Abstract
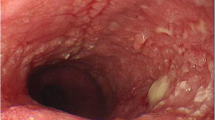
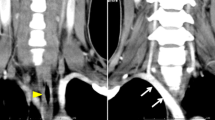
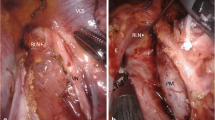
Right non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve is a rare nerve anomaly that communicates the right vagal nerve trunk to the laryngeal nerve directly in the neck, and is usually accompanied by an aberrant right subclavian artery. We report a case of thoracic esophagectomy with intraoperative neuromonitoring undertaken in a patient with these abnormalities. This case report concerns a 66-year-old man with thoracic esophageal carcinoma who was referred to our hospital. An aberrant right subclavian artery that gave us a prediction of a right non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve was detected preoperatively using computed tomography, and identified visually with intraoperative neuromonitoring. Identification of this nerve anomaly during cervical lymph node dissection was considered important to avoid unexpected neural injuries. For a successful esophagectomy with lymph node dissection in patients with this anomaly, intraoperative neuromonitoring for the non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve may provide a useful contribution to surgical safety.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henry JF, Audiffret J, Denizot A, Plan M. The non-recurrent inferior nerve: review of 33 cases, including two on the left side. Surgery. 1988;104:977–84.
Sanders G, Uyeda RY, Karlan MS. Nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerves and their association with a recurrent branch. Am J Surg. 1983;146:501–3.
Yatabe T, Kitagawa H, Yamashita K, Hanazaki K, Yokoyama M. Comparison of the perioperative outcome of esophagectomy by thoracoscopy in the prone position with that of thoracotomy in the lateral decubitus position. Surg Today. 2013;43:386–91.
Yoshida N, Watanabe M, Baba Y, Iwagami S, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M, Sakamoto Y, Miyamoto Y, Ozaki N, Baba H. Risk factors for pulmonary complications after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Surg Today. 2014;44:526–32.
Gockel I, Kneist W, Keilmann A, Junginger T. Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis (RLNP) following esophagectomy for carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005;31:277–81.
Hulscher JB, van Sandick JW, Devriese PP, van Lanschot JJ, Obertop H. Vocal cord paralysis after subtotal oesophagectomy. Br J Surg. 1999;86:1583–7.
Baba M, Natsugoe S, Shimada M, Nakano S, Noguchi Y, Kawachi K, Kusano C, Aikou T. Does hoarseness of voice from recurrent nerve paralysis after esophagectomy for carcinoma influence patient quality of life? J Am Coll Surg. 1999;188:231–6.
Taniyama Y, Miyata G, Kamei T, Nakano T, Abe S, Katsura K, Sakurai T, Teshima J, Hikage M, Ohuchi N. Complications following recurrent laryngeal nerve lymph node dissection in oesophageal cancer surgery. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg. 2015;20:41–6.
Page C, Monet P, Peltier J, Bonnaire B, Strunski V. Non-recurrent laryngeal nerve related to thyroid surgery: report of three cases. J Laryngol Otol. 2008;122:757–61.
Avisse C, Marcus C, Delattre JF, Marcus C, Cailliez-Tomasi JP, Palot JP, Ladam-Marcus V, Menanteau B, Flament JB. Right non recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve and arteria lusoria: the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of an anatomic anomaly. Review of 17 cases. Surg Radiol Anat. 1998;20:227–32.
Shimada T, Terashima H, Shimizu T, Abe R, Hirayama K. Esophageal carcinoma with nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve. Ann Thrac Surg. 2000;70:1722–3.
Brauckhoff M, Walls G, Brauckhoff K, Thanh PN, Thomusch O, Dralle H. Identification of the non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve using intraoperative neurostimulation. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2002;386:482–7.
Chiang FY, Lu IC, Tsai CJ, Hsiao PJ, Lee KW, Wu CW. Detecting and identifying nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve with the application of intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroid and parathyroid operation. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012;33:1–5.
Brauckhoff M, Machens A, Sekulla C, Lorenz K, Dralle H. Latencies shorter than 3.5 ms after vagus nerve stimulation signify a nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve before dissection. Ann Surg. 2011;253:1172–7.
Cai Q, Guan Z, Huang X, Yuan J, Pan Y, Zheng Y, Liang M, Fan S. The usefulness of preoperative computed tomography and intraoperative neuromonitoring identification of the nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270:2135–40.
Kamani D, Potenza AS, Cernea CR, Kamani YV, Randolph GW. The nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve: anatomic and electrophysiologic algorithm for reliable identification. Laryngoscope. 2015;125:503–8.
Pramesh CS, Saklani AP, Parmar V, Acharya S, Badwe RA. Aberrant subclavian artery causing difficulty in transhiatal esophageal dissection. Dis Esophagus. 2003;16:173–6.
Toniato A, Mazzarotto R, Piotto A, Bernante P, Pagetta C, Pelizzo MR. Identification of the nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery. World J Surg. 2004;28:659–61.
Temes RT, Tullis MJ, Lee P, Wernly JA. Transhiatal esophagectomy in a patient with aberrant right subclavian artery. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68:2341–2.
Pramesh CS, Saklani AP, Parmar V, Acharya S, Badwe RA. Aberrant subclavian artery causing difficulty in transhiatal esophageal dissection. Dis Esophagus. 2003;16:173–6.
Pantvaidya GH, Mistry RC, Ghanekar VR, Upasani VV, Pramesh CS. Injury of an aberrant subclavian artery: a rare complication of video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;11:35–7.
Sato H, Tsubosa Y, Ugumori T. Esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection for esophageal carcinoma with a nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;53:502–4.
Tanaka O, Kiyozaki H, Yoshida T, Konishi F. Nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve in patients with esophageal cancer: report of two cases. Esophagus. 2007;4:41–5.
Qi H, Wang L, Wumar M, Kelimu H. Aberrant retroesophageal right subclavian artery with esophageal cancer infiltration: surgical treatment. Chin Med J. 2009;122:1115–6.
Sabljak P, Stojakov D, Davidovic L, Ivanovic A, Ebrahimi K, Velickovic D, Pesko P. Pharyngolaryngoesophagectomy in a patient with an aberrant right subclavian artery: report of a case. Surg Today. 2011;41:1112–6.
Pop D, Venissac N, Nadeemy AS, Schneck AS, Aze O, Mouroux J. Lesson to be learned: beware of lusoria artery during transhiatal esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;94:1010–1.
Kasashima H, Kubo N, Ohira M, Sakurai K, Toyokawa T, Tanaka H, Muguruma K, Shibutani M, Yamazoe S, Kimura K, Nagahara H, Amano R, Ohtani H, Yashiro M, Maeda K, Hirakawa K. Successful resection of esophageal carcinoma with aberrant right subclavian artery using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: report of two cases. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:899–904.
Ethical Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, K., Miyata, H., Kanemura, T. et al. Successful esophageal carcinoma resection with intraoperative neuromonitoring in a patient with non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve. Esophagus 13, 97–103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-015-0493-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-015-0493-5