen, B., H. K. Iversen, P. Ibsen, J. M. Moller, F. Mahmood, et al. Preclinical validation of electrochemotherapy as an effective treatment for brain tumors. Cancer Res. 71:3753–3762, 2011.
Ahmed, M., C. L. Brace, F. T. Lee, and S. N. Goldberg. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 258:351–369, 2011.
Al-Sakere, B., F. Andre, C. Bernat, E. Connault, P. Opolon, et al. Tumor ablation with irreversible electroporation. PLoS One 2:e1135, 2007.
Au, J. T., J. Wong, A. Mittra, S. Carpenter, D. Haddad, et al. Irreversible electroporation is a surgical ablation technique that enhances gene transfer. Surgery 150:474–479, 2011.
Cheung, W., H. Kavnoudias, S. Roberts, B. Szkandera, W. Kemp, et al. Irreversible electroporation for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: initial experience and review of safety and outcomes. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 12:233–241, 2013.
Davalos, R., L. Mir, and B. Rubinsky. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:223–231, 2005.
Duck, F. A. Physical properties of tissue: a comprehensive reference book. New York: Academic Press, 1990.
Edd, J. F., L. Horowitz, R. V. Davalos, L. M. Mir, and B. Rubinsky. In vivo results of a new focal tissue ablation technique: irreversible electroporation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:1409–1415, 2006.
Foster, K. R., and H. P. Schwan. Dielectric properties of tissues and biological materials: a critical review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17:25–104, 1989.
Gabriel, S., R. W. Lau, and C. Gabriel. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 41:2251–2269, 1996.
Garcia, P. A., T. Pancotto, J. H. Rossmeisl, Jr., N. Henao-Guerrero, N. R. Gustafson, et al. Non-thermal irreversible electroporation (N-TIRE) and adjuvant fractionated radiotherapeutic multimodal therapy for intracranial malignant glioma in a canine patient. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 10:73–83, 2011.
Garcia, P., J. Rossmeisl, R. Neal, T. Ellis, J. Olson, et al. Intracranial nonthermal irreversible electroporation: in vivo analysis. J. Membr. Biol. 236:127–136, 2010.
Garcia, P. A., J. H. Rossmeisl, Jr., J. L. Robertson, J. D. Olson, A. J. Johnson, et al. 7.0-T magnetic resonance imaging characterization of acute blood–brain-barrier disruption achieved with intracranial irreversible electroporation. PLoS ONE 7:e50482, 2012.
Garrido, W., M. Munoz, R. San Martin, and C. Quezada. FK506 confers chemosensitivity to anticancer drugs in glioblastoma multiforme cells by decreasing the expression of the multiple resistance-associated protein-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 411:62–68, 2011.
Heller, R., M. J. Jaroszeski, D. S. Reintgen, C. A. Puleo, R. C. DeConti, et al. Treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors with electrochemotherapy using intralesional bleomycin. Cancer 83:148–157, 1998.
Hjouj, M., D. Last, D. Guez, D. Daniels, S. Sharabi, et al. MRI study on reversible and irreversible electroporation induced blood–brain barrier disruption. PLoS ONE 7:e42817, 2012.
Hochberg, F. H., and A. Pruitt. Assumptions in the radiotherapy of glioblastoma. Neurology 30:907–911, 1980.
Jarm, T., M. Cemazar, D. Miklavcic, and G. Sersa. Antivascular effects of electrochemotherapy: implications in treatment of bleeding metastases. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 10:729–746, 2010.
Lee, E. W., C. T. Loh, and S. T. Kee. Imaging guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation: ultrasound and immunohistological correlation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 6:287–293, 2007.
Linnert, M., and J. Gehl. Bleomycin treatment of brain tumors: an evaluation. Anticancer Drugs 20:157–164, 2009.
Miklavcic, D., D. Semrov, H. Mekid, and L. M. Mir. A validated model of in vivo electric field distribution in tissues for electrochemotherapy and for DNA electrotransfer for gene therapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1523:73–83, 2000.
Miklavcic, D., D. Semrov, H. Mekid, and L. M. Mir. A validated model of in vivo electric field distribution in tissues for electrochemotherapy and for DNA electrotransfer for gene therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1523:73–83, 2000.
