Abstract
Purpose
Acoustic radiation force (ARF) elastography has recently become available. The previous animal studies have revealed lung injuries induced by diagnostic ultrasound, but the effects on the lung resulting from exposure to ultrasound with ARF are unknown. This study aimed to assess the risk of lung injury associated with ultrasound with ARF.
Methods
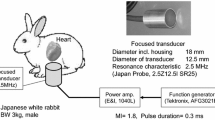
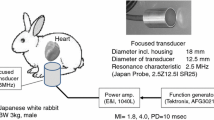
A focused 2.5-MHz transducer that emits ultrasound with ARF was used. A rabbit was anesthetized, and the transducer was placed in the right subcostal region. Exposure settings of mechanical index (MI) 0.80, pulse duration 10 ms, pulse repetition time 5 s, and exposure time 150 s were applied.
Results
One red spot (7 × 6 mm) was observed on the surface of the right lung corresponding to the area of exposure. Alveolar hemorrhage was observed microscopically. This lesion was visible across a range of 20–170 μm in depth from the pleural surface.
Conclusion
The first example of lung hemorrhage induced by ultrasound with ARF was observed in this study. This observation suggests the possibility of lung injury in humans when ARF elastography is applied with the transducer directed toward the lung. Further studies are needed to determine the safety of this modality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller DL. Induction of pulmonary hemorrhage in rats during diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:1476–82.
O’Brien WD Jr, Zachary JF. Rabbit and pig lung damage comparison from exposure to continuous wave 30-kHz ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22:345–53.
Doherty JR, Trahey GE, Nightingale KR, et al. Acoustic radiation force elasticity imaging in diagnostic ultrasound. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013;60:685–701.
Ishiguro Y, Nitta N, Taniguchi N, et al. Ultrasound exposure (mechanical index 1.8) with acoustic radiation force impulse evokes extrasystolic waves in rabbit heart under concomitant administration of an ultrasound contrast agent. J Med Ultrasonics. 2016;43:3–7.
Ishiguro Y, Sasanuma H, Nitta N, et al. The arrhythmogenic effect of ultrasonic exposure with acoustic radiation force (ARF) impulse on the rabbit heart with ultrasound contrast agent perfluorobutane. J Med Ultrasonics. 2015;42:47–50.
Nitta N, Ishiguro Y, Sasanuma H, et al. Experimental system for in situ measurement of temperature rise in animal tissue under exposure to acoustic radiation force impulse. J Med Ultrasonics. 2015;42:39–46.
Asian Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology (homepage on the internet). The Federation; 1993–2016 (cited 2014 Nov 27). Basic concepts of safety of diagnostic ultrasonic equipment (p 16). http://www.afsumb.org/safety_of_ultrasound_equipment4web2014.pdf.
Holland CK, Deng CX, Apfel RE, et al. Direct evidence of cavitation in vivo from diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22:917–25.
Miller DL. Overview of experimental studies of biological effects of medical ultrasound caused by gas body activation and inertial cavitation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007;93:314–30.
Zachary JF, Blue JP Jr, Miller RJ, et al. Lesions of ultrasound-induced lung hemorrhage are not consistent with thermal injury. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32:1763–70.
Skurczynski MJ, Duck FA, Shipley JA, et al. Evaluation of experimental methods for assessing safety for ultrasound radiation force elastography. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:666–74.
Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1126–47.
American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. Section 4—bioeffects in tissues with gas bodies. J Ultrasound Med. 2000;19:97–108.
Shankar H, Pagel PS. Potential adverse ultrasound-related biological effects: a critical review. Anesthesiology. 2011;115:1109–24.
O’Brien WD Jr, Yang Y, Simpson DG, et al. Threshold estimation of ultrasound-induced lung hemorrhage in adult rabbits and comparison of thresholds in mice, rats, rabbits and pigs. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32:1793–804.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (23300194) and C (26350544) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and a Research and Development Committee Program of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine. This work was also supported in part by a project of the Ultrasound Equipment and Safety Committee of the Japanese Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical consideration
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
About this article
Cite this article
Takayama, N., Ishiguro, Y., Taniguchi, N. et al. The effect of ultrasound with acoustic radiation force on rabbit lung tissue: a preliminary study. J Med Ultrasonics 43, 481–485 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-016-0730-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-016-0730-0