Abstract
Purpose
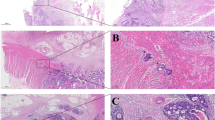
By defining perineural invasion of colorectal cancer as invasion to Auerbach’s plexus, we examined the usefulness of this pathologic finding as a prognostic factor.
Methods
A total of 509 consecutive patients who underwent curative surgery for pT3 or pT4 colorectal cancer between May 1997 and December 2001 were reviewed. All the surviving patients were followed for more than five years. All the pathologic findings, including perineural invasion, were described prospectively in the pathology report forms.
Results
Perineural invasion was detected in 132 of 509 patients (26 percent) and was significantly associated with lymph node status, lymphatic invasion, and venous invasion. Incidences of local and systemic recurrence were significantly higher in patients with perineural invasion than in those without perineural invasion. The disease-free survival of the perineural invasion-positive group was significantly poorer than that of the perineural invasion-negative group for Stages II and III colon cancer, irrespective of the use of adjuvant chemotherapy. This improved disease-free survival also was seen in patients with Stage II rectal cancer not treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. There was a nonsignificant difference in disease-free survival for Stage II rectal cancer and Stage III rectal cancer treated with chemotherapy, that of the perineural invasion-positive group being poorer. Multivariate analysis showed that lymph node status, perineural invasion, depth of invasion, and cancer site were significant prognostic factors.
Conclusions
Perineural invasion defined as cancer invasion to Auerbach’s plexus is an important prognostic factor for colorectal cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasna MJ, Flancbaum L, Cody RP, Shneibaum S, Ben Ari G. Vascular and neural invasion in colorectal carcinoma. Incidence and prognostic significance. Cancer 1988;61:1018-3.
Mulcahy HE, Toner M, Patchett SE, Daly L, O’Donoghue DP. Identifying stage B colorectal cancer patients at high risk of tumor recurrence and death. Dis Colon Rectum 1997;40:326-1.
Guerra A, Borda F, Javier Jimenez F, Martinez-Penuela JM, Larrinaga B. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in resected colorectal cancer: a new prognostic index. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998;10:51-.
Di Fabio F, Nascimbeni R, Villanacci V, et al. Prognostic variables for cancer-related survival in node-negative colorectal carcinomas. Dig Surg 2004;21:128-3.
Onate-Ocana LF, Montesdeoca R, Lopez-Graniel CM, et al. Identification of patients with high-risk lymph node-negative colorectal cancer and potential benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34:323-.
Seefeld PH, Bargen JA. The spread of carcinoma of the rectum: invasion of lymphatics, veins and nerves. Ann Surg 1943;118:76–90.
Knudsen JB, Nilsson T, Sprechler M, Johansen A, Christensen N. Venous and nerve invasion as prognostic factors in postoperative survival of patients with resectable cancer of the rectum. Dis Colon Rectum 1983;26:613-.
Bentzen SM, Balslev I, Pedersen M, et al. A regression analysis of prognostic factors after resection of Dukes-B and C carcinoma of the rectum and rectosigmoid. Does postoperative radiotherapy change the prognosis? Br J Cancer 1988;58:195–201.
Horn A, Dahl O, Morild I. Venous and neural invasion as predictors of recurrence in rectal adenocarcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum 1991;34:798–804.
Shirouzu K, Isomoto H, Kakegawa T. Prognostic evaluation of perineural invasion in rectal cancer. Am J Surg 1993;165:233-.
Bognel C, Rekacewicz C, Mankarios H, et al. Prognostic value of neural invasion in rectal carcinoma: a multivariate analysis on 339 patients with curative resection. Eur J Cancer 1995;31:894-.
Moreira LF, Kenmotsu M, Gochi A, Tanaka N, Orita K. Lymphovascular and neural invasion in low-lying rectal carcinoma. Cancer Detect Prev 1999;23:123-.
Galindo-Gallego M, Fernandez-Acenero MJ, Sanz-Ortega J, Aljama A, Lopez-Elzaurdia C. Prognostic significance of microvascular counts in rectal carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 2000;196:607-2.
Ueno H, Hase K, Mochizuki H. Criteria for extramural perineural invasion as a prognostic factor in rectal cancer. Br J Surg 2001;88:994–1000.
Law WL, Chu KW. Anterior resection for rectal cancer with mesorectal excision: a prospective evaluation of 622 patients. Ann Surg 2004;240:260-.
Guillem JG, Chessin DB, Cohen AM, et al. Long-term oncologic outcome following preoperative combined modality therapy and total mesorectal excision of locally advanced rectal cancer. Ann Surg 2005;241:829-6.
Krebs B, Kozelj M, Kavalar R, Gajzer B, Gadzijev EM. Prognostic value of additional pathological variables for long-term survival after curative resection of rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:4565-.
Compton C, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Pettigrew N, Fielding LP. American Joint Committee on Cancer Prognostic Factors Consensus Conference: Colorectal Working Group. Cancer 2000;88:1739-7.
Fujita S, Shimoda T, Yoshimura K, Yamamoto S, Akasu T, Moriya Y. Prospective evaluation of prognostic factors in patients with colorectal cancer undergoing curative resection. J Surg Oncol 2003;84:127-1.
Wied U, Nilsson T, Knudsen JB, Sprechler M, Johansen A. Postoperative survival of patients with potentially curable cancer of the colon. Dis Colon Rectum 1985;28:333-.
Takahashi Y, Tucker SL, Kitadai Y, et al. Vessel counts and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor as prognostic factors in node-negative colon cancer. Arch Surg 1997;132:541-.
Burdy G, Panis Y, Alves A, Nemeth J, Lavergne-Slove A, Valleur P. Identifying patients with T3-T4 node-negative colon cancer at high risk of recurrence. Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44:1682-.
Bellis D, Marci V, Monga G. Light microscopic and immunohistochemical evaluation of vascular and neural invasion in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 1993;189:443-.
Anwar S, Frayling IM, Scott NA, Carlson GL. Systematic review of genetic influences on the prognosis of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 2004;91:1275-1.
Ross A, Rusnak C, Weinerman B, et al. Recurrence and survival after surgical management of rectal cancer. Am J Surg 1999;177:392-.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, S., Nakanisi, Y., Taniguchi, H. et al. Cancer Invasion to Auerbach’s Plexus is an Important Prognostic Factor in Patients with pT3-pT4 Colorectal Cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 50, 1860–1866 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-007-9072-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-007-9072-8