Abstract
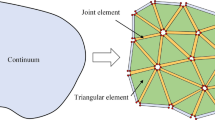
A new well test model for a vertical fractured well is developed based on a discrete-fracture model in which the fractures are discretized as one dimensional (1-D) entities. The model overcomes the weakness of complex meshing, a large number of grids, and instability in conventional stripe-fracture models. Then, the discrete-fracture model is implemented using a hybrid element finite-element method. Triangular elements are used for matrix and line elements for the fractures. The finite element formulation is validated by comparing with the semi-analytical solution of a single vertical fractured well. The accuracy of the approach is shown through several examples with different fracture apertures, fracture conductivity, and fracture amount. Results from the discrete-fracture model agree reasonably well with the stripe-fracture model and the analytic solutions. The advantages of the discrete-fracture model are presented in mesh generation, computational improvement, and abilities to handle complex fractures like wedge-shaped fractures and fractures with branches. Analytical results show that the number of grids in the discrete-fracture model is 10 % less than stripe-fracture model, and computational efficiency increases by about 50 %. The more fractures there are, the more the computational efficiency increases.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gringarten, A.C., Ramey, J., Raghavan, R.: Unsteady-state pressure distributions created by a well with a single infinite-conductivity vertical fracture. J. Pet. Technol. 14, 347–360 (1972). doi:10.2118/4051-PA
Heber Cinco, L., F Samaniego, V., N. Dominguez, A.: Transient pressure behavior for a well with a finite-conductivity vertical fracture. Acta Mech. Sin. 18, 253–264 (1978). doi:10.2118/6014-PA
Weiyang, X., Xiaoping, L.: Research on fractured horizontal wells productivity and productivity influence in shale gas reservoir. Paper SPE 167674 presented at SPE/EAGE European Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, 25–27 Feb 2014. doi:10.2118/167674-MS
AI Rbeawi, S, Tiab, D.: Partially penetrating hydraulic fractures: pressure responses and flow dynamics. Paper SPE 16450 presented at SPE Production and Operations Symposium, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, 23–26 Mar 2013. doi:10.2118/164500-MS
Aimene, Y.E., Nairn, J.A.: Modeling multiple hydraulic fractures interacting with natural fractures using the material point method. Paper SPE 167801 presented at SPE/EAGE European Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Vienna. 25–27 Feb 2014. doi:10.2118/167801-MS
Liu, Y.W., Ouyang, W.P., Zhao, P.H., et al.: Numerical well test for well with finite conductivity vertical fracture in coalbed. Appl. Math. Mech. Engl. Ed. 35, 729–740 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10483-014-1825-6
Tan, X., Li, X.: Transient flow model and pressure dynamic features of tree-shaped fractal reservoirs. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B. 26, 654–663 (2014). doi:10.1016/S1001-6058(14)60072-X
Zhou, R., Liu, Y.W., Zhou, F.X.: Numerical solutions for the transient flow in the homogenous closed circle reservoirs. Acta Mech. Sin. 19, 40–45 (2003). doi:10.1007/BF02487451
Ran, Q.Q., Gu, X.H., Li, S.L.: A coupled model for multiphase fluid flow and sedimentation deformation in oil reservoir and its numerical simulation. Acta Mech. Sin. 13, 264–272 (1997). doi:10.1007/BF02487708
Zheng, H., Liu, F., Du, X.L.: Complementarity problem arising from static growth of multiple cracks and MLS-based numerical manifold method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 295, 150–171 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.cma.2015.07.001
Ouyang, W.: A study of unsteady and non-isothermal flow in porous coalbed media. [Ph.D. Thesis], Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing (2014)
Moinfar, A., Narr, W., Hui, M.-H., et al.: Comparison of discrete-fracture and dual-permeability models for multiphase flow in naturally fractured reservoirs. Paper SPE 142295 presented at SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium, Texas, 21–23 Feb 2011. doi:10.2118/142295-MS
Ma, K., Ren, G., Matten, K., et al.: Modeling techniques for foam flow in porous media. J. Pet. Technol. 20, 453–470 (2014). doi:10.2118/169104-PA
Noorishad, J., Mehran, M.: An upstream finite element method for solution of transient transport equation in fractured porous media. Water Resour. 18, 588–596 (1982). doi:10.1029/WR018i003p00588
Baca, R., Arneet, R., Langford, D.: Modeling fluid flow in fractured-porous rock masses by finite-element techniques. Int. J. Num. Methods Fluids. 4, 337–348 (1984). doi:10.1002/fld.1650040404
Kim, J., Deo, M.D., Langford, D.: Finite element, discrete-fracture model for multiphase flow in porous media. AIChE J. 46, 1120–1130 (2000). doi:10.1002/aic.690460604
Karimi-Fard, M., Firoozabadi, A.: Numerical simulation of water injection in fractured media using the discrete-fracture model and the galerkin method. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 6, 117–126 (2003). doi:10.2118/83633-PA
Karimi-Fard, M., Durlofsky, L.J., Aziz, K.: An efficient discrete fracture model applicable for general purpose reservoir simulators. J. Pet. Technol. 9, 227–236 (2004). doi:10.2118/88812-PA
Zhang, Y., Yuan, X.C., Yao, J., et al.: Discrete fracture numerical simulation methods for reservoirs. J. Daqing Pet. Inst. 34, 80–85 (2010)
Hui, M.-H., Mallison, B., Heidary-Fyrozjaee, M., et al.: The upscaling of discrete fracture models for faster, coarse-scale simulations of IOR and EOR processes for fractured reservoirs. Paper SPE 166075 presented at SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, 30 Sept–2 Oct 2013 doi:10.2118/166075-MS
Hazlett, R.D., Krishna Babu, D.: Discrete wellbore and fracture modeling for unconventional wells and unconventional reservoirs. Paper SPE 159379 presented at SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, Texas, 8–10 Oct 2012. doi:10.2118/159379-MS
Li, X.S., Demmel, J., Gilbert, J., et al.: http://crd-legacy.lbl.gov/~xiaoye/SuperLU/
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51404232), the National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant 2011ZX05038003), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant 2014M561074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, W. et al. A numerical approach for pressure transient analysis of a vertical well with complex fractures. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 640–648 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0568-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-016-0568-0