Abstract
Objective
The quantification of magnetic resonance relaxation parameters T 1 and T 2 have the potential for improved disease detection and classification over standard clinical weighted imaging. Performing a mono-exponential fit on multi spin-echo (MSE) data provides quantitative T 2 values in a clinically acceptable scan-time. However, due to technical imperfections of refocusing pulses, stimulated echo contributions to the signals lead to significant deviations in the resulting T 2 values. In this work, a simple auto-calibrating correction procedure is presented, allowing the accurate estimation of T 2 from MSE acquisitions.
Materials and methods
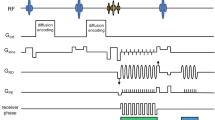
Correction factors for T 2 values obtained from MSE acquisitions with a mono-exponential fit are derived from simulations following the extended phase graph formulation. A closed formula is given for the calculation of the required correction factors directly from the measured data itself.
Results
Simulations and phantom experiments show high accuracy of corrected T 2 values for a wide range of clinically relevant T 2 values and for different nominal refocusing flip angles. In addition, corrected T 2 maps of the human brain are presented.
Conclusion
A simple recipe is provided to correct T 2 values obtained from MSE acquisitions via a mono-exponential fit for the influence of stimulated echoes. Since all required parameters are extracted from the data themselves, no additional acquisitions are required.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whittall KP, MacKay AL, Graeb DA et al (1997) In vivo measurement of T2 distributions and water contents in normal human brain. Magn Reson Med 37:34–43. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910370107
MacKay A, Laule C, Vavasour I et al (2006) Insights into brain microstructure from the T2 distribution. Magn Reson Imaging 24:515–525. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2005.12.037
Kurki T, Lundbom N, Valtonen S (1995) Tissue characterisation of intracranial tumours: the value of magnetisation transfer and conventional MRI. Neuroradiology 37:515–521. doi:10.1007/s002340050147
Rugg-Gunn FJ, Boulby PA, Symms MR et al (2005) Whole-brain T2 mapping demonstrates occult abnormalities in focal epilepsy. Neurology 64:318–325
Farraher SW, Jara H, Chang KJ et al (2006) Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic metastasis from cysts and hemangiomas with calculated T2 relaxation times and the T1/T2 relaxation times ratio. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1333–1341. doi:10.1002/jmri.20758
Dardzinski BJ, Mosher TJ, Li S et al (1997) Spatial variation of T2 in human articular cartilage. Radiology 205:546–550
Meiboom S, Gill D (1958) Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum 29:688. doi:10.1063/1.1716296
Deoni SCL, Rutt BK, Peters TM (2003) Rapid combined T1 and T2 mapping using gradient recalled acquisition in the steady state. Magn Reson Med 49:515–526. doi:10.1002/mrm.10407
Pell GS, Briellmann RS, Waites AB et al (2006) Optimized clinical T2 relaxometry with a standard CPMG sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:248–252. doi:10.1002/jmri.20490
Hennig J (1988) Multiecho imaging sequences with low refocusing flip angles. J Magn Reson 1969 78:397–407. doi:10.1016/0022-2364(88)90128-X
Hennig J (1991) Echoes—How to generate, recognize, use or avoid them in MR-imaging sequences. Part I: Fundamental and not so fundamental properties of spin echoes. Concepts Magn Reson 3:125–143. doi:10.1002/cmr.1820030302
Hennig J (1991) Echoes—How to generate, recognize, use or avoid them in MR-imaging sequences. Part II: Echoes in imaging sequences. Concepts Magn Reson 3:179–192. doi:10.1002/cmr.1820030402
Huang C, Bilgin A, Barr T, Altbach MI (2013) T2 relaxometry with indirect echo compensation from highly undersampled data. Magn Reson Med 70:1026–1037. doi:10.1002/mrm.24540
Lebel RM, Wilman AH (2010) Transverse relaxometry with stimulated echo compensation. Magn Reson Med 64:1005–1014
Doneva M, Börnert P, Eggers H et al (2010) Compressed sensing reconstruction for magnetic resonance parameter mapping. Magn Reson Med 64:1114–1120. doi:10.1002/mrm.22483
Block KT, Uecker M, Frahm J (2009) Model-based iterative reconstruction for radial fast spin-echo MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1759–1769
Huang C, Graff CG, Clarkson EW et al (2012) T2 mapping from highly undersampled data by reconstruction of principal component coefficient maps using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med 67:1355–1366. doi:10.1002/mrm.23128
Deichmann R, Haase A (1992) Quantification of T1 values by SNAPSHOT-FLASH NMR Imaging. J Magn Reson 96:608–612
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Siemens Healthcare, the German Research Foundation (DFG JA 827/9-1) and the Bavarian Ministry of Economic Affairs, Infrastructure, Transport and Technology (BayStMWIVT) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neumann, D., Blaimer, M., Jakob, P.M. et al. Simple recipe for accurate T 2 quantification with multi spin-echo acquisitions. Magn Reson Mater Phy 27, 567–577 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-014-0438-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-014-0438-3