Abstract
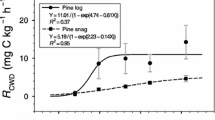
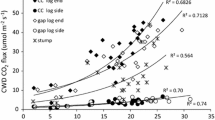
Measuring coarse woody debris (CWD) respiration (R CWD) may have advantages over other approaches in determining CWD decomposition rates to accurately estimate forest carbon budgets and effects of warm temperatures on decomposition; however, studies on R CWD are insufficient. The R CWD from Quercus variabilis logs of different sizes (e.g., different surface area to weight ratios or weights) was measured under homogeneous conditions by using a closed-chamber system with a non-dispersive infrared sensor. The size effect on R CWD measured on a weight or volume basis was not significant, but it was significant on a surface area basis. This indicates that R CWD on a weight or volume basis would be a reliable measure, regardless of the size and cross-sectional area effects, while R CWD on a surface area basis must vary geometrically according to the change in sample size. R CWD did not change significantly over time until 122 h after sampling. An exponential model with a Q 10 of 2.34 was fitted only at temperatures below 22.6 °C because R CWD was suppressed at high temperatures due to constantly decreasing moisture. Instead, a logistic model was applied for all temperatures. The annual R CWD and the decay rate constant were estimated to be 53.4 g C kg−1 year−1 and 0.107 year−1, respectively. The decomposition rate estimate through R CWD might not correspond to that using the mass loss approach. It remains uncertain whether the methodological differences may lead to potential errors in measuring the actual CWD decomposition rate; therefore, a multiple approach study for CWD decomposition should be conducted.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldocchi DD (2003) Assessing the eddy covariance technique for evaluating carbon dioxide exchange rates of ecosystems: past, present and future. Glob Change Biol 9:479–492
Bond-Lamberty B, Gower S (2008) Decomposition and fragmentation of coarse woody debris: Re-visiting a boreal black spruce chronosequence. Ecosystems 11:831–840
Carson H (1997) CARBOCAP®—new carbon dioxide sensor-electrically tuneable interferometer for infrared gas analysis. Sens Rev 17:304–306
Chambers J, Schimel J, Nobre A (2001) Respiration from coarse wood litter in central Amazon forests. Biogeochemistry 52:115–131
Forrester JA, Mladenoff DJ, Gower ST, Stoffel JL (2012) Interactions of temperature and moisture with respiration from coarse woody debris in experimental forest canopy gaps. For Ecol Manag 265:124–132
Gough CM, Vogel CS, Kazanski C, Nagel L, Flower CE, Curtis PS (2007) Coarse woody debris and the carbon balance of a north temperate forest. For Ecol Manag 244:60–67
Hagemann U, Moroni MT, Gleißner J, Makeschin F (2010) Disturbance history influences downed woody debris and soil respiration. For Ecol Manag 260:1762–1772
Harmon ME, Sexton J (1996) Guidelines for measurements of woody detritus in forest ecosystems. Long-Term Ecological Research Network Office, University of Washington, Seattle
Harmon ME, Franklin JF, Swanson FJ, Sollins P, Gregory SV, Lattin JD, Anderson NH, Cline SP, Aumen NG, Sedell JR, Lienkaemper GW, Cromack K Jr, Cummins KW (1986) Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. Adv Ecol Res 15:133–302
Harmon ME, Krankina ON, Sexton J (2000) Decomposition vectors: a new approach to estimating woody detritus decomposition dynamics. Can J For Res 30:76–84
Herrmann S, Bauhus J (2008) Comparison of methods to quantify respirational carbon loss of coarse woody debris. Can J For Res 38:2738–2745
Herrmann S, Bauhus J (2013) Effects of moisture, temperature and decomposition stage on respirational carbon loss from coarse woody debris (CWD) of important European tree species. Scand J For Res 28:346–347
Janisch JE, Harmon ME, Chen H, Fasth B, Sexton J (2005) Decomposition of coarse woody debris originating by clearcutting of an old-growth conifer forest. Ecoscience 12:151–160
Jomura M, Kominami Y, Kanazawa Y (2005) Long-term measurements of the CO2 flux from coarse woody debris using an automated chamber system. J Jpn For Soc 87:138–144 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Jomura M, Kominami Y, Tamai K, Miyama T, Goto Y, Dannoura M, Kanazawa Y (2007) The carbon budget of coarse woody debris in a temperate broad-leaved secondary forest in Japan. Tellus 59B:211–222
Jomura M, Kominami Y, Dannoura M, Kanazawa Y (2008) Spatial variation in respiration from coarse woody debris in a temperate secondary broad-leaved forest in Japan. For Ecol Manag 255:149–155
Jomura M, Kominami Y, Ataka M (2012) Differences between coarse woody debris and leaf litter in the response of heterotrophic respiration to rainfall events. J For Res 17:305–311
