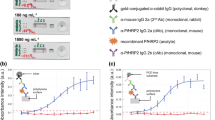
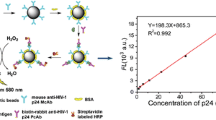
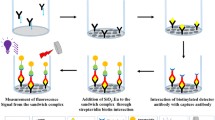
Abstract
A highly sensitive, precisely specific, environmentally friendly, high-throughput, microwell-plate and microchip-based sandwich assay was developed to detect HIV-1 p24 antigen, a protein biomarker using fluorescent carbon dots. High quantum yield carbon dots were synthesized using citric acid and ethylenediamine as carbon and nitrogen sources by a single-step hydrothermal reaction. The desired amine groups confirmed by FTIR on the carbon dots were coupled to streptavidin by amine–amine coupling reaction using glutaraldehyde. The detection range of the carbon dot based immunoassay (CDIA) was found to be between 20 and 1000 pg/mL in a linear dose-dependent manner. CDIA tested for HIV negative plasma samples showed no false positive results in the detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen. The CDIA was extended to develop a microfluidic carbon dot immunoassay (μCDIA) which exhibited analytical sensitivity in the range of 30–1000 pg/mL. The CDIA and μCDIA can easily be adapted to a lab-on-a-chip platform for use in resource limited settings and can also be multiplexed for the detection of other pathogens like TB and Hepatitis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amjadi M, Abolghasemi-Fakhri Z, Hallaj T (2015) Carbon dots-silver nanoparticles fluorescence resonance energy transfer system as a novel turn-on fluorescent probe for selective determination of cysteine. J Photochem Photobiol A 309:8–14
Barroso MM (2011) Quantum dots in cell biology. J Histochem Cytochem 59(3):237–251
Dong Y, Chen C, Zheng X, Gao L, Cui Z, Yang H, Guo C, Chi Y, Li CM (2012) One-step and high yield simultaneous preparation of single- and multi-layer graphene quantum dots from CX-72 carbon black. J Mater Chem 22(18):8764–8766
Fang M, Yuan J-P, Peng C-W, Pang D-W, Li Y (2013) Quantum dots-based in situ molecular imaging of dynamic changes of collagen IV during cancer invasion. Biomaterials 34(34):8708–8717
Feng J, Shan G, Maquieira A, Koivunen ME, Guo B, Hammock BD, Kennedy IM (2003) Functionalized europium oxide nanoparticles used as a fluorescent label in an immunoassay for atrazine. Anal Chem 75(19):5282–5286
Feng Y, Zhong D, Miao H, Yang X (2015) Carbon dots derived from rose flowers for tetracycline sensing. Talanta 140:128–133
Gibbs J, Kennebunk M (2001) Immobilization principles-selecting the surface. ELISA Tech Bull 1:1–8
Haleyur Giri Setty MK, Hewlett IK (2014) Point of care technologies for HIV. AIDS Res Treat 2014:20
Härmä H, Toivonen J, Soini JT, Hänninen P, Parak WJ (2011) Time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay for C-reactive protein using colloidal semiconducting nanoparticles. Sensors 11(12):11335
He J, Lei B, Zhang H, Zheng M, Dong H, Zhuang J, Xiao Y, Liu Y (2015) Using hydrogen peroxide to mediate through a one-step hydrothermal method for the fast and green synthesis of N-CDs. RSC Adv 5(116):95744–95749
Hötzer B, Medintz IL, Hildebrandt N (2012) Fluorescence in Nanobiotechnology: sophisticated fluorophores for novel applications. Small 8(15):2297–2326
Jana J, Ganguly M, Pal T (2015) Intriguing cysteine induced improvement of the emissive property of carbon dots with sensing applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(4):2394–2403
Li L, Wu G, Yang G, Peng J, Zhao J, Zhu J-J (2013) Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 5(10):4015–4039
Liu M, Zhao H, Chen S, Yu H, Zhang Y, Quan X (2011) Label-free fluorescent detection of Cu(ii) ions based on DNA cleavage-dependent graphene-quenched DNAzymes. Chem Commun 47(27):7749–7751
Liu J, Du B, Zhang P, Haleyurgirisetty M, Zhao J, Ragupathy V, Lee S, DeVoe DL, Hewlett IK (2014) Development of a microchip Europium nanoparticle immunoassay for sensitive point-of-care HIV detection. Biosens Bioelectron 61:177–183
Min H, Yi P, Hao L (2013) Preparation method of carbon quantum dot test paper strip for detecting P24 antigen. Google Patents, China
Moerke NJ (2009) Fluorescence polarization (FP) assays for monitoring peptide-protein or nucleic acid-protein binding. Curr Protoc Chem Biol 1:1–15
Pandori MW, Hackett J, Louie B, Vallari A, Dowling T, Liska S, Klausner JD (2009) Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol 47(8):2639–2642
