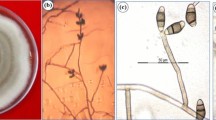
Abstract
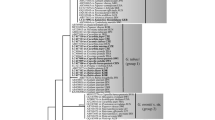
Most of the many Stemphylium species on record as plant pathogens in Japan have been identified by morphology. Using molecular phylogenetic analysis of four loci (rDNA-ITS, EF-1α, GPD, and vmaA-vpsA) combined, we re-examined the taxonomy of 31 Stemphylium strains that had been identified morphologically before or after their deposit in the NIAS Genebank, Japan. In the present study, these Japanese strains were separated into three groups (Groups A, C, and E). Sixteen Japanese strains formed a new subgroup (designated Subgroup C2) that contained no type or ex-type strains of existing species. Four of the strains had been identified correctly, whereas the other 27 strains appear to have been misidentified based on our phylogenetic analysis. We examined the conidial morphology of four representative misidentified strains selected from each clade. While the morphological characteristics of a strain isolated from Welsh onion resembles those of the S. vesicarium type, this strain belongs to Subgroup C2 rather than Subgroup C1 and, therefore, could not be identified at the species level. Conversely, three pathogenic strains isolated from aster, asparagus, and Chinese chive were re-identified based on our combined morphological and phylogenetic data. We propose the scientific names of the aster leaf spot pathogen as S. lycopersici, and the asparagus Stemphylium leaf spot and Chinese chive brown leaf blight pathogens as S. herbarum.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE T Automat Contr 19:716–723
Câmara MPS, O’Neill NR, van Berkum P (2002) Phylogeny of Stemphylium spp. based on ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia 94:660–672
Deng JX, Paul NC, Li MJ, Cho HS, Lee HB, Yu SH (2014) Stemphylium platycodontis sp. nov., isolated from Platycodon grandiflorus in Korea. Mycol Progress 13:477–482
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Enjoji S (1931) Two diseases of tomato (2) (in Japanese). J Plant Prot 18:48–53
Farr DF, Rossman AY (2014) Fungal databases, Systematic Mycology and Microbiology Laboratory, ARS, USDA, Beltsville, MD, USA. http://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/. Accessed 3 May 2014
Hosen MI, Ahmed AU, Zaman J, Ghosh S, Hossain KMK (2009) Cultural and physiological variation between isolates of Stemphylium botryosum the causal of stemphylium blight disease of lentil (Lens culinaris). World J Agric Sci 5:94–98
Ichikawa K, Sato T (1994) Leaf and stem spot of aster caused by Stemphylium vesicarium (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopath Soc Japan 60:523–526
Inderbitzin P, Mehta YR, Berbee ML (2009) Pleospora species with Stemphylium anamorphs: a four locus phylogeny resolves new lineages yet does not distinguish among species in the Pleospora herbarum clade. Mycologia 101:329–339
Jobb G, Von Haeseler A, Strimmer K (2004) TREEFINDER: a powerful graphical analysis environment for molecular phylogenetics. BMC Evol Biol 4:18
Kubota M (2010) Alternaria and Phoma pathogens of vegetable plants (in Japanese). MAFF Microorg Genet Resources Manual 30:1–22
Kurose D, Hoang LH, Furuya N, Takeshita M, Sato T, Tsushima S, Tsuchiya K (2014) Pathogenicity of Stemphylium lycopersici isolated from rotted tobacco seeds on seedlings and leaves. J Gen Plant Pathol 80:147–152
Kurose D, Kanegae Y, Misawa T, Ebihara Y, Tanaka C, Watanabe T, Uematsu S, Tsushima S, Sato T (2015) Yellow spot of white lace flower caused by Pleospora herbarum in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 81:169–172
Leach CM, Aragaki M (1970) Effects of temperature on conidium characteristics of Ulocladium chartarum and Stemphylium floridanum. Mycologia 62:1071–1076
Miller PM (1955) V-8 juice agar as a general purpose medium for fungi and bacteria. Phytopathology 45:461–462
Minegishi N, Kono T, Zenbayashi R (1991) Occurrence of leaf spot of Aster sp. (in Japanese). Proceedings of the Kanto-Tosan Plant Protection Society 38:113–115