Mir, L. M., and S. Orlowski. Mechanisms of electrochemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 35:107–118, 1999.
Mirimanoff, R. O., T. Gorlia, W. Mason, M. J. Van den Bent, R. D. Kortmann, et al. Radiotherapy and temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: recursive partitioning analysis of the EORTC 26981/22981-NCIC CE3 phase III randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 24:2563–2569, 2006.
Neal, II, R. E., W. Cheung, H. Kavnoudias, and K. R. Thomson. Spectrum of imaging and characteristics for liver tumors treated with irreversible electroporation. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 5:813–818, 2012.
Neal, II, R. E., P. A. Garcia, J. L. Robertson, and R. V. Davalos. Experimental characterization and numerical modeling of tissue electrical conductivity during pulsed electric fields for irreversible electroporation treatment planning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59:1076–1085, 2012.
Neal, II, R. E., J. H. Rossmeisl, Jr., P. A. Garcia, O. I. Lanz, N. Henao-Guerrero, et al. Successful treatment of a large soft tissue sarcoma with irreversible electroporation. J. Clin. Oncol. 29:e372–e377, 2011.
Onik, G., P. Mikus, and B. Rubinsky. Irreversible electroporation: implications for prostate ablation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 6:295–300, 2007.
Prados, M. D., and V. Levin. Biology and treatment of malignant glioma. Semin. Oncol. 27:1–10, 2000.
Qian, J., G. S. Feng, and T. Vogl. Combined interventional therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 9:1885–1891, 2003.
Roux, S., C. Bernat, B. Al-Sakere, F. Ghiringhelli, P. Opolon, et al. Tumor destruction using electrochemotherapy followed by CpG oligodeoxynucleotide injection induces distant tumor responses. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 57:1291–1300, 2008.
Rubinsky, J., G. Onik, P. Mikus, and B. Rubinsky. Optimal parameters for the destruction of prostate cancer using irreversible electroporation. J. Urol. 180:2668–2674, 2008.
Sabel, M. S. Cryo-immunology: a review of the literature and proposed mechanisms for stimulatory versus suppressive immune responses. Cryobiology 58:1–11, 2009.
Salford, L. G., B. R. Persson, A. Brun, C. P. Ceberg, P. C. Kongstad, et al. A new brain tumour therapy combining bleomycin with in vivo electropermeabilization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 194:938–943, 1993.
Sersa, G., T. Jarm, T. Kotnik, A. Coer, M. Podkrajsek, et al. Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine sarcoma. Br. J. Cancer. 98:388–398, 2008.
Sersa, G., D. Miklavcic, M. Cemazar, Z. Rudolf, G. Pucihar, et al. Electrochemotherapy in treatment of tumours. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 34:232–240, 2008.
Thomson, K. R., W. Cheung, S. J. Ellis, D. Federman, H. Kavnoudias, et al. Investigation of the safety of irreversible electroporation in humans. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 22:611–621, 2011.
Venkatesan, A. M., B. J. Wood, and D. A. Gervais. Percutaneous ablation in the kidney. Radiology 261:375–391, 2011.
Yordanova, Y. N., S. Moritz-Gasser, and H. Duffau. Awake surgery for WHO Grade II gliomas within “noneloquent” areas in the left dominant hemisphere: toward a “supratotal” resection. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 115:232–239, 2011.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Coulter Foundation, NSF CAREER Award CBET-1055913, and Whitaker International Scholars Program. The authors thank Kathy Lowe for assistance with cell morphology and histology work.
Conflict of Interest
REN, JHR, PAG, RVD, JLR: Patent holders of “Irreversible Electroporation to Treat Aberrant Masses,” and have pending patents in the area of irreversible electroporation in general, but which does not directly relate to the content submitted here. RVD provides minimal consulting and has received research funding in the area of numerical modeling of electric fields. This manuscript has not been previously published, in whole or in part, nor is it concurrently under consideration elsewhere.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Agata A. Exner oversaw the review of this article.
R.E. Neal II and J.H. Rossmeisl Jr. have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neal, R.E., Rossmeisl, J.H., D’Alfonso, V. et al. In Vitro and Numerical Support for Combinatorial Irreversible Electroporation and Electrochemotherapy Glioma Treatment. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 475–487 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0923-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0923-2