Qian W, Yao D, Yu F, Xu B, Zhou R, Bao X, Lu Z (2000) Immobilization of antibodies on ultraflat polystyrene surfaces. Clin Chem 46(9):1456–1463
Shen J, Li Y, Gu H, Xia F, Zuo X (2014) Recent development of sandwich assay based on the nanobiotechnologies for proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, and ions. Chem Rev 114(15):7631–7677
Shi Y, Pan Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Li M-J, Yi C, Yang M (2014) A dual-mode nanosensor based on carbon quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for discriminative detection of glutathione in human plasma. Biosens Bioelectron 56:39–45
Shi W, Fan H, Ai S, Zhu L (2015) Preparation of fluorescent graphene quantum dots from humic acid for bioimaging application. New J Chem 39(9):7054–7059
Sun YP, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KS, Pathak P et al (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128(24):7756–7757
Tang S, Hewlett I (2010) Nanoparticle-based immunoassays for sensitive and early detection of HIV-1 capsid (p24) antigen. J Infect Dis 201(Supplement 1):S59–S64
Tang S, Zhao J, Wang A, Viswanath R, Harma H, Little RF, Yarchoan R, Stramer SL, Nyambi PN, Lee S, Wood O, Wong EY, Wang X, Hewlett IK (2010) Characterization of immune responses to capsid protein p24 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and implications for detection. Clin Vaccine Immunol 17(8):1244–1251
Tang L, Ji R, Cao X, Lin J, Jiang H, Li X, Teng KS, Luk CM, Zeng S, Hao J, Lau SP (2012) Deep Ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6(6):5102–5110
Teeparuksapun K, Hedström M, Wong EY, Tang S, Hewlett IK, Mattiasson B (2010) Ultrasensitive detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen using nanofunctionalized surfaces in a capacitive immunosensor. Anal Chem 82(20):8406–8411
Wang W, Lu YC, Huang H, Feng JJ, Chen JR, Wang AJ (2014) Facile synthesis of water-soluble and biocompatible fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging. Analyst 139(7):1692–1696
Wang R, Xu Y, Zhang T, Jiang Y (2015) Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using aptamer-conjugated carbon dots as fluorescence probe. Anal Methods 7(5):1701–1706
Wu Y, Wei P, Pengpumkiat S, Schumacher EA, Remcho VT (2015) Development of a carbon dot (C-Dot)-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of human α-fetoprotein. Anal Chem 87(16):8510–8516
Yang ST, Wang X, Wang H, Lu F, Luo PG, Cao L, Huang Y (2009) Carbon dots as nontoxic and high-performance fluorescence imaging agents. J Phys Chem C 113(42):18110–18114
Yang Z, Li Z, Xu M, Ma Y, Zhang J, Su Y, Gao F, Wei H, Zhang L (2013) Controllable synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots and their detection application as nanoprobes. Nano Micro Lett 5(4):247–259
Zhao M-X, Li Y, Zeng E-Z, Wang C-J (2014) The application of CdSe quantum dots with multicolor emission as fluorescent probes for cell labeling. Chem Asian J 9(5):1349–1355
Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L, Zhang J, Song Y, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun H, Wang H, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(14):3953–3957
Zhu L, Cui X, Wu J, Wang Z, Wang P, Hou Y, Yang M (2014a) Fluorescence immunoassay based on carbon dots as labels for the detection of human immunoglobulin G. Anal Methods 6(12):4430–4436
Zhu Y-D, Peng J, Jiang L-P, Zhu J-J (2014b) Fluorescent immunosensor based on CuS nanoparticles for sensitive detection of cancer biomarker. Analyst 139(3):649–655
Zuo J, Jiang T, Zhao X, Xiong X, Xiao S, Zhu Z (2015) Preparation and application of fluorescent carbon dots. J Nanomater 2015:13
Acknowledgements
All authors are grateful to Bhagawan Sri Sathya Sai Baba for his constant inspiration and guidance. L. A. Avinash Chunduri acknowledges UGC Govt. of India for BSR fellowship. We acknowledge with gratitude Prof. S. Sampath (IPC Department, IISc Bangalore, India) for providing TEM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclaimer The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the Food and Drug Administration, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chunduri, L.A.A., Haleyurgirisetty, M.K., Patnaik, S. et al. Development of carbon dot based microplate and microfluidic chip immunoassay for rapid and sensitive detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1825-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1825-z