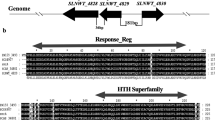
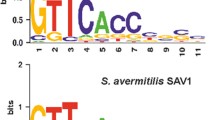
Abstract
The genome sequence of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) has revealed the presence of about 40 protein serine/threonine or tyrosine kinases. AfsK, which is able to phosphorylate AfsR, a transcriptional activator with ATPase activity, represents the first instance in which a bacterial Hanks-type protein kinase phosphorylates a specific protein and exerts biologically important functions. The AfsK-AfsR system in S. coelicolor A3(2) globally controls secondary metabolism. The signal transduction pathway so far demonstrated or suggested is as follows: AfsK loosely attached to the membrane autophosphorylates threonine and serine residues, perhaps on sensing some external stimulus, and enhances its kinase activity. The kinase activity is modulated by KbpA, an AfsK-binding protein, by means of protein-protein interactions. The activated AfsK phosphorylates threonine and serine residues of AfsR in the cytoplasm, by which the DNA-binding activity of AfsR is greatly enhanced. In addition to AfsK, other kinases—including PkaG and AfsL—also phosphorylate AfsR, suggesting that AfsR serves as an integrator of multiple signals sensed by these kinases. The phosphorylated AfsR binds the promoter of afsS, which encodes a protein of 63 amino acids, and forms a closed complex with RNA polymerase. The closed complex is then converted to a transcriptionally active open complex by the energy available from ATP hydrolysis by AfsR. AfsS induced in this way activates transcription of pathway-specific transcriptional activators, such as actII-ORF4 for actinorhodin production and redD for undecylprodigiosin, in an as yet unknown manner.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson TB, Brian P, Champness WC (2001) Genetic and transcriptional analysis of absA, an antibiotic gene cluster-linked two-component system that regulates multiple antibiotics in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 39:553–566
Ansari AZ, Chael ML, O'Halloran TV (1992) Allosteric underwinding of DNA is a critical step in positive control of transcription by Hg-MerR. Nature 355:87–89
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O'Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Chakraburtty R, Bibb M (1997) The ppGpp synthetase gene (relA) of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) plays a conditional role in antibiotic production and morphological differentiation. J Bacteriol 179:5854–5861
Chater KF (1993) Genetics of differentiation in Streptomyces. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:685–713
Cozzone AJ (1997) Diversity and specificity of protein-phosphorylating systems in bacteria. Folia Microbiol 42:165–170
Fernández-Moreno MA, Caballero JL, Hopwood DA, Malpartida F (1991) The act cluster contains regulatory and antibiotic export genes, direct targets for translational control by the bldA tRNA gene of Streptomyces. Cell 66:769–780
Floriano B, Bibb M (1996) afsR is a pleiotropic but conditionally required regulatory gene for antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 21:385–396
Frankel AD, Kim PS (1991) Modular structure of transcriptional factors: implications for gene regulation. Cell 65:717–719
Hara O, Horinouchi S, Uozumi T, Beppu T (1983) Genetic analysis of A-factor synthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces griseus. J Gen Microbiol 129:2939–2944
Hidalgo E, Demple B (1997) Spacing of promoter elements regulates the basal expression of the soxS gene and converts SoxR from a transcriptional activator into a repressor. EMBO J 16:1056–1065
Hong S-K, Horinouchi S (1998) Effects of protein kinase inhibitors on in vitro protein phosphorylation and on secondary metabolism and morphogenesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Microbiol Biotechnol 8:325–332
Hong S-K, Kito M, Beppu T, Horinouchi S (1991) Phosphorylation of the afsR product, a global regulatory protein for secondary-metabolite formation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 173:2311–2318
Hong S-K, Matsumoto A, Horinouchi S, Beppu T (1993) Effects of protein kinase inhibitors on in vitro protein phosphorylation and cellular differentiation of Streptomyces griseus. Mol Gen Genet 236:347–354
Horinouchi S, Beppu T (1984) Production in large quantities of actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin induced by afsB in Streptomyces lividans. Agric Biol Chem 48:2131–2133
Horinouchi S, Hara O, Beppu T (1983) Cloning of a pleiotropic gene that positively controls biosynthesis of A-factor, actinorhodin, and prodigiosin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 155:1238–1248
Horinouchi S, Malpartida F, Hopwood DA, Beppu T (1989) afsB stimulates transcription of the actinorhodin biosynthetic pathway in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet 215:355–357
Horinouchi S, Kito M, Nishiyama M, Furuya K, Hong S-K, Miyake K, Beppu T (1990) Primary structure of AfsR, a global regulatory protein for secondary metabolite formation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Gene 95:49–56