Khomik M, Arain MA, Liaw K-L, McCaughey JH (2009) Debut of a flexible model for simulating soil respiration–soil temperature relationship: Gamma model. J Geophys Res 114:G03004
Li Q, Chen J, Moorhead DL (2012) Respiratory carbon losses in a managed oak forest ecosystem. For Ecol Manag 279:1–10
Lim H, Choi W-J, Ahn K, Lee K-H (2012) Ecosystem respiration and tree growth influenced by thinning in a red pine forest in southern Korea. For Sci Tech 8:192–204
Liski J, Palosuo T, Peltoniemi M, Sievänen R (2005) Carbon and decomposition model Yasso for forest soils. Ecol Model 189:168–182
Liu W, Bryant D, Hutyra L, Saleska S, Hammond-Pyle E, Curran E, Wofsy S (2006) Woody debris contribution to the carbon budget of selectively logged and maturing mid-latitude forests. Oecologia 148:108–117
Mackensen J, Bauhus J (2003) Density loss and respiration rates in coarse woody debris of Pinus radiata, Eucalyptus regnans and Eucalyptus maculata. Soil Biol Biochem 35:177–186
Mackensen J, Bauhus J, Webber E (2003) Decomposition rates of coarse woody debris; review with particular emphasis on Australian tree species. Aust J Bot 51:27–37
Marra JL, Edmonds RL (1994) Coarse woody debris and forest floor respiration in an old-growth coniferous forest on the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, USA. Can J For Res 24:1811–1817
Marra JL, Edmonds RL (1996) Coarse woody debris and soil respiration in a clearcut on the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, USA. Can J For Res 26:1337–1345
Ohtsuka T, Mo W, Satomura T, Inatomi M, Koizumi H (2007) Biometric based carbon flux measurements and net ecosystem production (NEP) in a temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest beneath a flux tower. Ecosystems 10:324–334
Olajuyigbe S, Tobin B, Nieuwenhuis M (2012) Temperature and moisture effects on respiration rate of decomposing logs in a Sitka spruce plantation in Ireland. Forestry 85:485–496
Pichler V, Homolák M, Skierucha W, Pichlerová M, Ramírez D, Gregor J, Jaloviar P (2012) Variability of moisture in coarse woody debris from several ecologically important tree species of the Temperate Zone of Europe. Ecohydrology 5:424–434
Progar RA, Schowalter TD, Freitag CM, Morrell JJ (2000) Respiration from coarse woody debris as affected by moisture and saprotroph functional diversity in Western Oregon. Oecologia 124:426–431
Pumpanen J, Kolari P, Ilvesniemi H, Minkkinen K, Vesala T, Niinistö S, Lohila A, Larmola T, Morero M, Pihlatie M, Janssens I, Yuste JC, Grünzweig JM, Reth S, Subke J-A, Savage K, Kutsch W, Østreng G, Ziegler W, Anthoni P, Lindroth A, Hari P (2004) Comparison of different chamber techniques for measuring soil CO2 efflux. Agr Forest Meteorol 123:159–176
R Development Core Team (2011) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, http://www.R-project.org
Richardson AD, Braswell BH, Hollinger DY, Burman P, Davidson EA, Evans RS, Flanagan LB, Munger JW, Savage K, Urbanski SP, Wofsy SC (2006) Comparing simple respiration models for eddy flux and dynamic chamber data. Agric For Meteorol 141:219–234
Rodeghiero M, Cescatti A (2005) Main determinants of forest soil respiration along an elevation/temperature gradient in the Italian Alps. Glob Change Biol 11:1024–1041
Sollins P (1982) Input and decay of coarse woody debris in coniferous stands in western Oregon and Washington. Can J For Res 12:18–28
Wang C, Bond-Lamberty B, Gower S (2002) Environmental controls on carbon dioxide flux from black spruce coarse woody debris. Oecologia 132:374–381
Wu J, Zhang X, Wang H, Sun J, Guan D (2010) Respiration of downed logs in an old-growth temperate forest in north-eastern China. Scand J For Res 25:500–506
Yasuda T, Yonemura S, Tani A (2012) Comparison of the characteristics of small commercial NDIR CO2 sensor models and development of a portable CO2 measurement device. Sensors 12:3641–3655
Yoon TK, Chung H, Son Y, Kim R-H, Noh NJ, Seo KW, Lee SK, Jo W (2011) Coarse woody debris mass dynamics in temperate natural forests of Mt. Jumbong, Korea. J Ecol Field Biol 34:115–125
Zhou L, Dai L, Gu H, Zhong L (2007) Review on the decomposition and influence factors of coarse woody debris in forest ecosystem. J For Res 18:48–54
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (2010-0014620; 2010-0020227) and the National Institution of Environmental Research (“National Long-Term Ecological Research Project”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, T.K., Han, S., Lee, D. et al. Effects of sample size and temperature on coarse woody debris respiration from Quercus variabilis logs. J For Res 19, 249–259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-013-0412-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-013-0412-3