Abstract
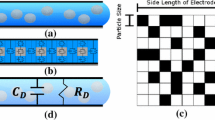
In this work, for the first time, we demonstrate nanoscale droplet generation from a continuous electrowetting microchannel using a simple and precise image-based droplet volume metering technique. One of the most popular ways of droplet generation in electrowetting devices is to split a droplet from a preloaded volume as a fluid reservoir. This method is effective, but lowers volume consistency after multiple droplets are generated. Impedance- and capacitance-based methods of volume metering have been successfully used in digital microfluidics, but require complex circuitry and feedback signal processing. In this work, we demonstrate nanoliter droplet generation from a continuous electrowetting channel used as a replenishable fluid reservoir which compensates for the loss of reservoir volume as droplets are sequentially split. This improves volume consistency especially for applications requiring multi-droplet generation. Based on the area of the electrode, the volume of each droplet split from the electrowetting channel can be obtained by a simple and precise image processing technique with no need for additional hardware and measurement errors of ±0.05 %. This simple technique can be used in a wide range of applications that require precise volume metering, such as immunoassay.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee A, Kreit E, Liu Y, Heikenfeld J, Papautsky I (2012a) Reconfigurable virtual electrowetting channels. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 12:758–764
Banerjee A, Liu Y, Heikenfeld J, Papautsky I (2012b) Deterministic splitting of fluid volumes in electrowetting microfluidics. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 12:5138–5141
Barbulovic-Nad I, Yang H, Park PS, Wheeler AR (2008) Digital microfluidics for cell-based assays. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 8:519–526
Barbulovic-Nad I, Au SH, Wheeler AR (2010) A microfluidic platform for complete mammalian cell culture. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 10:1536–1542
Berthier J, Clementz P, Raccurt O, Jary D, Claustre P, Peponnet C, Fouillet Y (2006) Computer aided design of an EWOD microdevice. Sens Actuators A Phys 127:283–294
Boles DJ, Benton JL, Siew GJ, Levy MH, Thwar PK, Sandahl MA, Rouse JL, Perkins LC, Sudarsan AP, Jalili R, Pamula VK, Srinivasan V, Fair RB, Griffin PB, Eckhardt AE, Pollack MG (2011) Droplet-based pyrosequencing using digital microfluidics. Anal Chem 83:8439–8447
Cho SK, Moon H, Kim C-J (2003) Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits. J Microelectromech Syst 12:70–80
Ding H, Sadeghi S, Shah GJ, Chen S, Keng PY, Kim C-J, Van Dam RM (2012) Accurate dispensing of volatile reagents on demand for chemical reactions in EWOD chips. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 12:3331–3340
Gong J, Kim C-J (2008) All-electronic droplet generation on-chip with real-time feedback control for EWOD digital microfluidics. Lab Chip Miniat Chem Biol 8:898–906
Jebrail MJ, Wheeler AR (2010) Let’s get digital: digitizing chemical biology with microfluidics. Curr Opin Chem Biol 14:574–581
Kreit E, Dhindsa M, Yang S, Hagedon M, Zhou K, Papautsky I, Heikenfeld J (2010) Laplace barriers for electrowetting thresholding and virtual fluid confinement. Langmuir 26:18550–18556
Lee J, Moon H, Fowler J, Schoellhammer T, Kim C-J (2002) Electrowetting and electrowetting-on-dielectric for microscale liquid handling. Sens Actuators, A 95:259–268
Lin YY, Welch ERF, Fair RB (2012) Low voltage picoliter droplet manipulation utilizing electrowetting-on-dielectric platforms. Sens Actuators, B Chem
Luk VN, Fiddes LK, Luk VM, Kumacheva E, Wheeler AR (2012) Digital microfluidic hydrogel microreactors for proteomics. Proteomics 12:1310–1318
Miller EM, Wheeler AR (2008) A digital microfluidic approach to homogeneous enzyme assays. Anal Chem 80:1614–1619
Miller EM, Ng AHC, Uddayasankar U, Wheeler AR (2011) A digital microfluidic approach to heterogeneous immunoassays. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:337–345
Ng AHC, Choi K, Luoma RP, Robinson JM, Wheeler AR (2012) Digital microfluidic magnetic separation for particle-based immunoassays. Anal Chem 84:8805–8812
Pollack MG, Shenderov AD, Fair RB (2002) Electrowetting-based actuation of droplets for integrated microfluidics. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 2:96–101
Ren H, Fair RB, Pollack MG (2004) Automated on-chip droplet dispensing with volume control by electro-wetting actuation and capacitance metering. Sensors Actuators B: Chem 98:319–327
Sadeghi S, Ding H, Shah GJ, Chen S, Keng PY, Kim C-CJ, Michael Van Dam R (2012) On chip droplet characterization: a practical, high-sensitivity measurement of droplet impedance in digital microfluidics. Anal Chem 84:1915–1923
Sista R, Hua Z, Thwar P, Sudarsan A, Srinivasan V, Eckhardt A, Pollack M, Pamula V (2008) Development of a digital microfluidic platform for point of care testing. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 8:2091–2104
Srigunapalan S, Eydelnant IA, Simmons CA, Wheeler AR (2012) A digital microfluidic platform for primary cell culture and analysis. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 12:369–375
Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Fair RB (2004) An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab on a Chip—Miniat Chem Biol 4:310–315
Welch ERF, Lin Y, Madison A, Fair RB (2011) Picoliter DNA sequencing chemistry on an electrowetting-based digital microfluidic platform. Biotechnol J 6:165–176
Wheeler AR, Moon H, Bird CA, Loo RRO, Kim CJ, Loo JA, Garrell RL (2005) Digital microfluidics with in-line sample purification for proteomics analyses with MALDI-MS. Anal Chem 77:534–540
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support by the National Science Foundation (ECCS-1001141) and the Ohio Center for Microfluidic Innovation (OCMI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Banerjee, A. & Papautsky, I. Precise droplet volume measurement and electrode-based volume metering in digital microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 17, 295–303 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1318-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1318-2