Horinouchi S, Ohnishi Y, Kang D-K (2001) The A-factor regulatory cascade and cAMP in the regulation of physiological and morphological development in Streptomyces griseus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27:177–182
Ishizuka H, Horinouchi S, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA, Beppu T (1992) A putative two-component regulatory system involved in secondary metabolism in Streptomyces spp. J Bacteriol 174:7585–7594
Kennelly PJ, Potts M (1996) Fancy meeting you here! A fresh look at "prokaryotic" protein phosphorylation. J Bacteriol 178:4759–4764
Lee P-C, Umeyama T, Horinouchi S (2002) afsS is a target of AfsR, a transcriptional factor with ATPase activity that globally controls secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 43:1413–1430
Martínez-Costa OH, Arias P, Romero NM, Parro V, Mellado RP, Malpartida F (1996) A relA/spoT homologous gene from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) controls antibiotic biosynthetic genes. J Biol Chem 271:10627–10634
Matsumoto A, Hong S-K, Ishizuka H, Horinouchi S, Beppu T (1994) Phosphorylation of the AfsR protein involved in secondary metabolism in Streptomyces species by a eukaryotic-type protein kinase. Gene 146:47–56
Matsumoto A, Ishizuka H, Beppu T, Horinouchi S (1995) Involvement of a small ORF downstream of the afsR gene in the regulation of secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Actinomycetologica 9:37–43
Narva KE, Feitelson JS (1990) Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the redD locus of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 172:326–333
North AK, Klose KE, Stedman KM, Kustu S (1993) Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol 175:4267–4273
Onaka H, Nakagawa T, Horinouchi S (1998) Involvement of two A-factor receptor homologues in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) in the regulation of secondary metabolism and morphogenesis. Mol Microbiol 28:743–753
Sekurova O, Sletta H, Ellingsen TE, Valla S, Zotchev S (1999) Molecular cloning and analysis of a pleiotropic regulatory gene locus from the nystatin producer Streptomyces noursei ATCC11455. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177:297–304
Shi L, Potts M, Kennelly PJ (1998) The serine, threonine, and/or tyrosine-specific protein kinases and protein phosphatases of prokaryotic organisms: a family portrait. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:229–253
Stein D, Cohen SN (1989) A cloned regulatory gene of Streptomyces lividans can suppress the pigment deficiency phenotype of different developmental mutants. J Bacteriol 171:2258–2261
Strohl WR (1992) Compilation and analysis of DNA sequences associated with apparent streptomycete promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 20:961–974
Süsstrunk U, Pidoux J, Taubert S, Ullmann A, Thompson CJ (1998) Pleiotropic effects of cAMP on germination, antibiotic biosynthesis and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 30:33–46
Takano E, Chakraburtty R, Nihira T, Yamada Y, Bibb MJ (2001) A complex role of the γ-butyrolactone SCB1 in regulating antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 41:1015–1028
Umeyama T, Horinouchi S (2001) Autophosphorylation of a bacterial serine/threonine kinase, AfsK, is inhibited by KbpA, an AfsK-binding protein. J Bacteriol 183:5506–5512
Umeyama T, Lee P-C, Ueda K, Horinouchi S (1999) An AfsK/AfsR system involved in the response of aerial mycelium formation to glucose in Streptomyces griseus. Microbiology 145:2281–2292
Umeyama T, Lee P-C, Horinouchi S (2002) Protein serine/threonine kinases in signal transduction for secondary metabolism and morphogenesis in Streptomyces. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:419–425
Vögtli M, Chang PC, Cohen SN (1994) afsR2: a previously undetected gene encoding a 63-amino-acid protein that stimulates antibiotic production in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Microbiol 14:643–653
Wedel A, Kustu S (1995) The bacterial enhancer-binding protein NTRC is a molecular machine: ATP hydrolysis is coupled to transcriptional activation. Genes Dev 9:2042–2052
Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ (2000) Regulation of transcription factor function by phosphorylation. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:1172–1183
Wietzorrek A, Bibb M (1997) A novel family of proteins that regulates antibiotic production in streptomycetes appears to contain an OmpR-like DNA-binding fold. Mol Microbiol 25:1181–1184
Zhang C-C (1996) Bacterial signalling involving eukaryotic-type protein kinases. Mol Microbiol 20:9–15
Acknowledgments
The work from this laboratory was supported by the Nissan Science Foundation, the Asahi Glass Foundation, the "Research for the Future" Program of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Bio Design Program of the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan (BDP-03-VI-2–3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Sir David A. Hopwood
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horinouchi, S. AfsR as an integrator of signals that are sensed by multiple serine/threonine kinases in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J IND MICROBIOL BIOTECHNOL 30, 462–467 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-003-0063-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-003-0063-z