Misawa T (2009a) Brown leaf blight of Chinese chive caused by Stemphylium botryosum Wallroth (Abstract in Japanese). Jpn J Phytopathol 75:87
Misawa T (2009b) Species composition of causal agent of leaf blight of Welsh onion in Hokkaido (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Rept Plant Prot North Jpn 60:55–57
Moralejo E, Clemente A, Descals E, Belbahri L, Calmin G, Lefort F, Spies CFJ, McLeod A (2008) Pythium recalcitrans sp. nov. revealed by multigene phylogenetic analysis. Mycologia 100:310–319
Nishi N, Muta T, Ito Y, Nakamura M, Tsukiboshi T (2009) Ray speck of chrysanthemum caused by Stemphylium lycopersici in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 75:80–82
Nishihara N (1961) Diseases of pastures (I), Clover and alfalfa (in Japanese). Miscellaneous publication of the Chiba-ken Agric Exp Stn. No. 1, Chiba, pp 54–59
Pei YF, Wang Y, Geng Y, O’Neill NR, Zhang XG (2011) Three novel species of Stemphylium from Sinkiang, China: their morphological and molecular characterization. Mycol Progress 10:163–173
Phytopathological Society of Japan (PSJ), National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences (NIAS) (eds) (2012) Common names of plant diseases in Japan, 2nd edn (in Japanese). Phase Out Inc., Nagoya
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA, Chen W, Fungal Barcoding Consortium (2012) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA bardode marker for Fungi. Proceedings of the National Academy Science USA 109:6241–6246
Shenoy BD, Jeewon R, Hyde KD (2007) Impact of DNA sequence-data on the taxonomy of anamorphic fungi. Fungal Divers 26:1–54
Shibata S, Horiuchi S, Satou M, Yamauchi N (2000) Stemphylium vesicarium, another causal agent of leaf blight of welsh onion in Japan (in Japanese with English summary). Annu Rept Plant Prot North Jpn 51:62–65
Simmons EG (1969) Perfect states of Stemphylium. Mycologia 61:1–26
Simmons EG (1985) Perfect states of Stemphylium II. Sydowia Ann Mycol SerII 38:284–293
Simmons EG (2001) Perfect states of Stemphylium—IV. Harv Pap Bot 6:199–208
Suzui T (1973) Stemphylium leaf spot (Stemphylium botryosum Wallr.) on asparagus plants (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopath Soc Jpn 39:364–366
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tanabe AS (2011) Kakusan4 and Aminosan: two programs for comparing nonpartitioned, proportional and separate models for combined molecular phylogenetic analyses of multilocus sequence data. Mol Ecol Resour 11:914–921
Tomioka K, Sato T (2011) Fruit rot of sweet pepper caused by Stemphylium lycopersici in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 77:342–344
Tomioka K, Sato T, Sasaya T, Koganezawa H (1997) Leaf spot of kalanchoe caused by Stemphylium lycopersici. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 63:337–340
Wang Y, Zhang XG (2006) Three new species of Stemphylium from China. Mycotaxon 96:77–81
Wang Y, Fu HB, O’Neill NR, Zhang XG (2009) Two new species of Stemphylium from Northwest China. Mycol Progress 8:301–304
Wang Y, Geng Y, Pei YF, Zhang XG (2010) Molecular and morphological description of two new species of Stemphylium from China and France. Mycologia 102:708–717
Watanabe T (1989) Soil fungal flora in Hachijo-jima Island. Trans Mycol Soc Jpn 30:427–435
Wiltshire SP (1938) The original and modern conceptions of Stemphylium. Trans Brit Mycol Soc 21:211–239
Yu SH (2001) Korean species of Alternaria and Stemphylium. Nat Inst Agric Sci Tech, Suwon, pp 159–162
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Dr. Harry Evans, CABI Europe-UK, for his help with improving this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper are available in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases as accessions AB704310 and AB979876–AB979994.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurose, D., Misawa, T., Suzui, T. et al. Taxonomic re-examination of several Japanese Stemphylium strains based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses. J Gen Plant Pathol 81, 358–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-015-0607-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-015-0607-x