Abstract
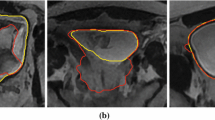
Diagnosis of bladder-related conditions needs critical measurements which require the segmentation of the inner and outer boundaries of the bladder wall. In T2-weighted MR images, the low-signal intensity bladder wall can be identified due to the large contrast with the high-signal intensity urine and perivesical fat. In this article, two deformable models are proposed to segment the bladder wall. Based on the imaging features of the bladder, a modified geodesic active contour is proposed to segment the inner boundary. This method uses the statistical information of the bladder lumen and can handle the intensity variation in MR images. Having obtained the inner boundary, a shape influence field is formed and integrated with the Chan–Vese (C–V) model to segment the outer boundary. The shape-guided C–V model can prevent the overlapping between the two boundaries when the appearance of the bladder wall is blurred. Segmentation examples are presented and analyzed to demonstrate the effectiveness of this novel approach.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., and J. A. Sethian. A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 118:269–277, 1995.
Barentsz, J. O., M. R. Engelbrecht, J. A. Witjes, J. J. de la Rosette, and M. van der Graaf. MR imaging of the male pelvis. Eur. Radiol. 9:1722–1736, 1999.
Barentsz, J. O., G. J. Jager, J. A. Witjes, and J. H. J. Ruijs. Primary staging of urinary bladder carcinoma: the role of MRI and a comparison with CT. Eur. Radiol. 6:129–133, 1996.
Caselles, V., R. Kimmel, and G. Sapiro. Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22:61–79, 1997.
Chan, T. F., and L. A. Vese. Active contour without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10:266–277, 2001.
Cheng, D., and C. M. C. Tempany. MR imaging of the prostate and bladder. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 19:67–89, 1998.
Dimopoulos, J., G. Schirl, A. Baldinger, T. H. Helbich, and R. Pötter. MRI assessment of cervical cancer for adaptive radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol. 185:282–287, 2009.
Gomes, J., and O. Faugeras. Reconciling distance functions and level sets. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 11:209–223, 2000.
Jaume, S., M. Ferrant, B. Macq, L. Hoyte, J. R. Fielding, A. Schreyer, R. Kikinis, and S. K. Warfield. Tumor detection in the bladder wall with a measurement of abnormal thickness in CT scans. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 50:383–390, 2003.
Jequier, S., and O. Rousseau. Sonographic measurements of the normal bladder wall in children. Am. J. Roentgenol. 149:563–566, 1987.
Lammle, M., A. Beer, M. Settles, C. Hannig, H. Schwaibold, and C. Drews. Reliability of MR imaging-based virtual cystoscopy in the diagnosis of cancer of the urinary bladder. Am. J. Roentgenol. 178:1483–1488, 2002.
Leventon, M. E., W. E. L. Grimson, and O. Faugeras. Statistical shape influence in geodesic active contours. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE Computer Society, South Carolina, 2000, pp. 316–323.
Ma, Z., R. N. M. Jorge, and J. M. R. S. Tavares. A shape guided C–V model to segment the levator ani muscle in axial magnetic resonance images. Med. Eng. Phys. 32:766–774, 2010.
Ma, Z., J. M. R. S. Tavares, R. N. M. Jorge, and T. Mascarenhas. A review of algorithms for medical image segmentation and their applications to the female pelvic cavity. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. 13:235–246, 2010.
Margot, S. D., and L. L. Steven. The effect of urinary bladder shape on its mechanics during filling. J. Biomech. 28:725–732, 1995.
Nicolas, V., and D. Beyersdorff. The urinary bladder. In: MR Imaging of the Abdomen and Pelvis, edited by B. Hamm, G. P. Krestin, M. Laniado, V. Nicolas, and M. Taupitz. New York: Georg Thieme Verlag, 2010, pp. 209–217.
Osher, S., and J. A. Sethian. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79:12–49, 1988.
Paramasivam, S., A. Proietto, and M. Puvaneswary. Pelvic anatomy and MRI. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. 20:3–22, 2006.
Song, J. H., I. R. Francis, J. F. Platt, R. H. Cohan, J. Mohsin, S. J. Kielb, M. Korobkin, and J. E. Montie. Bladder tumor detection at virtual cystoscopy. Radiology 218:95–100, 2001.
Tekes, A., I. Kamel, K. Imam, G. Szarf, M. Schoenberg, K. Nasir, R. Thompson, and D. Bluemke. Dynamic MRI of bladder cancer: evaluation of staging accuracy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 184:121–127, 2005.
Vining, D. J., R. J. Zagoria, K. Liu, and D. Stelts. CT cystoscopy: an innovation in bladder imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 166:409–410, 1996.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially done in the scope of the projects “Methodologies to Analyze Organs from Complex Medical Images—Applications to Female Pelvic Cavity,” “Aberrant Crypt Foci and Human Colorectal Polyps: Mathematical Modeling and Endoscopic Image Processing,” and “Cardiovascular Imaging Modeling and Simulation—SIMCARD,” with references PTDC/EEA-CRO/103320/2008, UTAustin/MAT/0009/2008, and UTAustin/CA/0047/2008, respectively, financially supported by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, in Portugal. The first author would like to thank FCT for his PhD grant with reference SFRH/BD/43768/2008.
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jing Bai oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Jorge, R.N., Mascarenhas, T. et al. Novel Approach to Segment the Inner and Outer Boundaries of the Bladder Wall in T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images. Ann Biomed Eng 39, 2287–2297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0324-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0324-3